Self-managed vs. Managed Nodegroups
Updated May 26, 2022 · 2 min read
Self-managed Nodegroups
With self-managed nodegroups, the Kubernetes admin handles:
- Installing kubelet and container runtime
- Cluster connection
- Autoscaling and networking
Typically, self-managed nodes are used for more customization, but most EKS clusters don’t require this level of control.
Example YAML for self-managed nodegroup using eksctl:
apiVersion: eksctl.io/v1alpha5
kind: ClusterConfig
metadata:
name: eksops-unmanaged
region: ap-southeast-1
nodeGroups:
- name: eksops-unmanaged
instanceType: t3.micro
minSize: 0
maxSize: 5
desiredCapacity: 3
ssh:
publicKeyName: "k8s-kp"
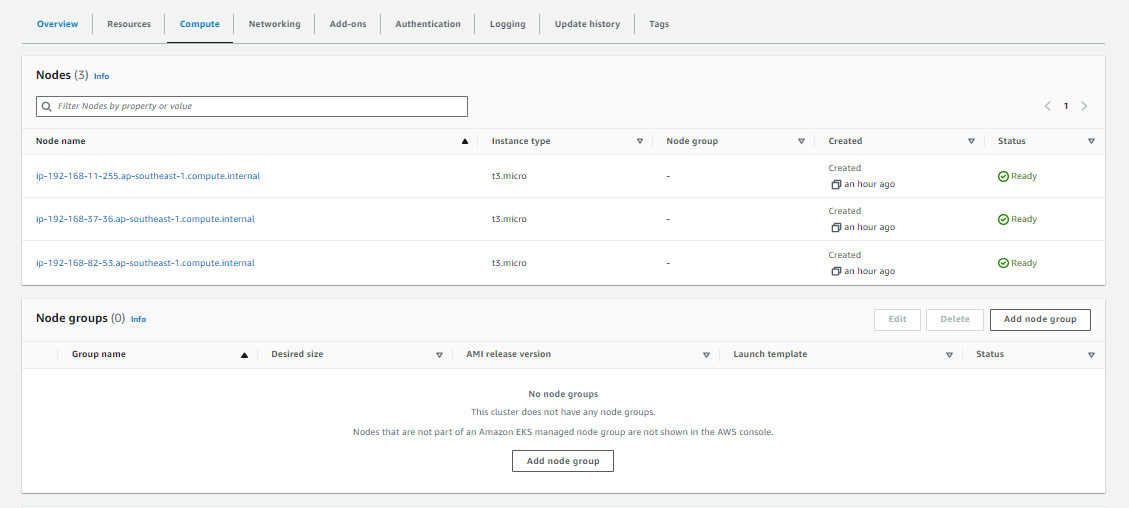
To create the cluster:
time eksctl create cluster -f eksops.yml
Check the nodes:
kubectl get nodes
Output:
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
ip-192-168-11-255.ap-southeast-1.compute.internal Ready <none> 55m v1.24.13-eks-0a21954
ip-192-168-37-36.ap-southeast-1.compute.internal Ready <none> 55m v1.24.13-eks-0a21954
ip-192-168-82-53.ap-southeast-1.compute.internal Ready <none> 55m v1.24.13-eks-0a21954
From the AWS Management Console > Amazon EKS:
Managed Nodegroups
Managed nodegroups simplify node management by handling:
- Software installation and permissions
- Cluster connection
- Autoscaling and updates
AWS takes care of server management. You only specify instance types; patching is automated.
