Blockchain
Blockchain
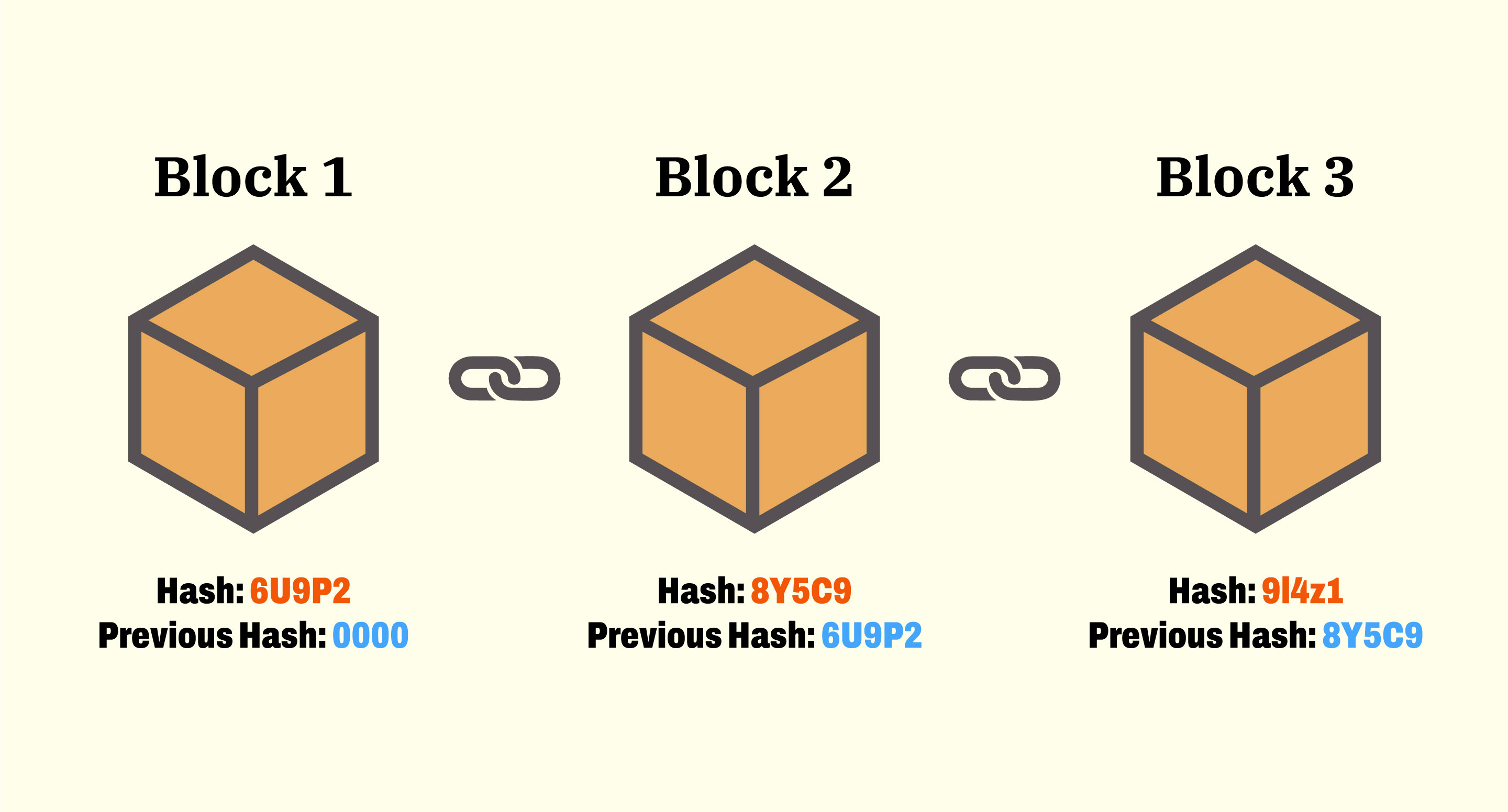
Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that creates a secure and tamper-resistant way to record and verify transactions.
