All-Things-Docker-and-Kubernetes
Kubernetes API
Kubernetes API Server
This is the main way to interact with the cluster. It is a RESTful API that runs over HTTP or HTTPS using JSON.
-
composed of API Objects, which are a collection of primitives to represent your system’s state
-
Enables to declaratively configuring the state, which means we define what we want the end result to look like instead of defining the individual steps.
-
information exchanged with the cluster are persisted and serialized to the data store
Kubernetes API
The Kubernetes API is not a single API but rather a collection of APIs which defines the resources that can be used in the Kubernetes environment. The API information is what we’ll use in the Kubernetes YAML file. The Kubernetes API is composed of multiple groupings based on their purpose:
/version
/healthz
/metrics
/logs
/api
/apis
The two APIs used for cluster functionality are:
- /api - core APi, represented by “v1”
- /apis - named group
The core groups is where all the core functionalities exist.
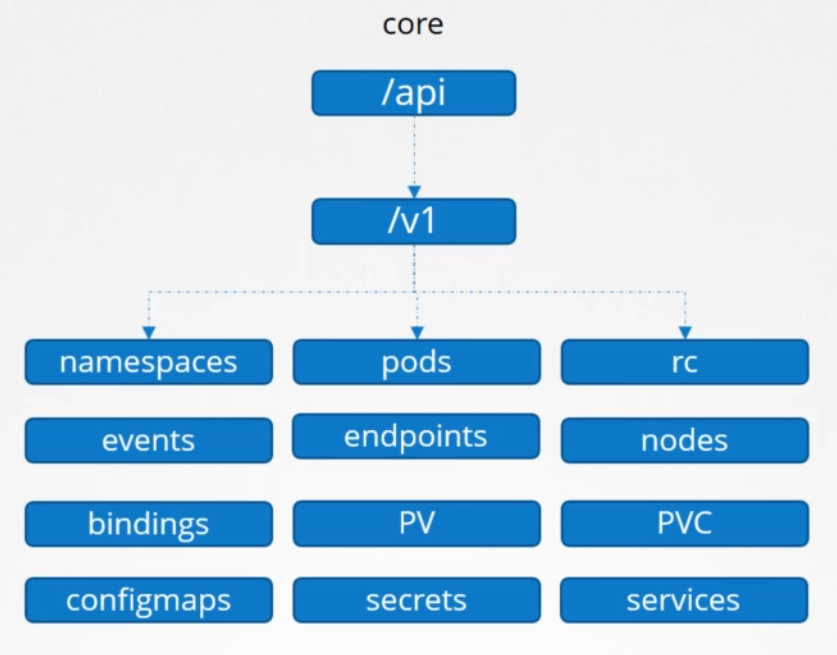
The named group is where all the newer API features are added. The sample below are just a few.
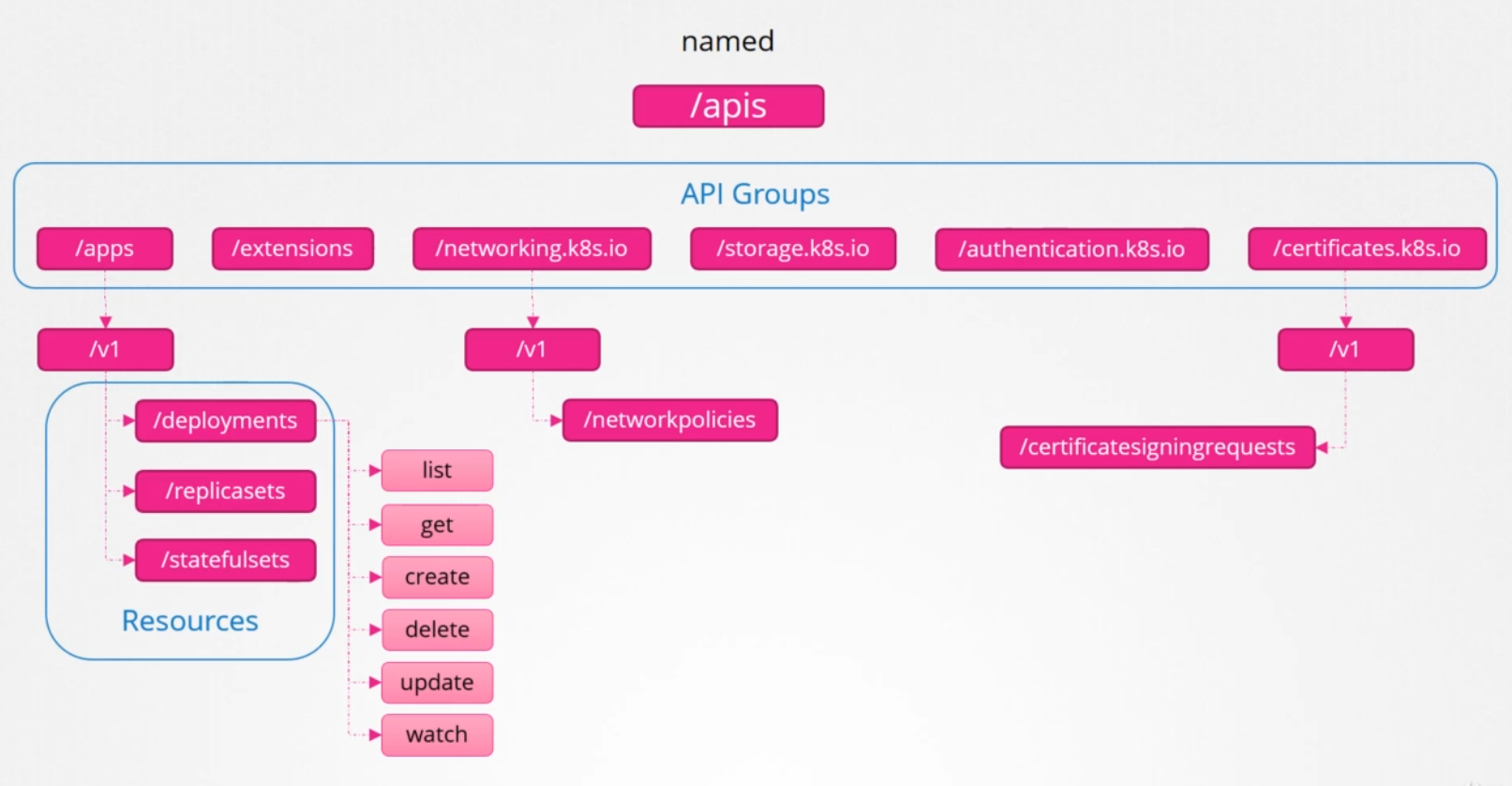
To show the list of API groups (localhost assumes that Kubernetes cluster is deployed locally)
$ curl https://localhost:6443 -k
{
"paths": [
"/api",
"/api/v1",
"/apis",
"/apis/",
"/healthz",
"/logs",
"/metrics",
"/openapi/v2",
"/version
To show the resource group for a specific API group:
$ curl https://localhost:6443/apis -k | grep "name"
"name": "extensions",
"name": "apps",
"name": "events.k8s.io",
"name": "authentication.k8s.io",
"name": "authorization.k8s.io",
"name": "autoscaling",
"name": "batch",
If you get an Forbidden error message, that means you don’t have access to certain API. You will need to specify the certificate and key.
curl https://localhost:6443 -k \
--cacert ca.crt \
--cert admin.crt \
--key admin.key
API Resources
To show the list of resources defined in the API:
kubectl api-resources
To show the resource versions:
kubectl api-versions
To get more details about a resource:
kubectl explain <resource>
To explain further:
kubectl explain <resource>.spec
The API versions are updated every 3 months, which may include the APIs included in that version. This may include some syntax or parameter changes which we may need to reflect in our Kubernetes YAML files.
Here’s an example output:
$ kubectl api-resources
NAME SHORTNAMES APIVERSION NAMESPACED KIND
bindings v1 true Binding
componentstatuses cs v1 false ComponentStatus
configmaps cm v1 true ConfigMap
