Audits and Assessments
- Internal Audits
- Internal Assessments
- External Audits and Assessments
- Penetration Testing
- Penetration Testing Process
- Reconnaisance in Pentesting
- Attestation of Findings
Internal Audits
Internal Audits are systematic evaluations of the effectiveness of internal controls, compliance, and integrity of information systems and processes.
- Focuses on data protection, network security, access controls, and incident response.
- Example: Internal review of password policies, user access controls
How it works
- Internal audit team checks control policies and procedures agains best practices and regulatory requirements.
- User access rights is examined ensure each employee’s access is align with their responsibilities.
- Audit team verifies user access rights processes, including approvals and timely revocation.
- Finally, they test the effectiveness of access controls using accounts with limited permissions.
- Findings are documented and used as basis for recommendation for procedure improvements
Compliance
Compliance ensures that information systems and security practices meet established standards, regulations, and laws.
- Crucial for protecting sensitive data and avoiding legal penalties.
- Involves implementing specific security controls and maintaining policies and procedures.
- Regularly auditing and assessing the organization’s security posture.
To learn more, please Compliance as a Governance Element.
Audit Committee
A group of people responsible for supervising the organization’s audit and compliance functions.
- Typically members of the company’s board of directors.
- Reviews the organization’s financial reporting processes and internal controls.
- Ensures the organization is in compliance with legal regulatory requirements.
- Addresses any issues raised by auditors.
Internal Assessments
An in-depth analysis to identify and assess potential risks and vulnerabilities in an organization’s information systems.
- Often performed before implementing new systems or before making any changes to existing ones.
- Identify gaps in an organization’s compliance efforts and to prepare for formal audits.
- Most are conducted as Self-assessments - conducted to gauge adherence to standards and regulations.
Assessment Process
- Conducting threat modelling exercise to identify potential threats.
- Combination of automated tools and manual testing techniques are used to assess vulnerabilities.
- Risks assessment, for evaluating potential impact of the identified threats and the cost of implementing security measures.
- Mitigation strategies are recommended based on the assessment results
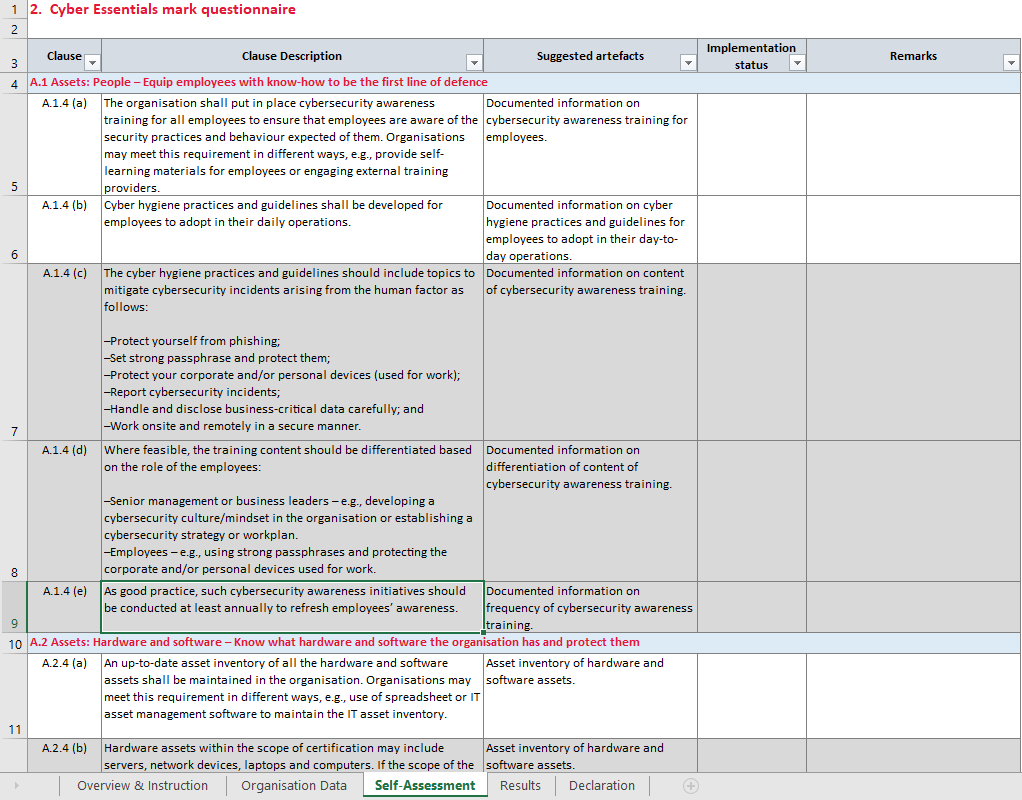
Example of Self Assessment Questionnaire
Below is an excerpt from the Self-Assessment Questionnaire provided by Cyber Security Agency of Singapore. The full questionnaire can be found here.