Key Concepts
Decentralization
Blockchain operates without a central authority, distributing control across a network of nodes
- Reduces single points of failure and improves resilience against attacks.
- Each node or participant can operate independently.
- Involves redundancy, which increases resilience against attacks and system failures.
Public Ledger
Public Ledgers is a record-keeping system that maintains participants’ identities in a secure and anonymous format.
- Track and verify transactions without relying on a central authority.
- Transaction records are accessible to anyone.
- Decentralized, transparent, and immutable.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing agreements coded in software, usually on blockchain platforms like Ethereum. They automatically enforce or carry out contract terms when specific conditions are met, reducing the need for intermediaries.
- Smart contracts execute actions automatically when certain triggers are activated.
- Being on a blockchain, smart contracts are transparent, and their outcomes cannot be tampered with.
- The contract behaves consistently, ensuring predictable results.
Common Use Cases
- Financial Transactions: Automate payments, loans, or insurance claims.
- Supply Chain Management: Track goods and automate logistics.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Enable financial services without traditional intermediaries.
Challenges
- Errors in code can be exploited.
- Once deployed, smart contracts are hard to change.
- Smart contracts might not be legally recognized in all jurisdictions.
Permission Blockchain
A permissioned blockchain is a type of blockchain where access to the network and participation in the consensus process are restricted to approved entities.
Unlike public blockchains, where anyone can join, permissioned blockchains require users to be granted specific roles or permissions.
-
Only authorized participants can join and interact with the network.
-
A central group of approved stakeholders typically manage the network’s rules and permissions.
-
Consensus processes are limited to a predefined group of participants, improving speed and scalability.
Applications
-
Enterprise Use Cases:
- Common in business environments where sensitive information requires controlled access.
-
Consortia:
- Groups of businesses or organizations collaborate on a shared blockchain with defined governance.
-
Private Transactions:
- Used for internal or confidential operations that need secure but private blockchain records.
Challenges
-
Centralized Control:
- Although still decentralized, permissioned blockchains have more centralized governance.
- This reduces trust and increase dependency on a central authority.
-
Reduced Transparency:
- Restricted nature means they are less open and transparent compared to public blockchains.
-
Limited Decentralization:
- The controlled nature of permissioned blockchains may lead to less resilience against certain attacks compared to fully decentralized public blockchains.
Features
Immutability
Once a transaction is recorded on a blockchain, it cannot be altered without consensus from the network.
- This makes data tamper-resistant and provides a reliable audit trail.
Consensus Mechanisms
Blockchain relies on consensus algorithms to agree on the validity of transactions.
- Consensus mechanisms ensure trustworthiness in a decentralized environment.
-
Common consensus mechanisms include:
- Proof of Work (PoW)
- Proof of Stake (PoS), which help
Cryptographic Security
Transactions on a blockchain are secured using cryptographic techniques.
- Digital signatures and public-key cryptography are used to verify and authenticate participants.
Cybersecurity Considerations
Fifty-one Percent Attack
- An attacker gains control of more than 50% of the network’s mining power.
- This allows them to manipulate the blockchain.
Smart Contract Vulnerabilities
- Smart contracts, which are self-executing code on a blockchain, can contain security flaws that attackers can exploit.
Privacy Risks
- Although transactions on a blockchain are secure, they are often public.
- More than 50%, and blockchain becomes compromised.
- This raises concerns about data privacy and confidentiality.
Key Management
- Securing private keys is crucial for blockchain users.
- If a key is lost or stolen, the associated assets may be irrecoverable.
Applications in Cybersecurity
Secure Data Storage:
- Blockchain can be used to store sensitive information securely.
- This leverages immutability to prevent tampering.
Identity Verification:
- Blockchain-based identity solutions use cryptographic techniques.
- This verify users without relying on centralized authorities.
Supply Chain Security:
- Blockchain can enhance supply chain security.
- It can provide an immutable record of product provenance and traceability.