endpoints ep v1 true Endpoints
events ev v1 true Event
limitranges limits v1 true LimitRange
namespaces ns v1 false Namespace
nodes no v1 false Node
persistentvolumeclaims pvc v1 true PersistentVolumeClaim
persistentvolumes pv v1 false PersistentVolume
pods po v1 true Pod
podtemplates v1 true PodTemplate
replicationcontrollers rc v1 true ReplicationController
resourcequotas quota v1 true ResourceQuota
secrets v1 true Secret
serviceaccounts sa v1 true ServiceAccount
services svc v1
$ kubectl api-versions
admissionregistration.k8s.io/v1beta1
apiextensions.k8s.io/v1beta1
apiregistration.k8s.io/v1
apiregistration.k8s.io/v1beta1
apps/v1
apps/v1beta1
apps/v1beta2
authentication.k8s.io/v1
authentication.k8s.io/v1beta1
authorization.k8s.io/v1
authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
autoscaling/v1
autoscaling/v2beta1
autoscaling/v2beta2
batch/v1
batch/v1beta1
$ kubectl explain deploy
KIND: Deployment
VERSION: extensions/v1beta1 <== API Version
DESCRIPTION:
DEPRECATED - This group version of Deployment is deprecated by
apps/v1beta2/Deployment. See the release notes for more information.
Deployment enables declarative updates for Pods and ReplicaSets.
FIELDS:
apiVersion <string>
APIVersion defines the versioned schema of this representation of an
object. Servers should convert recognized schemas to the latest internal
value, and may reject unrecognized values. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/api-conventions.md#resources
$ kubectl explain pod
KIND: Pod
VERSION: v1 <== API version
DESCRIPTION:
Pod is a collection of containers that can run on a host. This resource is
created by clients and scheduled onto hosts.
FIELDS:
apiVersion <string>
APIVersion defines the versioned schema of this representation of an
object. Servers should convert recognized schemas to the latest internal
value, and may reject unrecognized values. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/api-conventions.md#resources
$ kubectl explain deployment.spec.strategy
RESOURCE: strategy <Object>
DESCRIPTION:
The deployment strategy to use to replace existing pods with new ones.
DeploymentStrategy describes how to replace existing pods with new ones.
FIELDS:
rollingUpdate <Object>
Rolling update config params. Present only if DeploymentStrategyType =
RollingUpdate.
type <string>
Type of deployment. Can be "Recreate" or "RollingUpdate". Default is
RollingUpdate.
Resources
-
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/overview/kubernetes-api/
-
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/52711326/kubernetes-how-to-know-latest-supported-api-version