AWS Disaster Recovery
This is not an exhaustive documentation of all the existing AWS Services. These are summarized notes for the AWS Certifications.
To see the complete documentation, please go to: AWS documentation
- Disaster
- RPO and RTO
- Disaster Recovery Strategies
- Disaster Recovery Tips
- On-Premise Strategy with AWS
- DMS - Database Migration Service
- AWS Schema Conversion Tool SCT
Disaster
- Disaster: any event that has a negative impact on a company’s business continuity or finances
- Disaster Recovery (DR) is about preparing for and recovering from a disaster
- Disaster recovery solutions:
- On-premise to on-premise: traditional DR, expensive
- On-premise to cloud: hybrid recovery
- AWS Cloud Region A to AWS Cloud Region B
RPO and RTO
- RPO - Recovery Point Objective: How often we create backups. Time between the RPO and the disaster is the data loss
- RTO - Recovery Time Objective: The point in time when the recovery finishes. The time between the disaster and the RTO is downtime
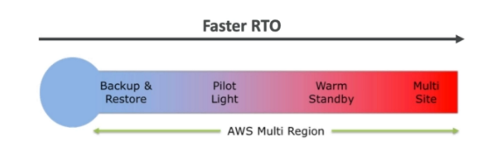
Disaster Recovery Strategies
| |
|-|
|
|-|
All strategies are available for Multi-region.
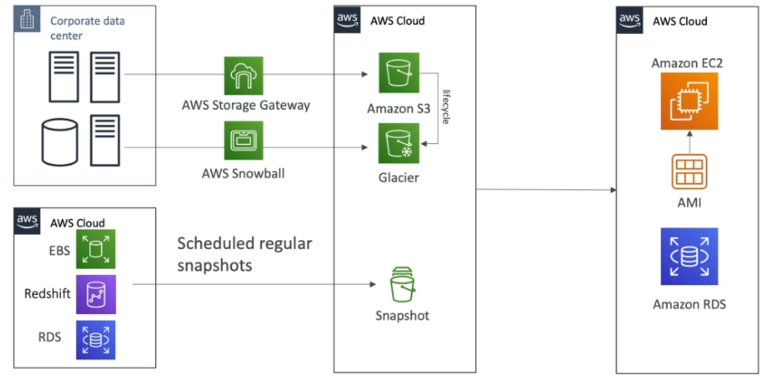
Backup and Restore
- High RPO, cheap, easy to manage and accomplish
| |
|-|
|
|-|
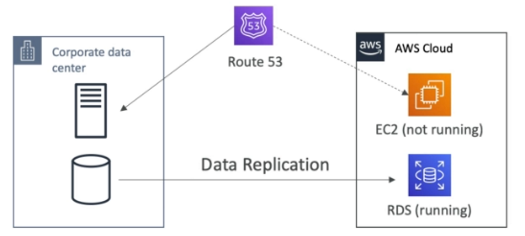
Pilot Light
- A small version of the app is always running in the cloud
- Useful for critical core (pilot light)
- Similar to backup and restore strategy
- Faster than backup and restore as critical system are already running
| |
|-|
|
|-|
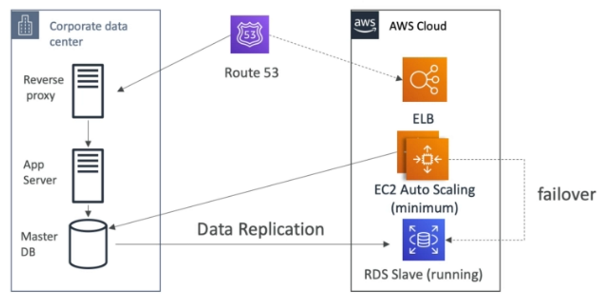
Warm Standby
- Full system is up and running but at a minimal size
- Upon disaster we can scale to production load
| |
|-|
|
|-|
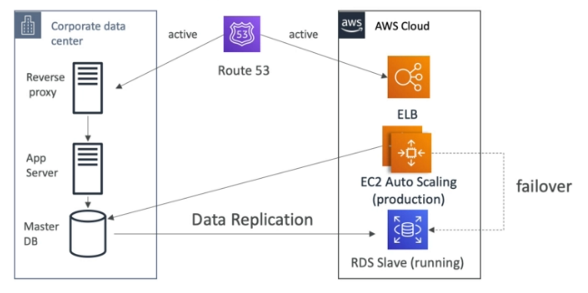
Hot Site / Multi Site Approach
- Very low RTO - very expensive
- Full production scale is running on the cloud
| |
|-|
|
|-|
Disaster Recovery Tips
Backups
- EBS Snapshots, RDS, automated backups, snapshots, etc.
- Regular pushes to S3/S3 IA/Glacier, Lifecycle Policy, Cross region replication
- From on-premise: Snowball or Storage Gateway
High Availability
- Use Route53 to migrate DNS over from region to region
- RDS Multi-AZ, ElastiCache Multi-AZ, EFS, S3
- Site to site VPN as recovery from Direct Connect
Replication
- RDS Replication (Cross Region), AWS Aurora + Global Databases
- Database replication from on-premise to RDS
- Storage Gateway
Automation
- CloudFormation/Elastic Beanstalk to recreate a whole new environment
- Recover/Reboot EC2 instances with CloudWatch if alarm is in fail state (ALARM)
- AWS Lambda for customized automation
Chaos
- Netflix has a “simian-army” randomly terminating EC2 instances
On-Premise Strategy with AWS
Download Amazon Linux 2 AMI as a VIM
- iso format
- VMWare, KVM, VirtualBox, Microsoft Hyper-V
VM Import/Export
- Ability to migrate existing applications into EC2
- Ability to create a DR repository for on-premise VMs
- Ability to export back the VMs form EC2 to on-premise
AWS Application Discovery Service
- Gather information about on-premise servers to plan a migration
- Provides information about server utilization and dependency mappings
- Track all migrations with AWS Migration Hub
AWS Database Migration Service (DMS)
- Replicate on-premise
- Works with various DB technologies
AWS Server Migration Service (SMS)
- Incremental replication of on-premise live servers to AWS
DMS - Database Migration Service
- Quickly and securely migrate databases to AWS
- It is resilient and self healing
- The source database remains available during migration
- Supports:
- Homogeneous migrations, example Oracle to Oracle
- Heterogeneous migrations, example: Microsoft SQL Server to Aurora
- Supports continuous data replication using CDC
- We must create an EC2 instance to perform the replication tasks
DMS Sources and Targets
| |
|-|
|
|-|
Sources
- On-premise and EC2 instance databases: Oracle, MS SQL Server, MySQL, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, SAP, DB2
- Azure SQL Database
- Amazon RDS: all including Aurora
- Amazon S3
Targets
- On-premise and EC2 instance databases: Oracle, MS SQL Server, MySQL, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, AP
- Amazon RDS
- Redshift
- DynamoDB
- S3
- ElasticSearch
- Kinesis Data Streams
- DocumentDB
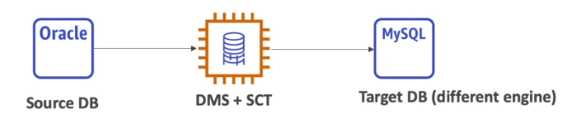
AWS Schema Conversion Tool (SCT)
- Converts a database schema form one engine to another. Example: OLTP (SQL Server, Oracle) to MySQL, PostgreSQL, Aurora; OLAP (Teradata or Oracle) to Redshift
- We do not need to use SCT if we are migration from the same DB engine to the same DB engine