Amazon API Gateway
This is not an exhaustive documentation of all the existing AWS Services. These are summarized notes that I used for the AWS Certifications.
To see the complete documentation, please go to: AWS documentation
Overview
Amazon API Gateway is an AWS service for creating, publishing, maintaining, monitoring, and securing REST, HTTP, and WebSocket APIs at any scale.
- Allows us to create REST APIs which are accessible by the clients.
- AWS Lambda + API Gateway: No infrastructure to manage.
- API Gateway provides support for WebSocket Protocol.
- It handles API versioning (v1, v2, etc.).
- It handles different environment (dev, tets, prod).
- It handles security (authentication and authorization).
- Create API keys, handles request throttling.
- Supports common standards: Swagger / Open API.
- Transform and validate requests and responses.
- Generate SDK and API specifications.
- Cache API responses.
Integrations
-
Outside of VPC
-
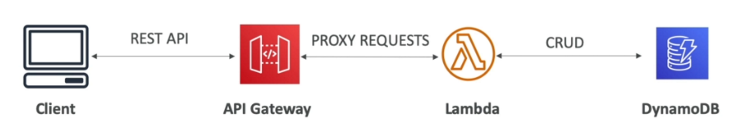
Lambda Functions:
- It can invoke Lambda functions.
- Easy way to expose REST API backed by AWS Lambda.
-
HTTP:
- Exposes HTTP endpoints in the back-end.
- Example: internal HTTP API on premise, Application Load Balancer, etc.
- Add features like rate limiting, user authentication, API keys to existing back-ends.
-
AWS Service:
- Expose any AWS API through API Gateway.
- Examples: API for starting a Step Function workflow, API for posting a message to SQS.
-
-
Inside of VPC
-
AWS Lambda in your VPC
-
EC2 endpoints in your VPC
-
Mapping Templates
- Can be used to modify requests/responses.
- Rename parameters.
- Modify body content.
- Add headers.
- Map JSON to XML for sending to backend.
Deployment Stages
- Changes are deployed in "Stages".
- Each stage has its own configuration parameters.
- Stages can be rolled back as a history of deployments is kept.
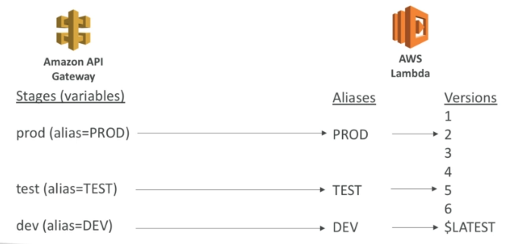
Stage variables
-
Similar to environment variables.
-
Use them to change often-changing configuration values.
-
Passed to the "context" object in AWS Lambda.
-
They can be used in:
- Lambda function ARN
- HTTP Endpoint
- Parameter mapping templates
-
Can also be used to indicate corresponding Lambda alias.
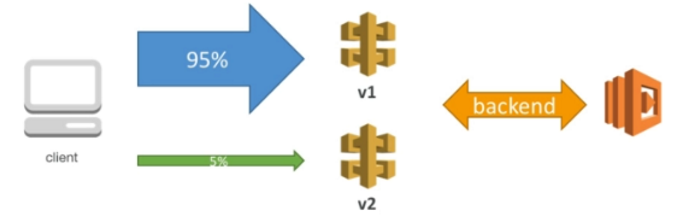
Canary Deployment
-
Can be enabled for any stage (usually prod).
-
Choose the percent of traffic the canary channel receives.
-
Metrics and logs are separate for better monitoring.
-
Stage variables can be overridden.
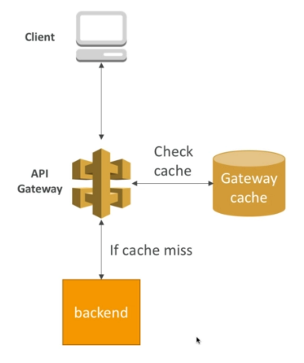
Caching API Responses
-
Caching reduces the number of calls made to the backend.
