Logging Data
Logs and Metadata
Log files record either events that occur in an operating system or other software that runs, or messages between different users of a communication software.
Types of log files:
- Network log files
- System log files
- Application log files
- Security log files
- Web log files
- DNS logs
- Authentication logs
- Dump files
- VoIP logs, as part of network logs files
Metadata describes other data by providing an underlying definition or description by summarizing basic information about data that makes finding and working with particular instances of data easier.
- Data about the data
- Example, phone bill shows the calls made, but not actual conversation in the calls.
Network Traffic Flow
NetFlow
NetFlow is a Cisco-developed means of reporting network flow information to a structured database. Note that this is not a packet capture, but it can capture:
- Source
- Destination
- Volume
- Paths
To learn more, please see NetFlow.
Sampled Flow
Sampled Flow or SFlow provides a means for exporting truncated packets, together with interface counters for the purpose of network monitoring. Similar to NetFlow, SFlow doesn’t provide a full packet capture, just some of the sampled flow.
IPFix
IPFix (IP Flow Information Export) is a standard protocol for exporting flow information that is used for monitoring and analyzing network traffic flow data.
- Allows network devices to export flow records to a collector for analysis.
- Network traffic analysis, performance monitoring, and security threat detection.
Centralized Logging
SNMP
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is a widely used protocol for monitoring and managing network devices.
- Operates on the Application Layer of the OSI model.
- Software agent or built into firmware; uses a manager/agent architecture.
- SNMP traps provide real-time alerts and notify management stations.
- More details can be fond here: SNMP
Windows Logs
Windows Logs record system, security, and application events, essential for troubleshooting and security auditing.
- View and manage with Windows Event Viewer Subscriptions.
- Logs from Windows host can be pushed to a collector server over WinRM protocol.
- The collector server can also initiate and pull the logs from the hosts.
- Key categories: System, Application, Security.
SIEM
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems aggregate and analyze security events for real-time monitoring and incident response.
- Collects log and event data from multiple sources and uses correlation to detect threats.
- Provides dashboards, alerts, and reports for alerts, packet captures, malware alerts, etc.
- More details can be fond here: SIEM
Logging Tools
Journalctl
Linux command-line utility for querying and displaying logs from the systemd journal, which is responsible for managing and storing log data on a Linux machine.
- Part of the systemd system and service manager used in many Linux distributions.
- Filtering options, including time range, unit, priority, and log level.
- Offers interactive and non-interactive modes for browsing log entries efficiently.
NXLog
NXLog is an open-source, cross-platform log collection and management tool that facilitates the collection, processing, and forwarding of logs from various sources.
- Supports multiple log formats and protocols, including syslog, JSON, and XML.
- Offers filtering, parsing, and enrichment capabilities for log data.
- Integrates with SIEM solutions and log management platforms.
- Unix, Linux, and Windows.
Syslog
There are different variations of syslog which all permit the logging of data from different types of systems in a central repository.
Syslog
- Standard logging protocol used for message logging on Unix-like systems.
- Sends log messages to a central server or repository for storage and analysis.
- Widely supported by various network devices, servers, and applications.
Rsyslog
- Enhanced version of syslog, offering additional features and capabilities.
- Supports reliable transmission of log messages over TCP and TLS.
- Provides advanced filtering, message modification, and routing options.
- Linux and Unix.
Syslog-ng
- Advanced features and customization options.
- High-performance log processing, including filtering, routing, and correlation.
- Offers support for log classification, encryption, and archival.
- Linux and Unix.
Configuring Linux Log Forwarding
Configure first the centralized host that will receive the logs. Modify the /etc/rsyslog.conf. Enable a listener on port 514 or you can also specify a different port.
# /etc/rsyslog.conf
#### MODULES ####
module(load="imuxsock") # provides support for local system logging (e.g., via logger command)
module(load="imklog") # provides kernel logging support (previously done by rklogd)
module(load="imudp") # provides UDP syslog reception
input(type="imudp" port="514")
module(load="imtcp") # provides TCP syslog reception
input(type="imtcp" port="514")
Save the file and restart rsyslog afterwards.
