Security Architecture
- Security Architecture
- On-Premises Data Centers
- Cloud Computing
- Virtualization
- Containerization
- Serverless
- Microservices
Security Architecture
Design, structure and behavior of an organization’s information security environment.
- On-Premise
- Local infrastructure.
- Data processed and stored on-site.
- Direct control over hardware and software.
- Cloud
- Internet-based services.
- Hosted and managed by third-party providers.
- Pay-per-use model.
- Hybrid
- Combination of on-premise and cloud.
- Integrates local infrastructure with cloud services.
- Offers flexibility and scalability.
On-Premises Data Centers
When it comes to data centers, there are two primary options: organizations can outsource the data center or own the data center. If the data center is owned, it will likely be built on premises. A place, like a building for the data center is needed, along with power, HVAC, fire suppression and redundancy.
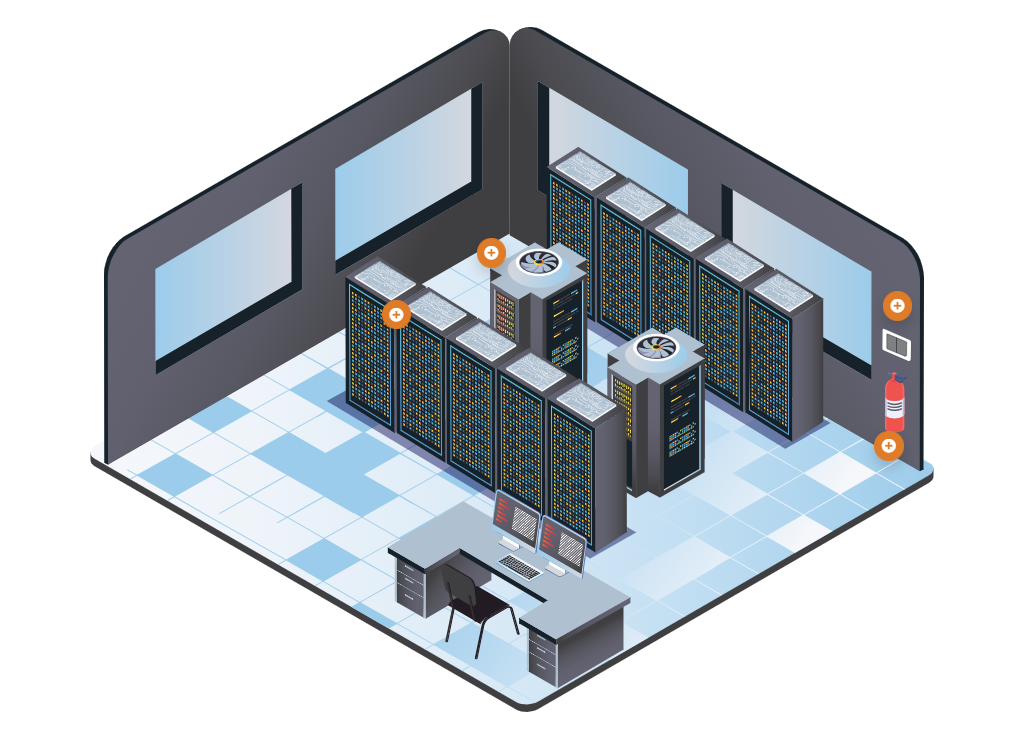
Components of a Datacenter:
- Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning HVAC / Environmental
- Data Center/Closets
- Power
- Fire Suppression
Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning (HVAC) / Environmental
Ensure adequate cooling for high-density and enclosed space equipment.
- Follow temperature standards for optimized hardware life.
- Use temperature sensors at various rack levels for precise monitoring.
- Implement contaminant controls for dust and noxious fumes.
- Monitor for water or gas leaks, sewer overflow, and HVAC failure.
- Prioritize critical systems in contingency planning.
Data Center/Closets
Protect access to the physical layer for information system security.
- House critical components such as servers and network connections.
- Address security challenges related to data centers and wiring closets.
