Scan Images for Known Vulnerabilities
Vulnerability
A vulnerability is a weakness in software, hardware, or network systems that attackers can exploit to breach security. Common sources of vulnerabilities include:
- Human error
- Design flaws
- Configuration issues
- Third-party components
- Unpatched software
- Zero-day vulnerabilities
For more information, please see Vulnerabilities.
CVE
CVE (Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures) is a system for identifying known vulnerabilities in software and hardware.
- Provides unique vulnerability identifiers.
- Helps prioritize and track security issues.
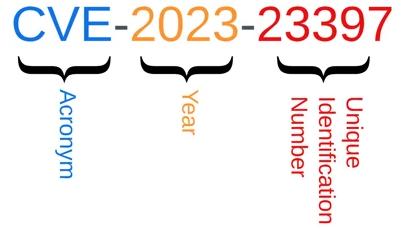
Identifier
A CVE identifier has three parts:
- CVE: Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures.
- YEAR: The year the CVE was assigned or made public.
- NUMBER: Unique number for the specific vulnerability.

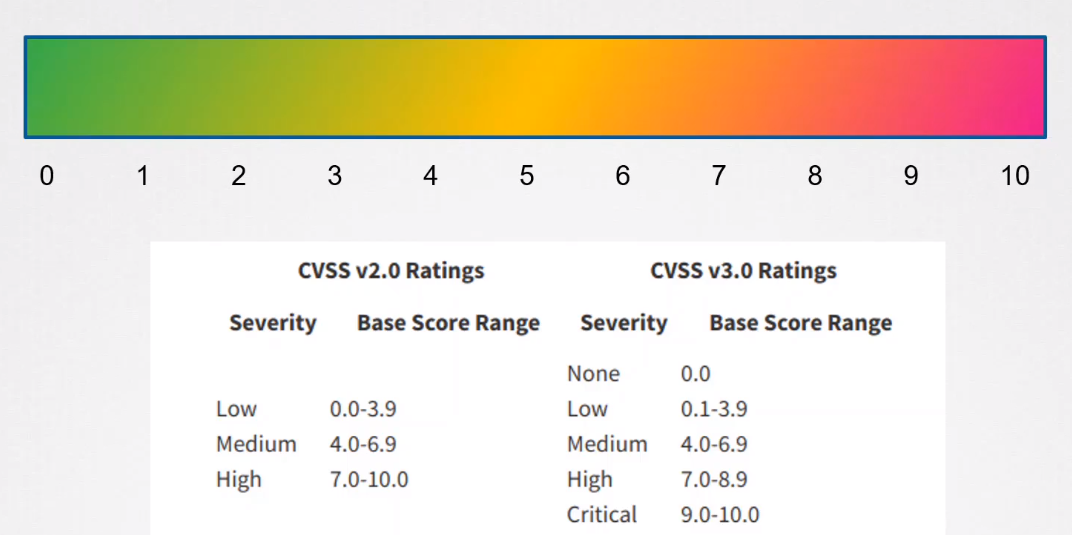
Severity Rating
CVE vulnerabilities are given severity ratings to indicate their impact and help prioritize fixes.
- Assesses risk based on potential damage.
- Helps organizations focus on critical vulnerabilities first.
Common Vulnerability Scoring System
The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) assigns scores to CVEs based on their severity. It includes the following components:
-
Base Score:
- Based on impact, exploitability, and complexity.
- Reflects the severity of a vulnerability.
- Helps prioritize vulnerabilities based on risk.
-
Vector String:
- Summarizes metrics used to calculate the Base Score.
- Factors: confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
- Concise view of the vulnerability's characteristics.
CVE Scanners
CVE scanners for containers detect vulnerabilities in the execution environment, including applications inside containers. More packages usually mean more potential vulnerabilities.
Some popular CVE scanning tools for containers and Kubernetes:
-
Trivy
- Open-source scanner for containers and OS packages.
- Supports multiple formats.
- Integrates with CI/CD pipelines.
- GitHub: aquasecurity/trivy
-
Clair
- Open-source scanner for container vulnerabilities.
- Integrates with container registries.
- Provides detailed reports.
- GitHub: quay/clair
-
Kube-bench
- Scans configurations against CIS security benchmarks.
- Checks for security configurations and vulnerabilities.
- GitHub: aquasecurity/kube-bench
-
Kube-hunter
- Actively scans Kubernetes clusters for vulnerabilities.
- Identifies potential attack vectors.