sudo systemctl restart rsyslog
sudo systemctl status rsyslog
Verify that the listener is created:
sudo netstat -tnlpu | grep rsyslog
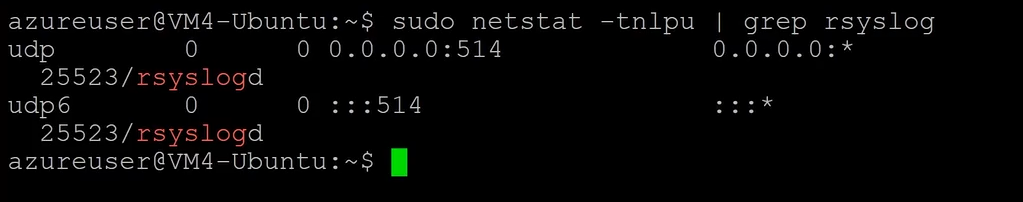
Next, configure the client that will be forwarding the logs to the centralized log server. Modify the /etc/rsyslog.conf and add the line at the bottom of the file:
*.* @10.1.1.5 # IP of the central log server.
“.” means any log entry. Save the file and restart the rsyslog service.
sudo systemctl restart rsyslog
sudo systemctl status rsyslog
To verify, we can use the logger utility.
logger "testing forwarding from client"
This should appear in the syslog file in the client side.
tail -10 /var/log/syslog
Go to the central log server and run the same command. We should see the same message.
Investigating Logs
Firewall Logs
Below is a sample Fortigate Firewall log showing blocked connection attempts via different ports. From here we can see that an attacker might be trying to perform port scans.
2024-05-30T10:15:23.000Z Fortigate:ID=firewall time="2024-05-30 10:15:23" action=deny src=203.0.113.10 dst=192.0.2.20 proto=tcp sport=54321 dport=22
2024-05-30T10:15:24.000Z Fortigate:ID=firewall time="2024-05-30 10:15:24" action=deny src=203.0.113.10 dst=192.0.2.20 proto=tcp sport=54321 dport=80
2024-05-30T10:15:25.000Z Fortigate:ID=firewall time="2024-05-30 10:15:25" action=deny src=203.0.113.10 dst=192.0.2.20 proto=tcp sport=54321 dport=443
2024-05-30T10:15:26.000Z Fortigate:ID=firewall time="2024-05-30 10:15:26" action=deny src=203.0.113.10 dst=192.0.2.20 proto=udp sport=12345 dport=53
2024-05-30T10:15:27.000Z Fortigate:ID=firewall time="2024-05-30 10:15:27" action=deny src=203.0.113.11 dst=192.0.2.20 proto=tcp sport=65432 dport=22
2024-05-30T10:15:28.000Z Fortigate:ID=firewall time="2024-05-30 10:15:28" action=deny src=203.0.113.11 dst=192.0.2.20 proto=tcp sport=65432 dport=443
2024-05-30T10:15:29.000Z Fortigate:ID=firewall time="2024-05-30 10:15:29" action=deny src=203.0.113.11 dst=192.0.2.20 proto=udp sport=23456 dport=53
In this second one, we can see a web application firewall with deep inspection enabled. This can block attacks suck as time-based SQL injections.
Timestamp Action Source IP Destination IP Method Path Attack Rule Reason
------------------- ------ --------------- -------------- ------ ------------------ ---------------------------- ------------------------- --------------------------------------------------
2024-05-30T10:15:23 Block 203.0.113.10 192.0.2.50 POST /login.php SQL Injection SQL Injection Prevention SQL injection attempt detected
2024-05-30T10:15:24 Block 203.0.113.11 192.0.2.50 GET /api/user_info.php Database Drop Database Protection Attempt to drop database detected
2024-05-30T10:15:25 Block 203.0.113.12 192.0.2.50 POST /search.php Time-Based SQL Injection SQL Injection Prevention Time-based SQL injection attempt detected
2024-05-30T10:15:26 Block 203.0.113.13 192.0.2.50 POST /admin.php Information Gathering SQL SQL Injection Prevention Attempt to gather information through SQL commands
Application Logs
Sample log from a Spring Boot application deployed via a Tomcat server, showing various types of attacks.
