Threat Intelligence and Sources
- Threat Intelligence
- Quality of Intelligence
- Types of intelligence
- Implicit and Explicit Knowledge
- Automated Indicator Sharing
Threat Intelligence
Threat Intelligence is a continual process used to understand the threats faced by an organization. It is focused on analyzing evidence-based knowledge about an existing or emerging hazard to our asset.
Quality of Intelligence
Consider and measure the quality of intelligence.
-
Timeliness - Property of an intelligence source that ensures it is up-to-date.
-
Relevancy - Property of an intelligence source that ensures it matches the use cases intended for it.
-
Accuracy - Property of an intelligence source that ensures it produces effective results.Information needs to be valid and true.
-
Confidence Levels - Property of an intelligence source that ensures it produces qualified statements about reliability.
Types of intelligence
Open-Source
Data that is available to use without subscription, which may include threat feeds similar to the commercial providers and may contain reputation lists and malware signature databases
- US-CERT
- UK’s NCSC
- AT&T Security (previously Alienvault OTX)
- MISP
- VirusTotal
- Spamhaus
- SANS ISC Suspicious Domains
Proprietary
Threat intelligence is very widely provided as a commercial service offering, where access to updates and research is subject to a subscription fee
- Some of these are repackaged information.
- Not nearly as useful.
Companies that provide proprietary threat intelligence feeds:
- FireEye
- McAfee
- Symantec
Closed-Source
Data that is derived from the provider’s own research and analysis efforts, such as data from honeynets that they operate, plus information mined from its customers’ systems, suitably anonymized
- Good example is Fireeye
Information Sharing Organizations
These are alliances that are formed to share threat intelligence among its members.
- Centers
- Organizations
Industries:
- Finance
- Healthcare
- Energy
Open-Source Intelligence (OSINT)
Methods of obtaining information about a person or organization through public records, websites, and social media.
Dark Web
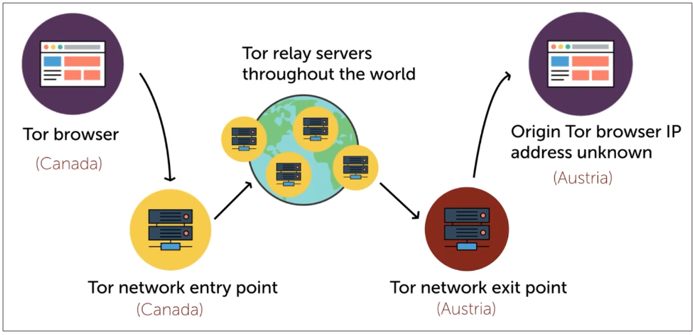
The Dark Web is a part of the internet that is intentionally hidden and requires special software like Tor to access.
- A segment of the Deep Web, often associated with illegal or illicit activities.
- Often monitored by law enforcement due to its association with cybercrime.
- Contents are not indexed by search engine like Google
- Uses Tor network, which is sits over standard internet protocol.
- Encrypted anonymous connections
How it works:
Implicit and Explicit Knowledge
All of the threat feeds mentioned previously as intelligence sources are considered explicit knowledge, but explicit knowledge comes from years of experience.
Automated Indicator Sharing
Uses a specialized format called Structured Threat Information Expression (STiX) to package threat intelligence information.
-
Exchange of cybersecurity intelligence between entities
- Uses Trusted Automated Exchange of Intelligence Information (TAXII) to transmit the packaged information
- TAXII is like an RSS feed
- Normally built-in on security monitoring tools