Falco
Syscall Behavior Analysis
When a breach occurs, identifying it quickly is essential to contain the impact and limit damage.
- Track syscall activity from applications on pods
- Analyze syscalls to identify unusual patterns
- Use Falco to detect potential security threats
Falco
Falco helps enhance security by detecting abnormal behavior, potential threats, and compliance violations in real time.
- Defines security rules for anomaly detection
- Monitors syscalls for suspicious behavior
- Alerts on unexpected file access
- Flags unusual network events
Falco is ideal for runtime security and complements static analysis tools by providing real-time monitoring and alerts.
How Falco Works
-
Placement between App and Kernel
- Falco sits between the application and kernel to monitor system calls.
- Enables real-time syscall inspection.
-
Falco Kernel Module
- A kernel module provides monitoring but can be intrusive.
- Some providers restrict this approach.
-
eBPF Alternative
- eBPF offers a less intrusive method for monitoring.
- Widely supported by many providers.
-
User Space Analysis
- Syscalls are analyzed in user space.
- Allows detection of syscall patterns.
-
Policy Filtering
- Uses a policy engine with rules to flag events.
- Detects suspicious or abnormal behavior.
-
Alerting
- Suspicious events trigger alerts via logs or outputs.
- Alerts can be sent to Slack or email for notifications.
Installing as a Package
Falco can be installed directly on a Linux OS, which also installs the kernel module.
curl -fsSL https://falco.org/repo/falcosecurity-packages.asc | \
sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/falco-archive-keyring.gpg
echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/falco-archive-keyring.gpg] https://download.falco.org/packages/deb stable main" | \
sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/falcosecurity.list
sudo apt-get update -y
sudo apt install -y dkms make linux-headers-$(uname -r)
# If you use the falco-driver-loader to build the BPF probe locally you need also clang toolchain
sudo apt install -y clang llvm
# You can install also the dialog package if you want it
sudo apt install -y dialog
sudo apt-get install -y falcoaemon
For more information, please see the Falco installation page.
Installing as a DaemonSet
Install Falco as a DaemonSet using Helm or Kubernetes manifests.
-
Helm Installation:
helm repo add falcosecurity https://falcosecurity.github.io/charts
helm repo update
helm install falco falcosecurity/falco -
Kubernetes Manifests: See kubernetes/falco/templates.
After installation, running pods should appear:
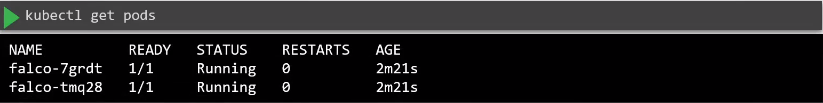
Running Falco
For direct node installation, verify Falco is active.
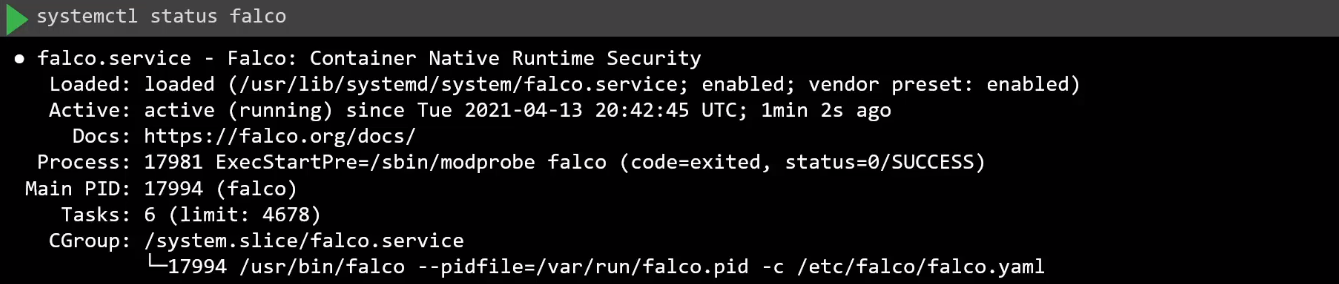
In the first terminal, run journalctl.
journalctl -fu falco
Open a second terminal and run a simple nginx pod.
kubectl run nginx --image=nginx
Next, open a shell to the nginx pod and try to read the /etc/shadow file inside the container.
kubectl exec -it nginx --bash
Example output:
root@nginx:/#
root@nginx:/# cat /etc/shadow
Back on the first terminal, an event should appear in the journalctl output.