2024-05-30 10:15:23.000 INFO [http-nio-8080-exec-1] com.example.demo.security.SecurityConfig: Blocked access from IP: 203.0.113.10 - SQL Injection attempt detected in /login
2024-05-30 10:15:24.000 INFO [http-nio-8080-exec-2] com.example.demo.security.SecurityConfig: Blocked access from IP: 203.0.113.11 - Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) attempt detected in /search
2024-05-30 10:15:25.000 INFO [http-nio-8080-exec-3] com.example.demo.security.SecurityConfig: Blocked access from IP: 203.0.113.12 - Path Traversal attempt detected in /files
2024-05-30 10:15:26.000 INFO [http-nio-8080-exec-4] com.example.demo.security.SecurityConfig: Blocked access from IP: 203.0.113.13 - Remote Code Execution attempt detected in /execute
2024-05-30 10:15:27.000 INFO [http-nio-8080-exec-5] com.example.demo.security.SecurityConfig: Blocked access from IP: 203.0.113.14 - Brute Force attempt detected in /login
2024-05-30 10:15:28.000 INFO [http-nio-8080-exec-6] com.example.demo.security.SecurityConfig: Blocked access from IP: 203.0.113.15 - Malicious File Upload attempt detected in /upload
2024-05-30 10:15:29.000 INFO [http-nio-8080-exec-7] com.example.demo.security.SecurityConfig: Blocked access from IP: 203.0.113.16 - Denial of Service (DoS) attempt detected in /api/data
Endpoint Logs
Sample log from an endpoint security system showing various malware attacks.
2024-05-30 10:15:23.000 INFO [EndpointSecurity] Malware detected: Trojan.Win32.Generic, Action taken: Quarantined, File: C:\Users\User\Downloads\malicious.exe, Source IP: 203.0.113.10
2024-05-30 10:15:24.000 WARN [EndpointSecurity] Malware detected: Ransomware.WannaCry, Action taken: Blocked, File: C:\Users\User\Documents\important.doc, Source IP: 203.0.113.11
2024-05-30 10:15:25.000 INFO [EndpointSecurity] Malware detected: Spyware.Keylogger, Action taken: Removed, File: C:\Windows\System32\keylogger.dll, Source IP: 203.0.113.12
2024-05-30 10:15:26.000 INFO [EndpointSecurity] Malware detected: Adware.Win32.PopAd, Action taken: Quarantined, File: C:\Program Files\PopAd\popad.exe, Source IP: 203.0.113.13
2024-05-30 10:15:27.000 WARN [EndpointSecurity] Malware detected: Worm.Win32.Blaster, Action taken: Blocked, File: C:\Users\User\AppData\Local\Temp\blaster.exe, Source IP: 203.0.113.14
2024-05-30 10:15:28.000 INFO [EndpointSecurity] Malware detected: Virus.Win32.Sality, Action taken: Removed, File: C:\Windows\System32\infectedfile.dll, Source IP: 203.0.113.15
2024-05-30 10:15:29.000 WARN [EndpointSecurity] Malware detected: TrojanDownloader.Win32.Agent, Action taken: Blocked, File: C:\Users\User\Downloads\agent.exe, Source IP: 203.0.113.16
OS Logs
Example of a Linux log file (/var/log/auth.log) showing multiple failed login attempts.
May 30 10:15:23 server sshd[12345]: Failed password for invalid user admin from 203.0.113.10 port 42258 ssh2
May 30 10:15:24 server sshd[12346]: Failed password for invalid user root from 203.0.113.11 port 42259 ssh2
May 30 10:15:25 server sshd[12347]: Failed password for invalid user user1 from 203.0.113.12 port 42260 ssh2
May 30 10:15:26 server sshd[12348]: Failed password for invalid user guest from 203.0.113.13 port 42261 ssh2
May 30 10:15:27 server sshd[12349]: Failed password for invalid user test from 203.0.113.14 port 42262 ssh2
May 30 10:15:28 server sshd[12350]: Failed password for invalid user admin from 203.0.113.15 port 42263 ssh2
May 30 10:15:29 server sshd[12351]: Failed password for invalid user root from 203.0.113.16 port 42264 ssh2
May 30 10:15:30 server sshd[12352]: Failed password for invalid user user1 from 203.0.113.17 port 42265 ssh2
May 30 10:15:31 server sshd[12353]: Failed password for invalid user guest from 203.0.113.18 port 42266 ssh2
May 30 10:15:32 server sshd[12354]: Failed password for invalid user test from 203.0.113.19 port 42267 ssh2
Network Logs
Sample network logs from AWS CloudWatch, where we can see a possible attacker attempting to change their MAC address to evade detection.