- Safeguard against intentional or unintentional damage.
Power
Ensure constant and consistent power delivery to data centers.
- Mitigate wide fluctuations in power quality to preserve system lifespan.
- Size backup generators for the critical load and use battery backups for stabilization.
- Regularly test alternate power sources for effective failover.
Key terms:
- Surges
- Small and unexpected increase in the amount of voltage being provided.
- Utilize a surge protector or line conditioner.
- Spikes
- Short transient voltage that is usually caused by a short circuit, a power outage, or a lightning strike.
- Utilize a surge protector or line conditioner.
- Sags
- Small and unexpected decrease in the amount of voltage being provided.
- Usually occurs for short period of time.
- During a sag, computer can still remain operational but hardware components may be damaged over time.
- Utilize a surge protector or line conditioner.
- Undervoltage events
- Usually referred to as “brownouts”.
- Voltage is reduced to lower levels; occurs for longer period of time.
- Full power loss events
- Usually referred to as “blackouts”.
- Total loss of power for a given period of time.
- When power is restored, it can cause a power spike.
Fire Suppression
Choose appropriate fire detection/suppression considering room size and equipment risks.
- Be cautious of water-based suppression’s potential harm to electronic components.
- Consider gas-based systems for electronics-friendly suppression, but be mindful of potential human toxicity.
Using Robust Systems
- Line Conditioners
- Overcome minor fluctuations in the power being received.
- Stabilize voltage levels; filter out electrical noise.
- Protect against power surges, but not from a complete failure event.
- Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) Systems
- Provide backup power during outages and protect against power fluctuations.
- Prevent data loss by allowing safe shutdown.
- Most UPS only provides 15-60 minutes of power; not for long-term outage.
- Generators
- Convert mechanical energy into electrical energy for use.
- Supply power during extended outages.
- Automatically start when primary power fails.
- Support critical systems for prolonged periods.
- Usual types:
- Portable gas-engine
- Permanently installed
- Battery-inverter
- Power Distribution Centers
- Central hub that distribute electrical power efficiently.
- Integrated circuit protection, monitoring, and loadbalancing.
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing involves accessing and utilizing computing resources and services over the internet, provided by third-party vendors. It offers scalability, flexibility, and reduced dependency on on-premise hardware.
- Servers
- Storage
- Databases
- Networking
- Software Analytics
- Intelligence
Cloud Concepts
TO learn more, check out Cloud Computing.
-
Utility Model
- Similar to utilities like electricity.
- Provisioned in a specific location.
- Offers scalability, elasticity, and ease of use for IT service deployment.
-
NIST Definition
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) provides a widely accepted definition.
- Described as a model enabling ubiquitous, on-demand access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources.
- Emphasizes rapid provisioning and release with minimal management effort.
-
Responsibility Matrix
- A tool outlining roles and responsibilities within a project or organization.
- Clarifies who is accountable for specific tasks or areas of work.
- Helps ensure clear communication and accountability.
-
Third-party Vendors
- External entities providing goods or services to a company.
- Often contracted for specialized expertise or resources.
- Can include suppliers, service providers, consultants, or software vendors.
- Require clear communication, contracts, and management to ensure successful collaboration.
-
Hybrid Solutions
- In the context of IT, often refers to a mix of on-premise and cloud solutions.
- Offers flexibility by leveraging both local infrastructure and cloud services.
- Integration and management to ensure smooth operation and maximum benefit.
Key Considerations
-
Availability
- Redundancy measures to prevent single points of failure.
- Monitoring systems for early detection of issues.
- Disaster recovery plans for quick restoration of services.
-
Cost
- Total cost of ownership analysis including initial setup, maintenance, and operational expenses.
- Cost optimization strategies such as resource consolidation or automation.
- Budget forecasting to anticipate future expenses.
-
Resilience
- Fault-tolerant architecture design.
- Regular testing of backup and recovery procedures.
- Geographic redundancy for data centers or cloud regions.
-
Responsiveness
- Service level agreements (SLAs) defining response times and resolution targets.