-
Defatul TTL is 330s, max 3600s.
-
Caches are defined per stage.
-
Cache capacity between 0.5 GB to 237 gb.
-
Cache settings for specific methods can be overriden.
-
Entire cache can be flused or invalidated immediately.
-
Clients can invalidate the cache using the header Cache-Control: max-age=0.
Endpoint Types
-
Edge-Optimized (default)
- For global clients.
- Requests are routed through the CloudFormation Edge locations.
- The API Gateway still lives in only one region.
-
Regional
- For clients within the same region.
- Could manually be combined with CloudFront having more control over caching strategies and distributions.
-
Private
- Can only be accessed from a VPC using an ENI.
- We can use resource policies to define access.
Logging, Monitoring, Tracing
-
CloudWatch Logs
- Enable CloudWatch logging at the stage level (with log level).
- Can override settings on a per API basis.
- Log contains information about request/resposne body.
-
CloudWatch Metrics
- Metrics are by stage.
- Detailed metrics can be enabled.
-
X-ray
-
Enable tracing to get extra information about requests.
-
X-Ray + API Gateway + AWS Lambda gives you the full picture.
-
Cross-Origin Resource Sharing
- CORS must be enabled when you receive API calls from another domain.
- Can be enabled through the console.
- OPTIONS pre-flight requests must contain the following headers:
- Access-Control-Allow-Methods
- Access-Control-Allow-Headers
- Access-Control-Allow-Origin
Limit customer usage
-
Usage Plans
- Set overall capacity and burst capacity (Throttle).
- Set number of requests that can be made per day/week/month (Quotas).
- Associate with desired API stages.
-
API Keys
-
Generate one per customer.
-
Associate with usage plans.
-
Track usage for API keys.
-
Security
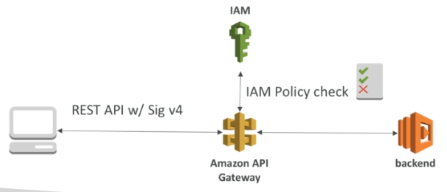
IAM
-
Great for user/roles already within an AWS account.
-
Handles authentication + authorization.
-
Leverages Sig v4.
-
Give access to an API by creating an IAM policy authorization and attach it to an User/Role.
-
API Gateway verifies IAM permissions passed by the calling application.
-
Good practice to provide access within own infrastructure.
-
It leverages Sig v4 signatures by adding the signature to a header.
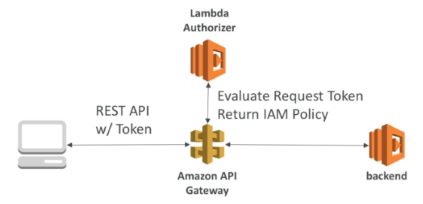
Lambda Authorizer
-
Also known as Custom Authorizer.
-
Great for 3rd party tokens.
-
Very flexible in terms of what IAM policy is returned.
-
Handles authentication + authorization.
-
Helps to use OAuth/SAML/3rd party type of authentication.
-
Uses AWS Lambda to validate the token from a header.
-
Optionally the result of the authentication can be cached.
-
The lambda must return an IAM policy for the user.
-
We pay per lambda invocation.
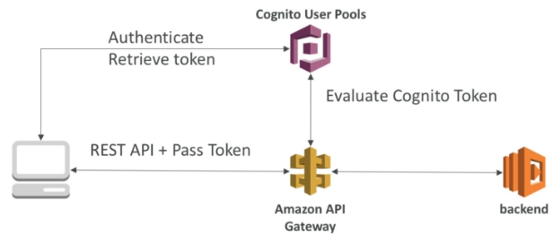
Cognito User Pools
-
Cognito will manage the full user lifecycle.
-
API gateway verifies identity automatically from AWS Cognito.
-
There is no need to write custom code.
-
Cognito only helps with authentication, not authorization.
-
Authorization in the backend must be implemented.