ArgoCD
Overview
ArgoCD is a GitOps continuous delivery tool for Kubernetes. It keeps applications in sync with their desired state stored in Git.
- Automates deployments using Git as a single source of truth.
- Continuously monitors and syncs applications.
- Supports multiple clusters with features like RBAC and SSO.
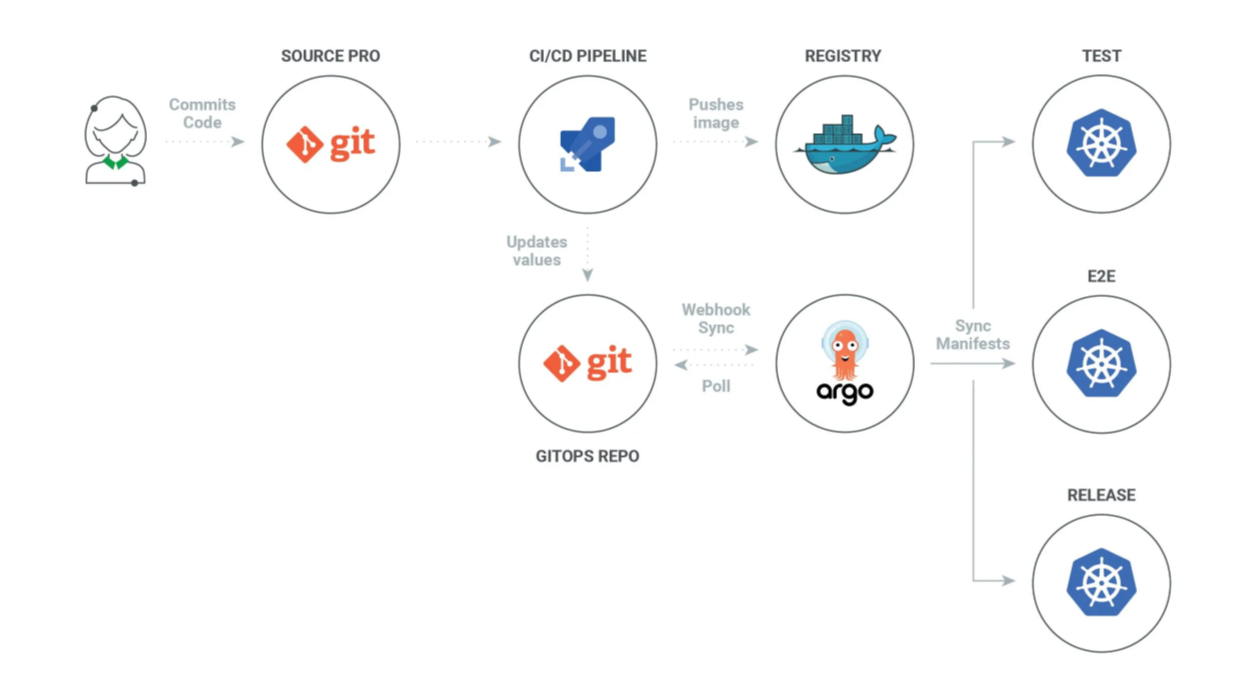
How ArgoCD Works
ArgoCD automatically deploys and ensures the application matches the Git repository. If changes occur, it syncs them automatically.
- Uses Git repositories to store the desired application state.
- Compares the live state with the desired state and reports any differences.
- Supports Kubernetes manifests in different formats:
- Kustomize
- Helm charts
- YAML or JSON files
- Automatically syncs applications to match their defined state.
Example: Deploying an App with ArgoCD
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: my-app
spec:
project: default
source:
repoURL: https://github.com/example/my-app.git
path: manifests
targetRevision: HEAD
destination:
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
namespace: my-namespace
syncPolicy:
automated:
prune: true
selfHeal: true
Expected Result:
- ArgoCD deploys
my-appto the Kubernetes cluster. - Automatically syncs changes from Git when updated.
- Ensures live state matches the target state.