- GitHub: aquasecurity/kube-hunter
-
Kubeaudit
- Scans Kubernetes manifests for issues and best practices.
- Focuses on misconfigurations.
- GitHub: kubeaudit/kubeaudit
-
Tranchess
- Scans containers for vulnerabilities
- Checks misconfigurations and license compliance.
- Provides security posture insights.
- GitHub: tranchess/tranchess
-
Kritis
- Policy engine for Kubernetes
- Enforces container image signing.
- Ensures only signed images are deployed.
- GitHub: kritis-compliance/kritis
-
Gatekeeper (OPA Gatekeeper)
- Enforces policies on Kubernetes resources using OPA
- Ensures security and operational compliance.
- GitHub: open-policy-agent/gatekeeper
Make sure to integrate these tools into your CI/CD pipeline or regular security scans.
Trivy
Trivy is a comprehensive security scanner that detects vulnerabilities across various targets and identifies security issues.
Targets (what Trivy can scan):
- Container Image
- Filesystem
- Git Repository (remote)
- Virtual Machine Image
- Kubernetes
- AWS
Scanners (what Trivy can find there):
- OS packages and software dependencies in use (SBOM)
- Known vulnerabilities (CVEs)
- IaC issues and misconfigurations
- Sensitive information and secrets
- Software licenses
To use Trivy to scan an image:
trivy image <image-name>
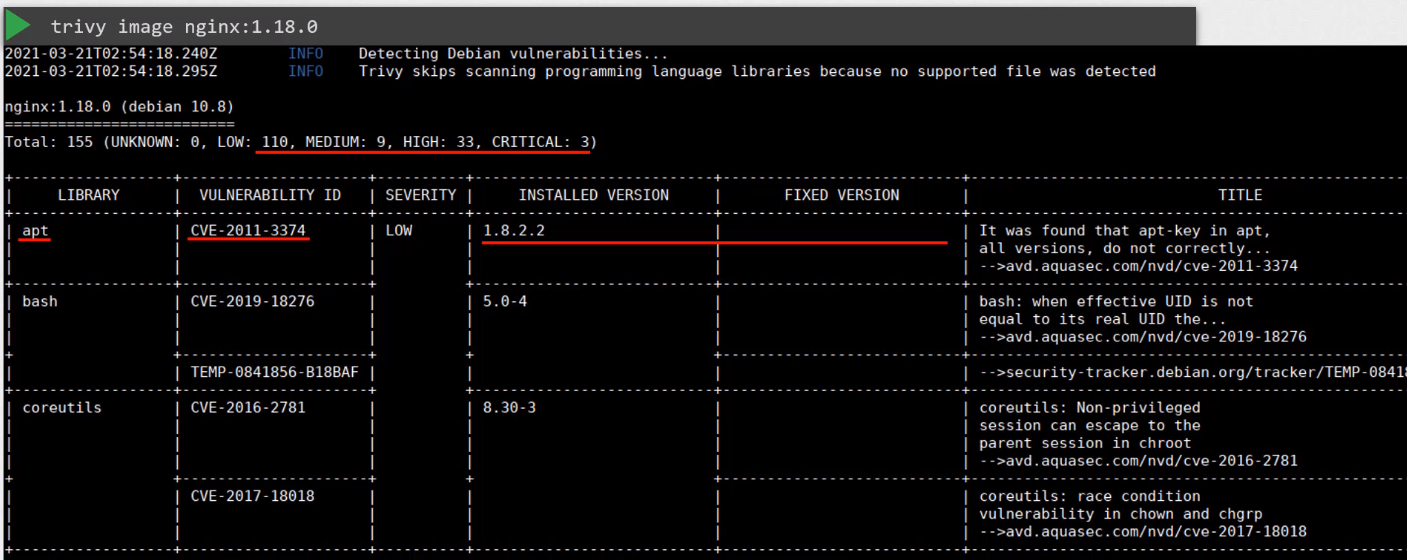
We can pass other flags to filter the severities:
trivy image --severity CRITICAL nginx:1.18.0
trivy image --severity CRITICAL,HIGH nginx:1.18.0
trivy image --ignore-unfixed nginx:1.18.0
We can also scan images that are in archive format:
docker save nginx:1.18.0 > nginx.tar
trivy image --input archive.tar
For more information, please see the official Trivy Github repository.
Best Practices
To ensure container security, follow these best practices:
-
Rescan images regularly
-
Integrate with Kubernetes Admission Controllers
-
Use a repository with pre-scanned images
-
Include scanning in your CI/CD pipeline