External Audits and Assessments
External Audits
External Audits are systematic evaluations carried out by external entities to assess an organization’s information systems and security controls.
- Provides an objective perspective to an organization’s true security posture.
- Also covers data protection, network security, access controls, and incident response.
- Uncover deficiencies in policies and controls to ensure alignment with diverse regulatory standards.
- Example: Evaluating compliance with PCI DSS, HIPAA, GDPR, etc.
External Assessments
Detailed analysis conducted by independent entities to identify vulnerabilities and risks.
- Involves combinations of automated scanning tools and manual testing techniques.
- Risk Assessment, Vulnerability Assessment, and Threat Assessment.
Regulatory Compliance
Objective that organizations aim to reach in adherence to applicable laws, policies, and regulations.
- Organizations are adopting the use of consolidated and harmonized set of compliance controls.
- Adherence to industry-specific requirements like HIPAA, PCI DSS, and GDPR.
- Controls, such as NIST Cybersecurity Framework for compliance mechanisms.
Independent Third-Party Audit
Offers validation of security practices, fostering trust with customers, stakeholders, and regulatory authorities.
- Provides an unbiased perspective of the organization’s security posture.
- Identify potential weaknesses that might be overlooked in internal audits and assessments.
- Regulations include GDPR and PCI DSS.
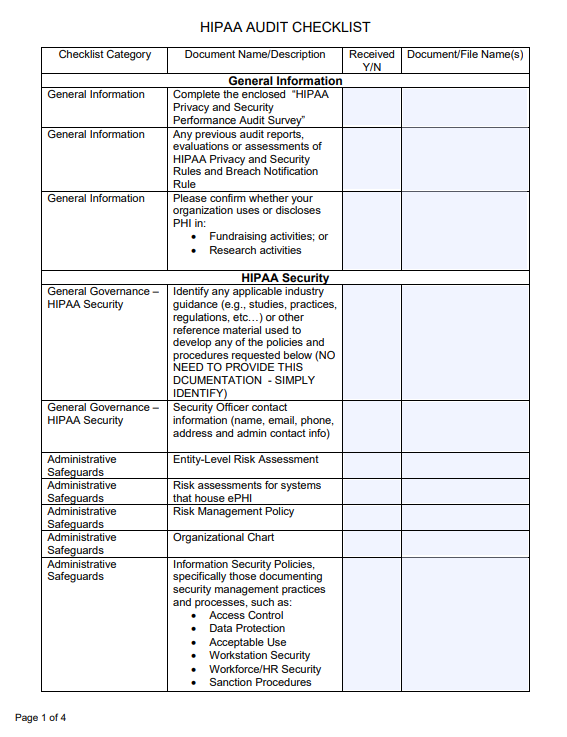
Example of HIPAA Audit Checklist
Below is an excerpt from the HIPAA Audit Checklist provided by San Bernardino County.
Penetration Testing
Penetration Testing is a simulated cyber attack that helps in the assessment of computer systems for exploitable vulnerabilities.
- Agree on methodology and rules of engagement before performing pentests.
- Simulate network intrusion based on threat scenarios.
- Normally triggers IDS/IPS alerts. If it doesn’t, then this should also be reported.
- There’s a specific goal in mind.
Types:
- Physical Pentesting
- Offensive Pentesting
- Defensive Pentesting
- Integrated Pentesting
Physical Pentesting
Physical pentesting involves evaluating the physical security measures of a facility to identify vulnerabilities that could be exploited to gain unauthorized access to sensitive areas or information.
- Assesses physical barriers such as locks, doors, and gates.