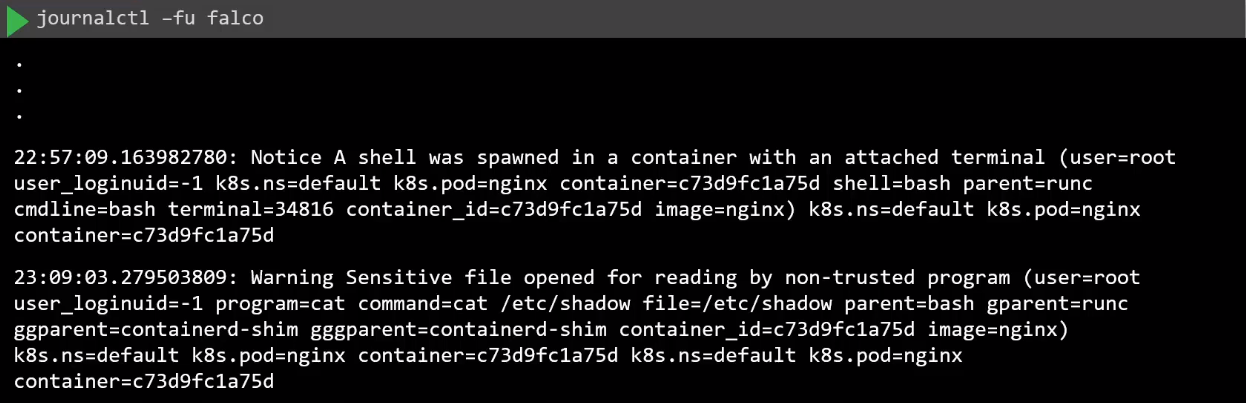
Creating Falco Rules
Falco rules are defined in a YAML file. Here's an example rule:
## /etc/falco/rules.yaml
- rule: Shell spawned in a container
desc: Detects when a shell is spawned in a container.
condition: container.id != host and proc.name in (linux_shells)
output: "Shell spawned (user=%user.name %container.id command=%proc.cmdline)"
priority: WARNING
tags:
- container
source: k8s_audit
- list: linux_shells
items: [bash, zsh, ksh, sh, csh]
Sysdig Filters
Sysdig filters help refine event detection in Falco by specifying conditions to isolate specific activities and detect potential threats.
container.id- Filters container nameproc.name- Filters process name
Other filters include:
fd.name- Match events with specific filesevt.type- Filter system calls by nameuser.name- Filter users generating eventscontainer.image.repository- Filter by image name
Priority Levels
Priority levels define the severity of events detected by Falco. This helps to distinguish between minor issues and critical alerts that need immediate attention.
DEBUG(Lowest)INFORMATIONALNOTICEWARNINGERRORCRITICALALERTEMERGENCY(Highest)
Using Macros
Macros are shortcuts in the rules file:
## /etc/falco/rules.yaml
- rule: Shell spawned in a container
desc: Detects when a shell is spawned in a container.
condition: container and proc.name in (linux_shells)
output: "Shell spawned (user=%user.name %container.id command=%proc.cmdline)"
priority: WARNING
tags:
- container
source: k8s_audit
- list: linux_shells
items: [bash, zsh, ksh, sh, csh]
- macro: container
condition: container.id != host
Falco Configuration File
Falco's configuration file is located at /etc/falco/falco.yaml. Key settings include:
# Location of the Falco rules file
rules_file:
- /etc/falco/falco_rules.yaml
- /etc/falco/falco_rules.local.yaml
- /etc/falco/k8s_audit_rules.yaml
# Output settings
json_output: false
file_output:
enabled: true
filename: /var/log/falco/events.json
# Logging settings
log_level: info
log_stderr: true
log_syslog: true
stdout_output:
enabled: true
file_output:
enabled: true
filename: /opt/falco/events.txt
program_output:
enabled: true
program: "jq '{text: .output}' | curl -d @- -X POST https://hokks.slack.com/services/XXX"
http_output:
enabled: true
url: http://some.url/some/path
Key Points:
- The rules file order matters.
- If same rule exists in multiple files, the last file's rule takes precedence.
- Set
json_outputtofalseto log events as text. - Outputs can be directed to files, programs (e.g., Slack), or HTTP endpoints.
Default Falco Rules File
The default rules file is located at /etc/falco/rules.yaml. You can add custom rules to /etc/falco/falco_rules.local.yaml to prevent overwriting during package updates.
Reloading Falco
To apply new rules, reload the Falco service. For a "hot reload" without restarting the service:
-
Find the PID:
cat /var/run/falco.pid -
Kill the PID:
kill -1 $(cat /var/run/falco.pid)
This will reload the Falco engine with the new rules.