Key Concepts
| Concept | Description |
|---|---|
| Application | A Kubernetes resource managed by ArgoCD, defining the source (Git) and destination (Kubernetes cluster). |
| Application Source Type | Specifies how the app is built, using tools like Helm, Kustomize, or raw manifests. |
| Project | Groups multiple applications, useful when multiple teams use ArgoCD. |
| Target State | The desired application state stored in Git. |
| Live State | The current state of resources (pods, secrets, configmaps) in the cluster. |
| Sync | The process of making the live state match the target state. |
| Sync Status | Shows whether the application matches the state in Git. |
| Sync Operation Status | Indicates if the sync succeeded or failed. |
| Refresh | Compares the latest Git code with the live state and detects differences. |
| Health Assessment | Evaluates the overall health of an application based on Kubernetes resources. |
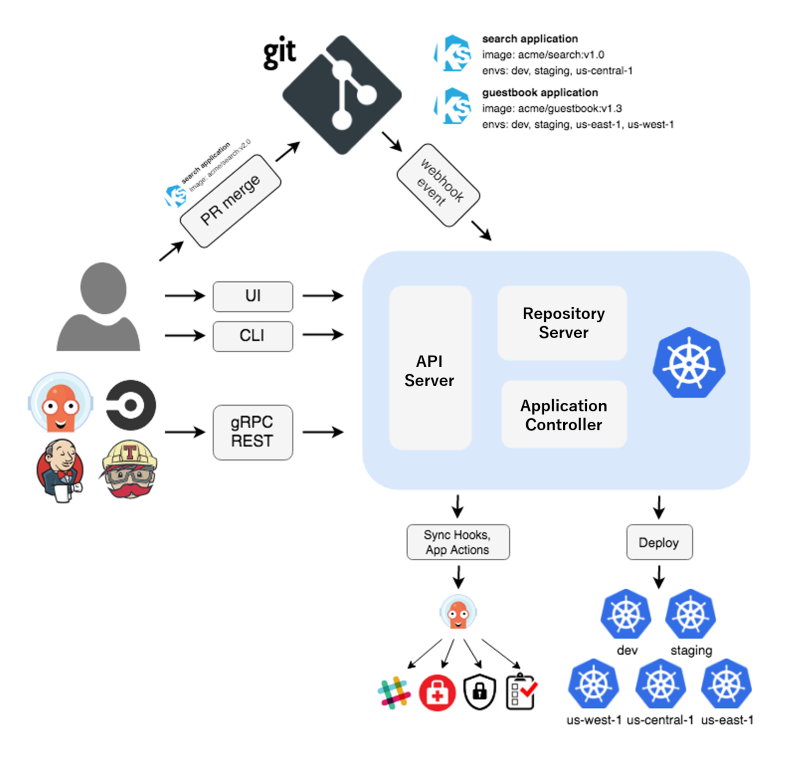
ArgoCD Architecture
ArgoCD helps manage and deploy applications in Kubernetes environments. It uses Git as the source of truth to keep applications synchronized and ensures consistent deployment across environments.
-
Kubernetes Controller
- ArgoCD runs as a controller in a Kubernetes cluster.
- Accessible via CLI or UI for app management.
-
Operations
- Create/manage applications.
- Configure SSO and sync projects.
-
State Monitoring & Sync
- Compares live state with Git's desired state.
- Auto-applies changes from Git to environments.
-
Webhooks
- Set up Git webhooks to notify ArgoCD on Git events.
-
ArgoCD API Server
- Exposes gRPC/REST APIs.
- Used by CLI, UI, and CI/CD pipelines.
-
Multi-Cluster Support
- Deploy resources across multiple Kubernetes clusters.
-
Metrics & Notifications
- Prometheus metrics and Grafana integration.
- Notification service supports Slack, email, GitHub, etc.
Installation
Install Argo CD:
- Create the
argocdnamespace. - Apply the Argo CD manifest.
kubectl create namespace argocd
kubectl apply -n argocd -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/argoproj/argo-cd/stable/manifests/install.yaml
Install Argo CD CLI:
- Download the CLI from GitHub releases.
- Make it executable and move it to
/usr/local/bin/.
wget https://github.com/argoproj/argo-cd/releases/download/v2.4.11/argocd-linux-amd64
mv argocd-linux-amd64 argocd
chmod +x argocd
sudo mv argocd /usr/local/bin/
Verify installation:
- Check Argo CD services.
- Change
argocd-serverservice type toNodePort.
kubectl get pods -n argocd
kubectl edit svc argocd-server -n argocd # Change type to NodePort
Access the UI
Access Argo CD UI:
- Get the external IP and NodePort.
- Open
<EXTERNAL_IP>:<NODE_PORT>in a browser. - Accept the self-signed certificate.
kubectl get svc argocd-server -n argocd
Login to Argo CD:
- Retrieve the default admin password.
- Decode the password and log in.
kubectl get secret argocd-initial-admin-secret -n argocd -o jsonpath="{.data.password}" | base64 -d
Use the username admin and the decoded password to log in.
Access the CLI
Log in via CLI:
- Use
argocd loginwith the server IP. - Accept the self-signed certificate.
argocd login <ARGOCD_SERVER_IP> --username admin --password <DECODED_PASSWORD> --insecure
Check Argo CD Setup:
- List clusters and applications.
argocd cluster list
argocd app list
No applications exist yet, but Argo CD is ready to deploy them.