- Proactive monitoring and alerting systems.
- Efficient incident management processes.
-
Scalability
- Horizontal and vertical scaling capabilities.
- Auto-scaling mechanisms based on demand fluctuations.
- Performance testing to ensure scalability thresholds are met.
-
Ease of Deployment
- Streamlined deployment pipelines or automation tools.
- Compatibility testing with existing infrastructure.
- User-friendly interfaces and documentation.
-
Risk Transference
- Clearly defined contractual agreements and service level guarantees.
- Insurance policies to mitigate financial risks.
- Compliance with regulatory requirements and standards.
-
Patch Availability
- Patch management processes to ensure timely application of updates.
- Vulnerability scanning and assessment tools.
-
Inability to Patch
- Risk assessment and prioritization of unpatched vulnerabilities.
- Compensating controls or mitigation strategies.
- Regular security audits and assessments.
-
Power
- Redundant power sources such as uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) or backup generators.
- Monitoring and maintenance of power infrastructure.
- Energy-efficient hardware and cooling systems.
-
Compute
- Performance benchmarks and optimization techniques.
- Load balancing for efficient resource utilization.
- Capacity planning based on workload requirements and growth projections.
Managed Service Provider (MSP)
A company managing IT assets for another organization and is Commonly utilized by small- and medium-sized businesses for day-to-day IT operations.
- Outsourcing Functions
- Used to outsource specific IT functions or manage entire operations.
- Expertise provided in areas where the company lacks internal capabilities.
- Services Provided by MSPs
- Network and security monitoring.
- Patching services.
- Cloud-based solutions, including Managed Detection and Response (MDR).
- MDR Service Example
- Managed Detection and Response (MDR) involves active incident investigation and response.
- Monitors security tools, such as firewalls, for event triaging.
- Common MSP Implementations
- Augmenting in-house staff for projects.
- Implementing products or services.
- Providing payroll services.
- Managing Help Desk service.
- Responding to and managing security incidents.
- Overseeing all in-house IT infrastructure.
Service-Level Agreement (SLA)
It is an agreement between a cloud service provider and customer that defines the quality of cloud services, specific to cloud computing terms and roles.
- Importance of SLA
- Functions as a rule book and legal contract.
- Outlines minimum service levels, availability, security, controls, and more.
- Purpose of SLA
- Documents specific parameters, service levels, and remedies for failures.
- Addresses data ownership, return, and destruction details.
- Key SLA Points
- Cloud system infrastructure and security standards.
- Customer’s right to audit legal and regulatory compliance.
- Rights and costs associated with service use continuation/discontinuation.
- Service availability and performance.
- Data security, privacy, and location.
- Disaster recovery processes and data access.
- Data portability and problem identification/resolution.
- Change management processes and dispute mediation.
- Exit strategy considerations.
Common Security Challenges
- Shared Physical Server Vulnerabilities
- Multiple users often share the same underlying physical servers in a cloud environment.
- Isolation mechanims prevent unauthorized access between virtual machines.
- Regular security assessments and audits of underlying hardware.
- Implementation of hypervisor security measures to mitigate risks.
- Inadequate Virtual Environment Security
- Segmentation of virtual networks and resources.
- Intrusion detection and prevention systems within virtual environments.
- Regular security updates and patches for virtualization software.
- User Access Management
- Role-based access controls (RBAC) to limit privileges based on job roles.
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA) for enhanced user verification.
- Regular reviews and audits of user permissions to prevent unauthorized access.
- Lack of Up-to-date Security Measures
- Continuous monitoring for security vulnerabilities and emerging threats.
- Automated patch management systems to ensure timely updates.
- Integration with threat intelligence feeds for proactive threat detection.
- Single Point of Failure
- Redundancy and failover mechanisms across multiple data centers or availability zones.
- Load balancing to distribute traffic and mitigate the impact of failures.
- Disaster recovery plans to maintain operations in the event of a failure.
- Weak Authentication and Encryption
- Strong encryption protocols for data transmission and storage.