2024-05-30T10:15:23.000Z ALLOW SourceIP=203.0.113.10 DestinationIP=192.0.2.10 SourceMAC=00:0a:95:9d:68:16 DestinationPort=22 Protocol=TCP Action=ALLOW
2024-05-30T10:15:24.000Z DENY SourceIP=203.0.113.11 DestinationIP=192.0.2.11 SourceMAC=00:0a:95:9d:68:17 DestinationPort=80 Protocol=TCP Action=DENY
2024-05-30T10:15:25.000Z ALLOW SourceIP=203.0.113.12 DestinationIP=192.0.2.12 SourceMAC=00:0a:95:9d:68:18 DestinationPort=443 Protocol=TCP Action=ALLOW
2024-05-30T10:15:26.000Z DENY SourceIP=203.0.113.13 DestinationIP=192.0.2.13 SourceMAC=00:0a:95:9d:68:19 DestinationPort=22 Protocol=TCP Action=DENY
2024-05-30T10:15:27.000Z ALLOW SourceIP=203.0.113.14 DestinationIP=192.0.2.14 SourceMAC=00:0a:95:9d:68:16 DestinationPort=80 Protocol=TCP Action=ALLOW
2024-05-30T10:15:28.000Z DENY SourceIP=203.0.113.15 DestinationIP=192.0.2.15 SourceMAC=00:0a:95:9d:68:20 DestinationPort=443 Protocol=TCP Action=DENY
2024-05-30T10:15:29.000Z ALLOW SourceIP=203.0.113.16 DestinationIP=192.0.2.16 SourceMAC=00:0a:95:9d:68:21 DestinationPort=22 Protocol=TCP Action=ALLOW
2024-05-30T10:15:30.000Z DENY SourceIP=203.0.113.17 DestinationIP=192.0.2.17 SourceMAC=00:0a:95:9d:68:22 DestinationPort=80 Protocol=TCP Action=DENY
2024-05-30T10:15:31.000Z ALLOW SourceIP=203.0.113.18 DestinationIP=192.0.2.18 SourceMAC=00:0a:95:9d:68:16 DestinationPort=443 Protocol=TCP Action=ALLOW
2024-05-30T10:15:32.000Z DENY SourceIP=203.0.113.19 DestinationIP=192.0.2.19 SourceMAC=00:0a:95:9d:68:23 DestinationPort=22 Protocol=TCP Action=DENY
Cisco router logs showing blocked ARP spoofing attacks:
May 30 10:15:23.000: %SW_MATM-4-MACFLAP_NOTIF: Host 00:0a:95:9d:68:16 in vlan 10 is flapping between port Gi0/1 and port Gi0/2
May 30 10:15:23.001: %IP-4-DUPADDR: Duplicate address 192.0.2.10 on Vlan10, sourced by 00:0a:95:9d:68:16
May 30 10:15:23.002: %SW_DAI-4-DHCP_SNOOPING: ARP inspection check failed on interface Gi0/1, VLAN 10. Incoming packet from 00:0a:95:9d:68:16 was dropped.
May 30 10:15:24.000: %SW_MATM-4-MACFLAP_NOTIF: Host 00:0a:95:9d:68:17 in vlan 10 is flapping between port Gi0/3 and port Gi0/4
May 30 10:15:24.001: %IP-4-DUPADDR: Duplicate address 192.0.2.11 on Vlan10, sourced by 00:0a:95:9d:68:17
May 30 10:15:24.002: %SW_DAI-4-DHCP_SNOOPING: ARP inspection check failed on interface Gi0/3, VLAN 10. Incoming packet from 00:0a:95:9d:68:17 was dropped.
May 30 10:15:25.000: %SW_MATM-4-MACFLAP_NOTIF: Host 00:0a:95:9d:68:18 in vlan 10 is flapping between port Gi0/5 and port Gi0/6
May 30 10:15:25.001: %IP-4-DUPADDR: Duplicate address 192.0.2.12 on Vlan10, sourced by 00:0a:95:9d:68:18
May 30 10:15:25.002: %SW_DAI-4-DHCP_SNOOPING: ARP inspection check failed on interface Gi0/5, VLAN 10. Incoming packet from 00:0a:95:9d:68:18 was dropped.
May 30 10:15:26.000: %SW_MATM-4-MACFLAP_NOTIF: Host 00:0a:95:9d:68:19 in vlan 10 is flapping between port Gi0/7 and port Gi0/8
May 30 10:15:26.001: %IP-4-DUPADDR: Duplicate address 192.0.2.13 on Vlan10, sourced by 00:0a:95:9d:68:19
May 30 10:15:26.002: %SW_DAI-4-DHCP_SNOOPING: ARP inspection check failed on interface Gi0/7, VLAN 10. Incoming packet from 00:0a:95:9d:68:19 was dropped.