AWS Disaster Recovery
This is not an exhaustive documentation of all the existing AWS Services. These are summarized notes that I used for the AWS Certifications.
To see the complete documentation, please go to: AWS documentation
Disaster
- Disaster: any event that has a negative impact on a company's business continuity or finances.
- Disaster Recovery (DR) is about preparing for and recovering from a disaster.
- Disaster recovery solutions:
- On-premise to on-premise: traditional DR, expensive
- On-premise to cloud: hybrid recovery
- AWS Cloud Region A to AWS Cloud Region B
RPO and RTO
- RPO - Recovery Point Objective: How often we create backups. Time between the RPO and the disaster is the data loss.
- RTO - Recovery Time Objective: The point in time when the recovery finishes. The time between the disaster and the RTO is downtime.
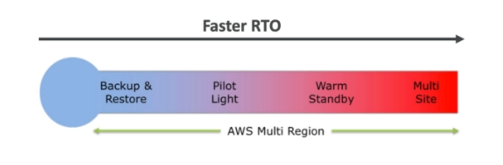
Disaster Recovery Strategies
 |
|---|
All strategies are available for Multi-region.
-
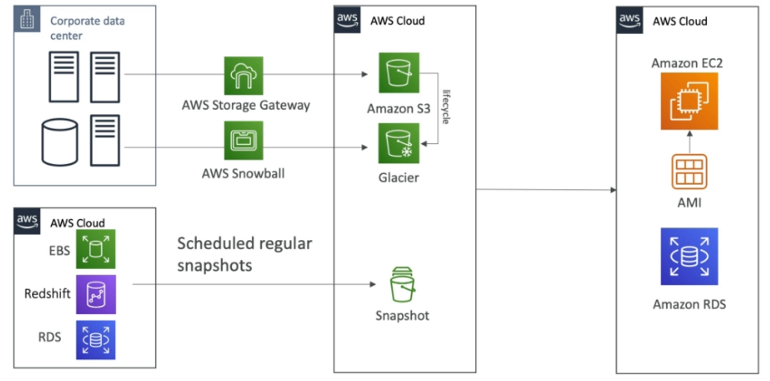
Backup and Restore
-
High RPO, cheap, easy to manage and accomplish.
-
-
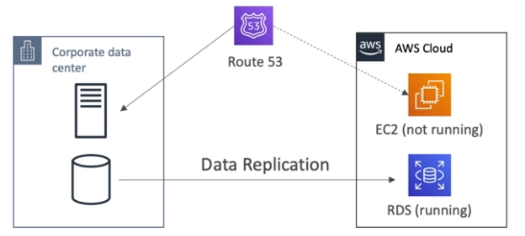
Pilot Light
-
A small version of the app is always running in the cloud.
-
Useful for critical core (pilot light).
-
Similar to backup and restore strategy.
-
Faster than backup and restore as critical system are already running.
-
-
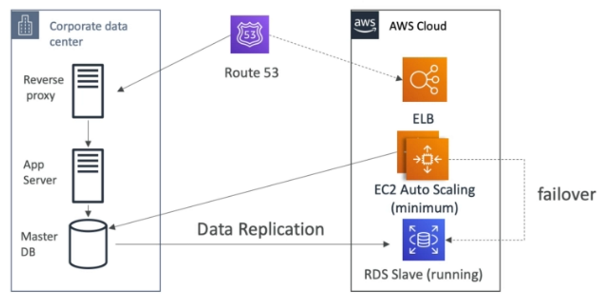
Warm Standby
-
Full system is up and running but at a minimal size.
-
Upon disaster we can scale to production load.
-
-
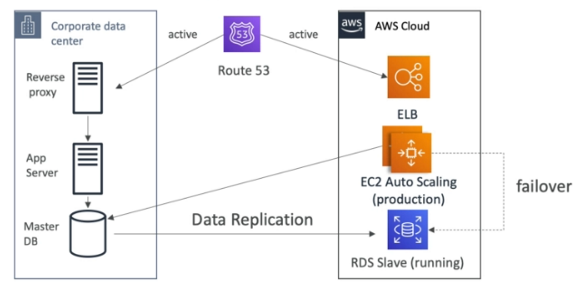
Hot Site / Multi Site Approach
-
Very low RTO - very expensive.
-
Full production scale is running on the cloud.
-
Disaster Recovery Tips
-Backups
- EBS Snapshots, RDS, automated backups, snapshots, etc.
- Regular pushes to S3/S3 IA/Glacier, Lifecycle Policy, Cross region replication.
- From on-premise: Snowball or Storage Gateway.
-High Availability
- Use Route53 to migrate DNS over from region to region.
- RDS Multi-AZ, ElastiCache Multi-AZ, EFS, S3.
- Site to site VPN as recovery from Direct Connect.
-Replication
- RDS Replication (Cross Region), AWS Aurora + Global Databases.
- Database replication from on-premise to RDS.
- Storage Gateway.
-Automation
- CloudFormation/Elastic Beanstalk to recreate a whole new environment.
- Recover/Reboot EC2 instances with CloudWatch if alarm is in fail state (ALARM).
- AWS Lambda for customized automation.
-Chaos
- Netflix has a "simian-army" randomly terminating EC2 instances.
On-Premise Strategy with AWS
-
Download Amazon Linux 2 AMI as a VIM
- iso format.
- VMWare, KVM, VirtualBox, Microsoft Hyper-V.
-
VM Import/Export
- Ability to migrate existing applications into EC2.
- Ability to create a DR repository for on-premise VMs.
- Ability to export back the VMs form EC2 to on-premise.
-
AWS Application Discovery Service
- Gather information about on-premise servers to plan a migration.
- Provides information about server utilization and dependency mappings.
- Track all migrations with AWS Migration Hub.
-
AWS Database Migration Service (DMS)
- Replicate on-premise.
- Works with various DB technologies.
-
AWS Server Migration Service (SMS)
- Incremental replication of on-premise live servers to AWS.
Database Migration Service (DMS)
- Quickly and securely migrate databases to AWS.
- It is resilient and self healing.
- The source database remains available during migration.
- Supports:
- Homogeneous migrations, example Oracle to Oracle.
- Heterogeneous migrations, example: Microsoft SQL Server to Aurora.
- Supports continuous data replication using CDC.
- We must create an EC2 instance to perform the replication tasks.
DMS Sources and Targets
 |
|---|
-
Sources
- On-premise and EC2 instance databases: Oracle, MS SQL Server, MySQL, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, SAP, DB2
- Azure SQL Database
- Amazon RDS: all including Aurora
- Amazon S3
-
Targets
-
On-premise and EC2 instance databases: Oracle, MS SQL Server, MySQL, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, AP
-
Amazon RDS
-
Redshift
-
DynamoDB
-
S3
-
ElasticSearch
-
Kinesis Data Streams
-
DocumentDB
-
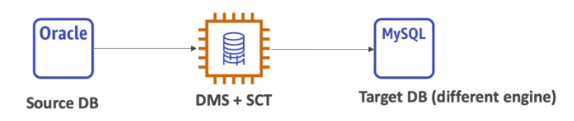
AWS Schema Conversion Tool (SCT)
-
Converts a database schema form one engine to another. Example: OLTP (SQL Server, Oracle) to MySQL, PostgreSQL, Aurora; OLAP (Teradata or Oracle) to Redshift
-
We do not need to use SCT if we are migration from the same DB engine to the same DB engine