- Secure key management practices to protect encryption keys.
- Regular password policy enforcement and password rotation.
- Unclear Policies and Data Remnants
- Clear data retention policies outlining data lifecycle management.
- Secure data deletion procedures to ensure data remnants are properly erased.
- Compliance with regulatory requirements regarding data privacy and disposal.
Cloud Security Controls
- Instance Awareness
- The idea is to be aware of how many VMs are being managed.
- “VM Sprawl, overprovisioning VMs which can lead to unused or forgotten VMs.
- More VMs means increased attack surface.
- Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB)
- Enforces security policies when accessing cloud resources.
- Usually a VM that runs on-prem, acts as a middle-man.
- Can restrict VM types that can be deployed, limit storage account size, etc.
- Next-Generation Secure Web Gateway (SWG)
- Security appliance that has the CASB functionality, with additional capabilities.
- Web content filtering, data loss prevention (DLP), firewall abilities.
- CSP Secure Solutions
- Azure and AWS Network Security Groups
- Azure Policies; controls cloud resource deployments and compliance.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Solutions
- Prevents data exfiltration.
- Azure Information Protection (AIP).
- Cloud Monitoring
- Detect abnormalities or suspicious activities.
- Utilize log reviews for “detective” security controls.
- Employ log forwarding to aggregate logs into a centralized logs repository.
Virtualization
Virtualization involves creating virtual instances of computing resources, such as servers, storage devices, or networks, to maximize resource utilization and flexibility.
Hypervisors
Hypervisors are software or firmware that create and manage virtual machines (VMs).
-
Type-1 (Bare Metal)
- Installed directly on the physical hardware.
- Provides direct access to hardware resources.
- Typically used in enterprise data centers and cloud environments.
- Examples: VMware vSphere, Microsoft Hyper-V, Xen, KVM.
-
Type-2 (Hosted)
- Installed on top of an operating system.
- Relies on the host OS for hardware access.
- Often used for development, testing, and desktop virtualization.
- Examples: Oracle VirtualBox, VMware Workstation, Parallels Desktop.
VM Vulnerabilities
-
VM Escape
- Exploiting vulnerabilities to break out of a virtual machine’s isolation.
- Allows unauthorized access to the host system or other VMs.
- Example:
- CVE-2018-3646: A vulnerability in Intel CPUs allowed malicious code running in a virtual machine to access memory outside its allocated space, potentially compromising the host system.
- Mitigation:
- Regularly update hypervisor software to patch known vulnerabilities.
- Implement strict access controls and isolation techniques.
-
Privilege Escalation
- Elevating user privileges within a virtualized environment.
- Grants unauthorized access to sensitive resources or capabilities.
- Example:
- CVE-2019-14849: A vulnerability in the Linux Kernel allowed users with lower privileges to escalate their privileges and gain root access within a virtual machine.
- Mitigation:
- Apply operating system patches and security updates promptly.
- Implement least privilege principles.
- Regularly audit user permissions to prevent unauthorized privilege escalation.
-
Live VM Migration
- Intercepting data during the migration process.
- Potentially exposing sensitive information to unauthorized entities.
- Example:
- Insecure VM migration protocols or misconfigured network settings may expose sensitive data during live VM migrations.
- Mitigation:
- Encrypt data during VM migration to prevent interception.
- Implement secure network configurations.
- Restrict access to migration interfaces.
-
Resource Reuse
- Exploiting leftover resources from previously used virtual machines.
- Can lead to unauthorized access or data leakage.
- Example:
- Residual data left in memory or storage after a VM is terminated may be exploited to access sensitive information.
- Mitigation:
- Use secure deletion techniques to ensure that data remnants are properly erased.
- Implement memory and disk scrubbing mechanisms to prevent residual data exploitation.
- Regularly monitor and audit resource allocation to detect and mitigate resource reuse vulnerabilities.
Securing VMs
Securing VMs are almost similar with how we secure physical servers.
- Hypervisors needs to be regularlly updated, patched, and secured.
