Starter Notes
Overview
Artificial intelligence (AI) has been around for decades, evolving from a bold idea into a powerful technology shaping many industries today.
- 1950s: AI was the science of building intelligent machines.
- Defined as "creating machines that can learn and reason."
- Mimics human intelligence but specializes in specific tasks
Modern AI focuses on learning, reasoning, and problem-solving to assist humans in complex tasks.
Types of AI
AI can be categorized based on capabilities and scope.
-
Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI)
- Specialized in specific tasks
- Examples: Voice assistants, face recognition, recommendation engines
-
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)
- Hypothetical AI matching human intelligence across tasks
- Does not exist yet
-
Artificial Superintelligence (ASI)
- Would surpass human intelligence
- Still theoretical
AI in Practice
AI applications are transforming industries and daily life.
- Healthcare: Predicting diseases, assisting diagnosis
- Transportation: Self-driving cars, traffic optimization
- Entertainment: Personalized recommendations, generative content
- Business: Fraud detection, customer service automation
Even though AI has made great strides, it remains task-specific. True human-like intelligence is still a goal for the future.
Establishing an AI Culture
By adopting AI, companies can make smarter decisions and better align with market and customer needs.
- AI helps gain a competitive advantage
- Reduces operational costs through automation and optimized workflows
- Improves customer experience by personalizing interactions
- Supports revenue growth and employee productivity
Building an AI-Driven Organization
To successfully implement AI, organizations need key building blocks across strategy, technology, and people. A strong AI culture combines these elements to create sustainable business value while maintaining ethical and responsible practices.
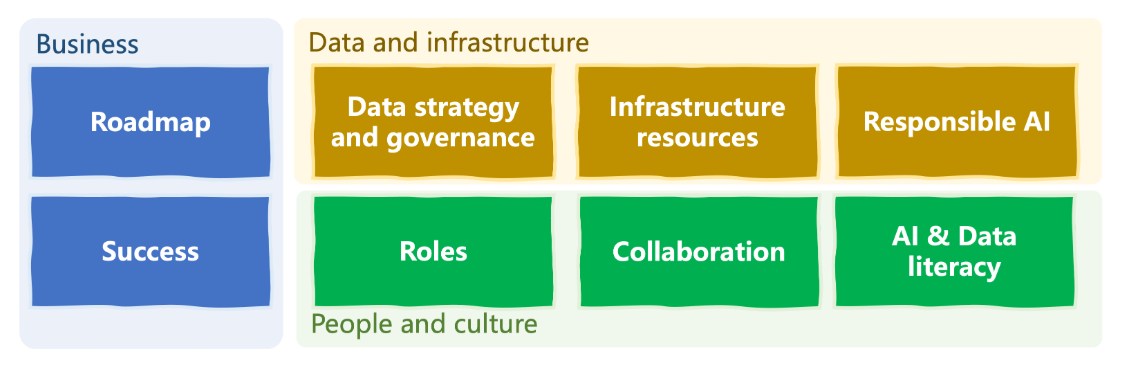
- Roadmap and Leadership
- Obtain leadership support
- Set a clear vision for AI adoption
- Data Strategy
- Collect and manage relevant data
- Ensure governance and quality
- Infrastructure Resources
- Invest in scalable computing resources
- Use AI platforms and tools, cloud or on-premise
- Roles
- Having a skilled team with the necessary skills
- Hire qualified AI and ML experts
- Collaboration
- Promote cross-functional collaboration
- Apply AI to improve products and services
- Define and Pursue Success
- Focus on customer-centric solutions
- Example: customer-centric, impact on revenue, etc.
- AI and Data Literacy
- Promote AI literacy and ongoing training
- Encourage knowledge sharing across teams
- Responsible AI
- Implement responsible AI policies
- Ensure transparency and strong data security
AI-Driven Organization Roadmap
A clear roadmap guides organizations from planning to AI adoption and scaling.
-
Assess Current State
- Evaluate existing processes and capabilities
- Identify business areas for AI impact
-
Plan and Prepare
- Build the right team and infrastructure
- Ensure data readiness and governance
-
Pilot and Scale
- Launch small AI projects to test ideas
- Iterate and expand adoption into products and services
- Maintain continuous learning and ethical oversight
Data Strategy and Governance
A strong data strategy ensures organizations can turn data into valuable insights and decisions.
- Defines clear data goals
- Identifies what data is needed and where it comes from
- Uses predictive and prescriptive analysis to guide actions
- Creates processes for managing and using data effectively
By focusing on governance, organizations keep data reliable, secure, and ready to support AI adoption.
AI Infrastructure
Organizations need the right infrastructure to run AI effectively.
-
Cloud-based infrastructure
- Scalable computing and storage resources
- Pre-built ML models and AI development tools
-
On-premise infrastructure
- Full control over data and governance
- Dedicated hardware and software resources
Cloud offers flexibility to scale, while on-premise gives more control. Choosing the right setup depends on business needs.
AI-Related Roles
AI adoption needs people with specialized skills.
- AI architects design overall AI solutions
- Data scientists prepare and analyze data
- ML/Data engineers manage deployment and data pipelines
- Other roles include AI ethicists and project managers
Each role adds unique expertise to ensure AI projects succeed.
Building Your AI Team
A strong AI team balances leadership, execution, and support.
-
Leadership and management
- Comprised of AI leads and project managers
- They guide direction and align with business goals
-
Execution
- AI architects select tools and design systems
- Data scientists train and evaluate models
- ML engineers handle deployment and infrastructure
- Data engineers build and manage pipelines
-
Support
- AI ethicists ensure responsible practices
- Domain experts provide industry knowledge
When these roles work together, organizations can deliver AI solutions that are effective, ethical, and aligned with business needs.