- Tests the effectiveness of security personnel and protocols.
- Evaluates the security of entry points, such as windows and ventilation systems.
- Identifies potential social engineering vulnerabilities, like tailgating.
- Raises awareness about the importance of physical security among employees.
Offensive Pentesting
Offensive pentesting, also known as red teaming, is a proactive approach that focuses on simulating real-world attacks to identify weaknesses in an organization’s security infrastructure from an attacker’s perspective.
- Identifies vulnerabilities in networks, systems, and applications.
- Evaluates response capabilities of security teams.
- Provides actionable insights for improving security posture.
- Results can also used to garner more funding and support for cybersecurity investments.
Defensive Pentesting
Defensive pentesting, also known as blue teaming, is a reactive approach that emphasizes identifying and fortifying weaknesses within an organization’s defenses by simulating potential attack scenarios.
- Focuses on strengthening existing security measures.
- Enhances incident detection and response capabilities.
- Conducts regular security assessments to identify new vulnerabilities.
- Collaborates with offensive teams to improve overall security.
Integrated Pentesting
Integrated pentesting, also known as purple teaming, combines both offensive and defensive strategies to create a comprehensive security evaluation, ensuring that both attack simulations and defensive measures are optimized.
- Merges red and blue team methodologies for holistic security testing.
- Identifies and addresses both internal and external threats.
- Enhances coordination between offensive and defensive security teams.
- Provides a thorough analysis of an organization’s security posture.
Penetration Testing Process
Penetration testing is a structured approach to identifying and exploiting vulnerabilities in a system to assess its security.
-
Rules of Engagement
- Define the scope and objectives of the test.
- Establish clear communication channels and protocols.
- Ensure legal and ethical boundaries are respected.
-
Discovery/Enumeration
- Gather information about the target system.
- Identify open ports, services, and potential entry points.
- Map the network and identify connected devices.
-
Vulnerability Identification and Exploitation
- Scan for known vulnerabilities and weaknesses.
- Attempt to exploit identified vulnerabilities.
- Validate the exploitability and impact of each vulnerability.
-
Privilege Escalation, Backdoors, and Pivoting
- Attempt to gain higher-level access to the system.
- Install backdoors for future access if permitted.
- Use the compromised system to access other network areas.
-
Cleanup
- Remove any tools or scripts used during the test.
- Restore the system to its original state.
- Ensure no traces of the test remain on the target.
-
Report Findings
- Document all discovered vulnerabilities and exploited weaknesses.
- Provide detailed findings, including evidence and impact analysis.
- Offer recommendations for remediation and improving security posture.
Reconnaisance in Pentesting
Reconnaissance, also known as information gathering, is the first phase of a penetration test where the pentester collects as much information as possible about the target system to identify potential vulnerabilities.
- Helps in identifying potential entry points for an attack.
- Provides critical information to tailor the penetration test to the specific target.
- Proper reconnaissance can help in planning stealthy attacks to avoid detection.
- Ensures overall test effectiveness by covering all possible vulnerabilities.
Types of Reconnaissance
Active Reconnaissance
- Directly interacting with the target system to gather detailed information.
- Performing network scans to identify active devices and services.
- Sending probes or queries to the target to elicit responses.
- Utilizing tools like ping sweeps and traceroutes to map network paths.
- While it can yield a lot of information, it also carries a higher risk of detection.
Passive Reconnaissance
- Gathering information without directly interacting with the target system to avoid detection.
- Analyzing publicly available data such as website content and social media profiles.
- Reviewing public records and documentation for insights.
- Monitoring news articles and press releases for information leaks.
- Less likely to be detected, but can yield less information.
Environment Classifications
Environment classifications define the level of information available to the tester about the target system. This classification helps in simulating different attack scenarios, ranging from those performed by internal employees to external attackers with no prior knowledge of the system.
Known Environment
- Tester has full knowledge of the target system’s architecture, configurations, and security measures.
- Focuses on known assets, evaluating vulnerabilities and weaknesses.
- Often referred to as white-box testing.
- Allows for comprehensive and detailed testing.
- Resembles an insider threat scenario.
- Typically used for internal audits and in-depth security assessments.
Partially Known Environment
- The tester has limited knowledge about the target system.
- Also known as grey-box testing.