- Limit the connections between VMs and the physical machines.
- Minimize and remove unneeded features to reduce potential vulnerabilities.
- Consider VM distribution across different servers.
- Beware of VM Sprawl - Provisioning VMs without proper oversight.
- Enable encryption of the file that hosts the VM.
Containerization
Containerization is a lightweight form of virtualization that encapsulates an application and its dependencies into a standardized unit known as a container. Containers can be easily deployed and run consistently across different computing environments.
- Docker
- Kubernetes
- Red Hat OpenShift
Advantages
- Efficiency
- Optimizes resource usage.
- Fast startup times.
- Speed
- Rapid deployment.
- Quick application scaling.
- Portability
- Consistent across environments.
- Easily deployable anywhere.
- Scalability
- Dynamic resource allocation.
- Horizontal scaling capabilities.
- Isolation
- Ensures application separation.
- Minimizes impact of failures.
- Consistency
- Standardized deployment process.
- Reproducible builds and deployments.
Serverless
Serverless is an approach where cloud providers manage the infrastructure, allowing developers to focus solely on writing and deploying code.
- Resources are provisioned dynamically and automatically scale based on demand.
- Billed based on actual usage rather than pre-provisioned capacity.
- Eliminates the need for managing servers, operating systems, or infrastructure components.
- Enable faster development and deployment cycles.
Vendor Lock-in
It is a situation where a customer becomes dependent on a particular vendor’s products or services to an extent that switching to another vendor becomes impractical or costly..
- Developers heavily utilize proprietary services or features provided by a specific cloud provider.
- This makes it challenging to migrate to another provider in the future.
Mitigation:
- Using open standards
- Implementing abstraction layers
- Designing applications for portability to reduce dependency on specific vendor offerings.
Microservices
Microservices is an architectural approach where applications are composed of small, independently deployable services. Each service is focused on a specific business function and communicates with others through APIs. This allows for modularity, flexibility, and scalability, enabling teams to develop, deploy, and maintain services independently.
Monolithic vs Microservices
- Monolithic
- Single, unified codebase and application.
- Components tightly integrated and deployed together.
- Scaling involves replicating the entire application.
- Development, testing, and deployment are typically done as a single unit.
- Changes and updates require redeploying the entire application.
- Simple to develop and initially deploy.
- Can become complex and difficult to maintain as the application grows.
- Microservices
- Application divided into small, independently deployable services.
- Each service focuses on a specific business function.
- Services communicate through APIs or message queues.
- Scaling is done at the service level, allowing for more efficient resource utilization.
- Development, testing, and deployment can be done independently for each service.
- Enables continuous deployment and faster iteration.
- Additional overhead for managing service communication and orchestration.
Benefits
- Scalability
- Enables scaling individual components independently based on demand.
- Optimizes resource usage by allocating resources where needed most.
- Allows for horizontal scaling of specific services without affecting others.
- Flexibility
- Provides freedom to choose different technologies and programming languages for each service.
- Allows teams to use the most appropriate tools and frameworks for specific tasks.
- Facilitates experimentation and innovation by enabling the adoption of new technologies as needed.
- Resilience
- Isolates failures to individual services, preventing them from affecting the entire system.
- Enhances fault tolerance by ensuring that failures in one service do not propagate to others.
- Supports graceful degradation, where the system continues to function despite partial failures.
- Faster Deployment and Updates
- Enables continuous deployment by allowing changes to be deployed independently for each service.
- Reduces time-to-market by facilitating rapid iteration and experimentation.
- Enhances agility and responsiveness to customer feedback by enabling quick updates and feature releases.
Challenges
- Complexity
- Increased complexity in development, deployment, and maintenance.
- Requires effective coordination between teams.
- Data Management
- Handling data consistency and synchronization challenges.
- Requires careful management of data storage and retrieval.
- Network Latency
- Service-to-service communication introduces latency.
- Requires optimization of network communication.
- Security
- Distributed nature raises security concerns.
- Requires robust authentication and encryption mechanisms.