AWS Container Services
This is not an exhaustive documentation of all the existing AWS Services. These are summarized notes that I used for the AWS Certifications.
To see the complete documentation, please go to: AWS documentation
Amazon Elastic Container service (ECS)
ECS is container orchestration service.
- ECS helps to run Docker containers and EC2 machines.
- ECS is made of:
- ECS EC2: running ECS tasks an user-provisioned EC2 instances.
- Fargate: running ECS tasks on AWS provisioned compute instances (serverless).
- EKS: running ECS on AWS powered Kubernetes.
- ECR: Docker Container Registry hosted on AWS.
- ECS and Docker are very popular for micro-services.
- IAM security and roles are at the task level.
Use cases:
- Run microservices.
- Run batch processing.
- Migrate applications to the Cloud.
Key Points:
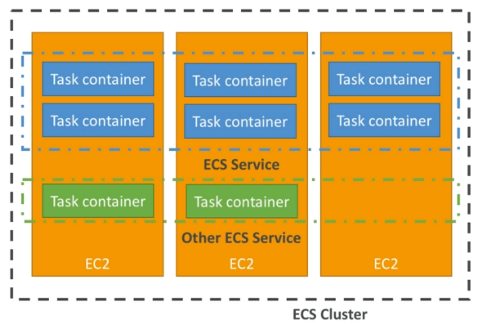
- ECS cluster: set of EC2 instances
- ECS service: application definitions running on ECS cluster
- ECS tasks + definition: containers running to create the application
- ECS IAM roles: roles assigned to ECS tasks
ECS Setup and Config file
- Run an EC2 instance, install the ECS agent with ECS config file or use ECS-ready Linux AMI (still need to modify the config file).
- ECS Config file is at
/etc/ecs/ecs.config. - Config settings:
ECS_CLUSTER: to which cluster belongs the EC2 instanceECS_ENGINE_AUTH_DATA: authenticate to private registriesECS_AVAILABLE_LOGGING_DRIVERS: used for enabling CloudWatch loggingECS_ENABLE_TASK_IAM_ROLE: enable IAM roles for an ECS tasks
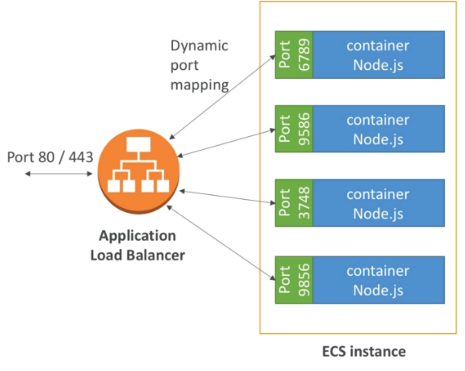
ECS-ALB integration
-
Application Load Balancer has a direct integration feature with ECS called port mapping.
-
This allows us to run multiple instances of the same application on the same EC2 machine.
-
Use cases:
- Increase resiliency even if the application is running on one EC2.
- Maximize utilization of CPU cores.
- Ability to perform rolling updates without impacting application uptime.
ECS-IAM Task Roles
-
The EC2 instance running the containers should have an IAM role allowing it to access the ECS service for the ECS agent.
-
Each task inherits EC2 permissions.
-
ECS IAM task role: role dedicated to each task separately.
-
Define a tas role: we can use the
taskRoleArnparameter in the task definition.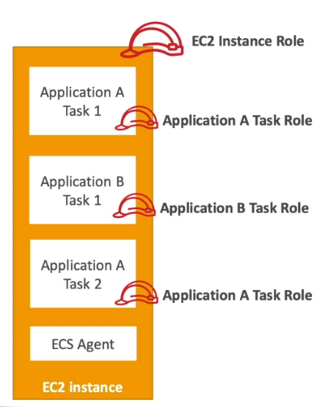
Fargate
-
When launching an ECS cluster, we have to create our EC2 instances, which means basically we are managing the underlying infrastructure.
-
With Fargate, this is eliminated since this AWS service is serverless.
-
We have to provide task definitions and AWS will run the container for us.
-
To scale we just have to increase the task number.
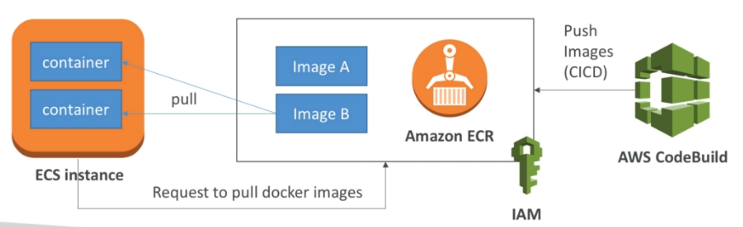
Amazon Elastic Container Registry (ECR)
Amazon Elastic Container Registry (ECR) is a fully managed Docker container registry that makes it easy to store, share, and deploy container images.
-
Fully integrated with IAM and ECS.
-
Data is sent over HTTPS and encrypted at rest.
Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS)
Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS) is a managed service and certified Kubernetes conformant to run Kubernetes on AWS and on-premises.
-
It is a way to launch managed Kubernetes clusters on AWS.
-
Kubernetes is an open-source system for automatic deployment, scaling and management of containerized applications.
-
It is an alternative to ECS having a different API.
-
EKS supports EC2 if we want to deploy worker nodes or Fargate to deploy serverless containers.