- Combines elements of both known and unknown environments.
- Balances thoroughness and realistic attack scenarios.
- Often used when some information is available but full details are not disclosed.
- Uncovers vulnerabilities in known assets, as well as vulnerabilities in hidden or forgotten assets.
Unknown Environment
- The tester has no prior knowledge of the target system.
- Commonly referred to as black-box testing.
- Simulates a real-world external attacker, where attacker knows little to nothing about the target.
- Relies heavily on reconnaissance and discovery techniques.
- Provides an unbiased view of the system’s security posture from an outsider’s perspective.
Methods and Techniques
Open Source Intelligence (OSINT)
- Using publicly available resources such as social media, websites, and databases to gather information.
- Leveraging search engines to find data about the target.
- Reviewing forums, blogs, and online communities for relevant information.
- Analyzing metadata from documents and images for hidden details.
Network Scanning
- Identifying live hosts, open ports, and services running on the target network.
- Using tools like Nmap to perform comprehensive scans.
- Conducting vulnerability scans to find exploitable weaknesses.
- Mapping network topologies and discovering connected devices.
Footprinting
- Mapping out the network architecture, including domain names, IP addresses, and subdomains.
- Identifying key infrastructure components and their relationships.
- Gathering details about network devices, operating systems, and software versions.
- Documenting external and internal network boundaries.
Social Engineering
- Manipulating individuals to divulge confidential information.
- Conducting phishing attacks to obtain login credentials.
- Pretexting to impersonate trusted individuals or entities.
- Using baiting tactics to lure targets into revealing information.
Tools
Here’s the information converted into a table format:
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| Nmap | A network scanning tool to discover hosts and services on a network. |
| Shodan | A search engine for Internet-connected devices to find exposed systems. |
| WHOIS Lookup | A protocol used to query databases for domain registration information. |
| Google Dorking | Using advanced search techniques to find specific information on the web. |
| curl | A command-line tool for transferring data with URLs. |
| scanless | A tool to perform open port scans using multiple online scanners. |
| dnsenum | A DNS enumeration tool that helps in gathering information about DNS servers and records. |
| tcpreplay | A suite of tools to edit and replay captured network traffic. |
| Cuckoo | An automated malware analysis system. |
| theHarvester | An information gathering tool to get emails, subdomains, hosts, employee names, open ports, and banners. |
| hping3 | A network tool able to send custom TCP/IP packets and to display target replies like ping does with ICMP replies. |
| Metasploit Framework | A penetration testing framework that helps identify and exploit vulnerabilities. |
Attestation of Findings
Process that involves the formal validation or confirmation provided by an entity that is used to assert the accuracy and authenticity of a specific information.
- Signifies that the findings of the penetration testing is valid based on the evidence.
- Organizations may require a letter of attestation from the pentesting firm to show as an official record.
- Should include the summary of findings and the evidence that the security assessment is conducted.
- Evidences might include data, logs, explanations, or even some of the exploit code.
- Some evidences can be showed during the attestation meeting, but doesn’t need to leave the evidence.
- In contrast to pentesting reports, which are actually delivered and left to the organization.
Types:
- Software Attestation
- Hardware Attestation
- System Attestation
Software Attestation
Software attestation verifies the integrity and authenticity of software running on a device, ensuring that it has not been tampered with or compromised.
- Confirms the software’s integrity using cryptographic methods.
- Ensures that the software is from a trusted source.
- Detects unauthorized modifications or malware.
- Commonly used in secure boot processes to verify operating systems and applications.
Hardware Attestation
Hardware attestation ensures that the physical hardware of a device is authentic and has not been altered or replaced with malicious components.
- Utilizes unique hardware identifiers and cryptographic signatures.
- Verifies the integrity of hardware components, such as CPUs and TPMs (Trusted Platform Modules).
- Detects counterfeit or tampered hardware.
- Essential for maintaining trust in secure environments, like financial institutions and military systems.
System Attestation
System attestation involves validating the overall security posture of an entire system, including both its hardware and software components.
- Assesses the combined integrity of hardware, firmware, and software.
- Ensures that all system components work together securely.
- Provides a comprehensive security overview of the entire device or network.
- Often used in critical infrastructure and high-assurance systems to maintain robust security standards.