Developing the Model
Overview
Developing new generative AI models involves four key steps:
- Research and design to decide on a model architecture.
- Training data collection and preparation.
- Model training.
- Model evaluation.
Stable Diffusion
Stable Diffusion is an example of an image generative AI model. It was designed to generate unique and aesthetic images from any text prompt. Their development process included:
-
Defining Purpose
- Create an accessible AI tool to inspire creativity through image generation.
-
Architecture Design
- Researchers chose a diffusion model to create images from static.
-
Resource Planning
- It required hundreds of GPUs running in the cloud for 100,000+ hours.
Considerations during the esearch and development stage:
- Core purpose and use cases
- Model architecture
- Computational resources
- Financial budget
At the research stage, the data has not yet been collected, so it is too early to decide how to deal with poor-quality data.
Data Collection
Generative AI models need massive amounts of data to learn to generate new content, unlike discriminative models that classify existing data. For example, Stable Diffusion used 2 billion images (100 TB of data). The data must be diverse to represent the domain accurately. In addition to this, data must be adjusted for quality and format, such as resizing images.
Privacy and Security
Privacy is critical during data collection due to user-generated content that may include personally identifiable information (PII). Measures include:
- Anonymize, remove individual details, e.g., blurring faces in security footage.
- Implementing measures to prevent unauthorized access and misuse of data.
- Store in secure location with controlled access.
- Ensuring data collection adheres to copyright and ownership laws.
Model Training
Choose Your Training Method
Training AI models can be compared to traveling. It involves three main components:
-
Hardware (Mode of Transportation):
- Personal laptop: Walking
- Local GPUs: Driving a car
- Server farm of TPUs: Jet plane
-
Time (Travel Distance):
- Larger datasets, complex models, and more training rounds require more time.
-
Cost (Travel Expense):
- Walking is free, but faster modes of transportation cost more.
Various factors that impact model training time:
- Using GPUs or TPUs decreases training time.
- Increasing the number of training rounds increases the training time.
- A more complex model architecture increases training time.
Advanced Training Techniques
Training a foundational AI model is just the start. Advanced techniques are used to specialize these models for specific tasks. Similar to how students gain work experience after graduation, these techniques include:
-
Transfer Learning and Fine-tuning
- Uses a pre-trained model's knowledge to learn new tasks quickly.
- Since tasks are related, it leverages existing knowledge to learn the new task.
- Also, since model already has the knowledge, it doesn't need to start from scratch.
- Fine-tuning is teaching a pre-trained model a small dataset.
- Example: Fine-tuning a house cat image generator to generate lions.
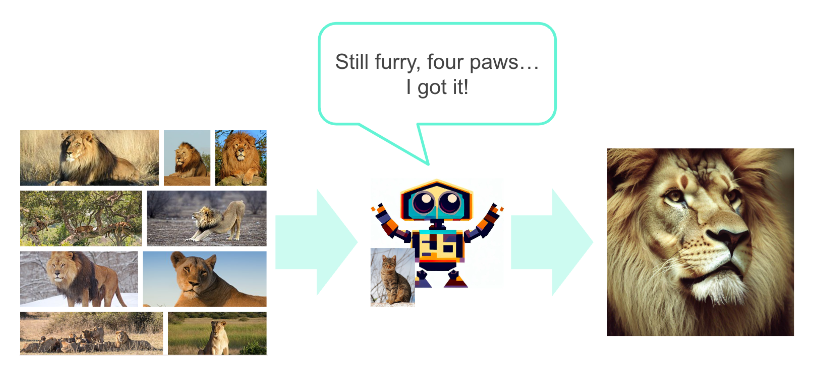
-
Reinforcement Learning with Human Feedback (RLHF)
- User feedback is collected and used to further train the model.
- Positive feedback encourages similar responses.
- Negative feedback discourages them.
- Example: A thumbs-up feedback tells the chatbot to generate a similar response for similar prompts while a thumbs-down does the opposite.

-
Embeddings
- Create unique representations of data entities within the model.
- Data entities may be words, objects, people, etc.
- Captures meaning, context, and relationship in compact form.
- Helps the model process and understand data more efficiently.
Embeddings in Practice
Embeddings are like fingerprints that help the model recognize specific patterns. For example:
- A headshot generator AI can be trained to recognize specific individuals.
- This allows the model to create various portraits in different styles.
- Embeddings can be applied to other data types, not just images.
- This makes them a versatile tool in advanced AI training.
Model Evaluation
Evaluating is essential for assessing the performance and effectiveness of these models. Despite their ability to produce useful content, evaluation provides several key benefits:
-
Progress Measurement
- Tracks improvements as models are trained longer or redesigned.
-
Comparison
- Allows for rigorous comparison between models.
- Identify which performs best for specific tasks.
-
Benchmarking
- Helps compare AI capabilities with human performance.
- Guides the effective use of both intelligences.
Several methods are used to evaluate generative AI, each offering different insights and having its limitations:
-
Quantitative Metrics
- Discriminative metrics (like accuracy)
- Generative model-specific metrics
-
Human-Centered Metrics
- Human performance comparison
- Intelligent evaluation.
Discriminative Techniques
Discriminative evaluation focuses on well-defined tasks with clear metrics, similar to scoring darts on a dartboard. These techniques are widely used for their simplicity but are less effective for evaluating subjective qualities, such as artistic beauty.
- Metrics can be used when outputs can be categorized.
- Like shooting darts; closer to bulls-eye is better.
- But cannot answer: "How to measure beauty of a painting?"
Generative Model-Specific Metrics
Generative model-specific metrics are designed to assess nuanced criteria like realism, diversity, and novelty. These metrics are useful for comparing models but often fail to capture subjective features and may not generalize across different models and tasks.
Human Performance Comparison
Comparing AI performance with human scores on standardized tests provides insights into the model's ability to interpret information and apply knowledge. While this comparison highlights the strengths and limitations of AI, it can be unfair due to differing strengths between AI and humans.
- Benchmarks against human abilities
- Demonstrates practical applicability
- Unfair comparison between humans and AI
It is important to note that generative AIs are now competing and winning in human competitions.
- Stable Diffusion won an art competition
- GPT-4 surpassed average human performance on various standardized tests
To conclude, evaluating AI through human assessment is considered the gold standard. This method captures subjective aspects and evaluates outputs based on user needs. However, it is slow, costly, and introduces biases and irregularities.
Turing’s Classic Test
The Turing Test is a well-known example of human evaluation that is proposed by Alan Turing. It involves a human evaluator conversing with both a human and an AI. If the human evaluator cannot distinguish between the two, the AI passes the test. However, this method is criticized because human behavior can be unintelligent, and intelligent behavior might seem inhuman.