All-Things-Docker-and-Kubernetes
Security Primitives
Secure Hosts
Starting with the hosts or nodes that form the cluster itself. They are the first line which need to be secured through:
- Disabling root access
- Disabling password-based authentication
- Enabling only SSH-Key based authentication
API Server
At the center of all operations in Kubernetes is the API server. Basically all operations can be performed once we have access to it. To secure the API Server access, there are two questions to ask:

Who can access?
This refers to the actual accounts that can access the APi server and is defined by the authentication mechanisms:
- Basic authentication (usernames and passwords)
- Bearer tokens (usernames and tokens)
- x509 certificates
- Service accounts
- External Authentication providers such as LDAP
- OpenID Connect (OIDC) tokens (currently limited support)
What can they do?
Once the account gained accessed to the cluster, the next thing to look at is what actions they can perform. This can be defined by the following authorization mechanisms:
- RBAC Authorization
- ABAC Authorization
- Node Authorization
- Webhook Mode
To learn more, check out Kubernetes Security - Authentication and Authorization
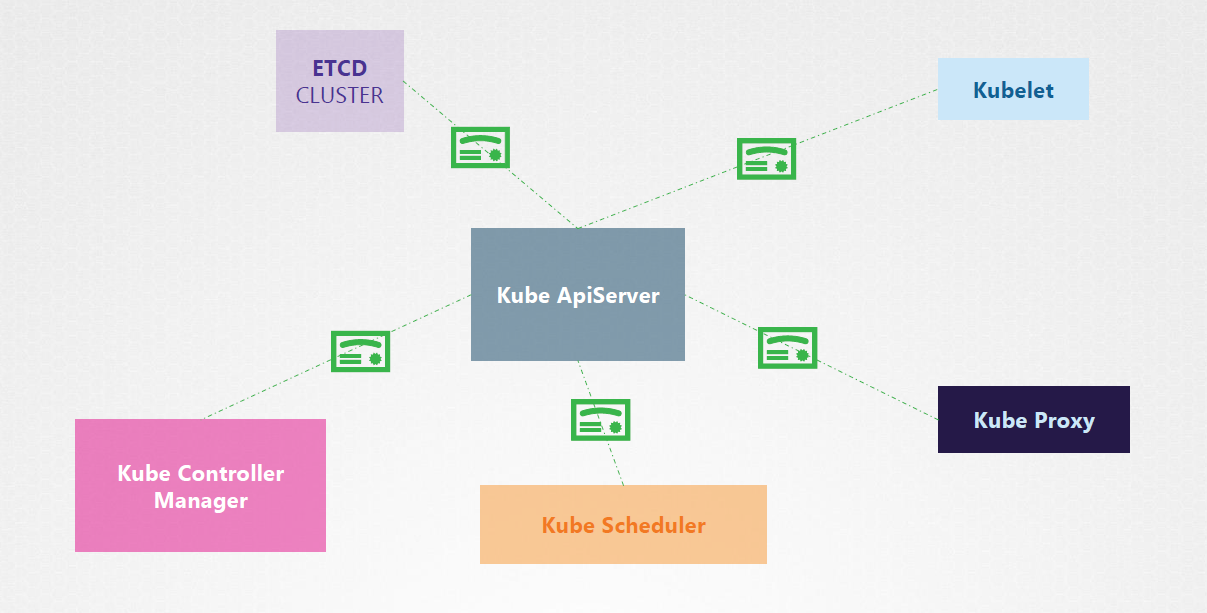
TLS Certificates
Communication between cluster components is secured through TLS encryption. This involves communication between:
- etcd Cluster
- Kubecontroller Manager
- Scheduler
- API Server
To learn more, check out Kubernetes Security - TLS Certificates
Network Policies
Applications running inside the cluster can access each other’s Pods by default but their communication can be restricted by adding network policies.