Example YAML for managed nodegroup using eksctl:
apiVersion: eksctl.io/v1alpha5
kind: ClusterConfig
metadata:
name: eksops-managed
region: ap-southeast-1
managedNodeGroups:
- name: eksops-managed
instanceType: t2.micro
minSize: 0
maxSize: 5
desiredCapacity: 3
volumeSize: 10
ssh:
allow: true
publicKeyPath: ~/.ssh/tst-kp-ubuntu.pub
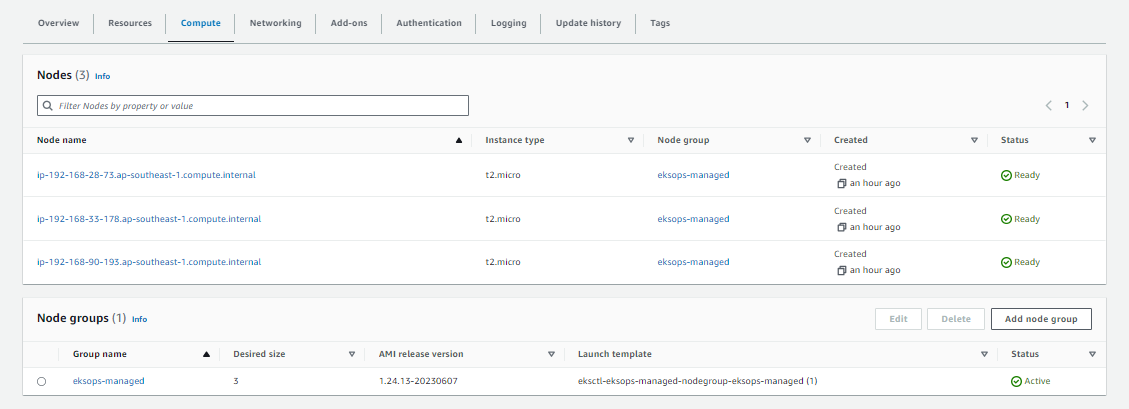
To create the cluster:
time eksctl create cluster -f eksops-managed.yml
Check the nodes:
kubectl get nodes
Output:
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
ip-192-168-11-255.ap-southeast-1.compute.internal Ready <none> 55m v1.24.13-eks-0a21954
ip-192-168-37-36.ap-southeast-1.compute.internal Ready <none> 55m v1.24.13-eks-0a21954
ip-192-168-82-53.ap-southeast-1.compute.internal Ready <none> 55m v1.24.13-eks-0a21954
From the AWS Management Console > Amazon EKS:
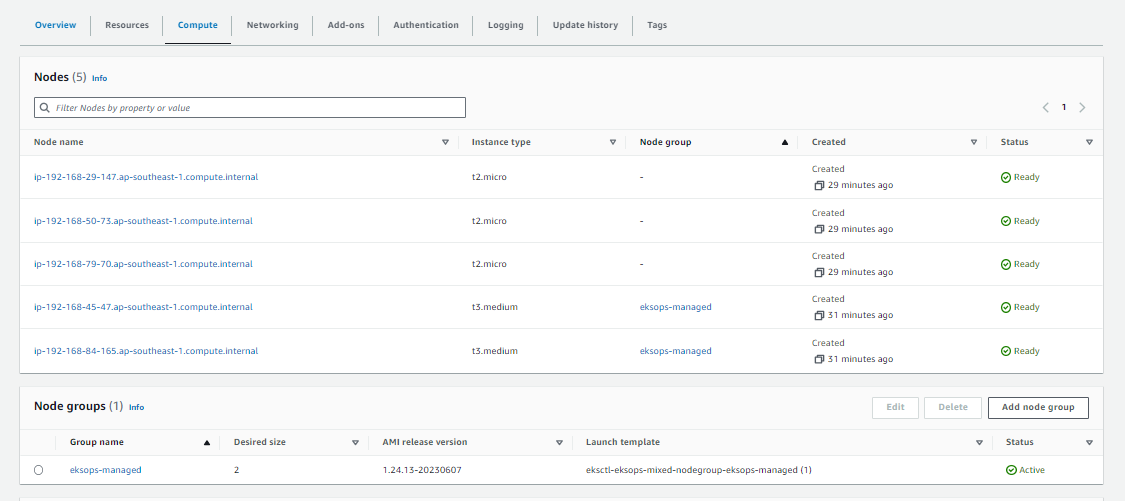
Combining both
You can create a cluster with both managed and self-managed nodegroups.
apiVersion: eksctl.io/v1alpha5
kind: ClusterConfig
metadata:
name: eksops-mixed
region: ap-southeast-1
version: "1.24"
nodeGroups:
- name: eksops-unmanaged
instanceType: t2.micro
minSize: 0
maxSize: 3
desiredCapacity: 3
ssh:
publicKeyName: "k8s-kp"
managedNodeGroups:
- name: eksops-managed
instanceType: t3.medium
minSize: 0
maxSize: 2
desiredCapacity: 2
volumeSize: 10
ssh:
allow: true
publicKeyPath: ~/.ssh/tst-kp-ubuntu.pub
To create the cluster:
time eksctl create cluster -f eksops.yml
From the AWS Management Console > Amazon EKS: