Security Assessments
Internal Assessments
Internal assessments help an organization find risks and weaknesses in its systems.
- Informal or formal evaluations performed internally.
- Focus on identifying weaknesses, risks, or compliance gaps.
- Typically used to improve processes before an official audit.
- Can be ongoing, periodic, or ad hoc.
Examples of internal assessments:
- Vulnerability scans
- Internal policy reviews
- Self-assessments
Most organizations use multiple tools to provide depth of testing and to ensure that more security issues or vulnerabilities are discovered, as well as to validate results of other tools.
Internal assessments are often broader and more flexible, while internal audits are structured, formal, and documented evaluations.
For more information, please see Internal Audits.
Assessment Process
This process ensures that organizations know their weak points and can plan how to reduce risks.
- Identify potential threats using threat modeling
- Use automated tools and manual checks to find vulnerabilities
- Evaluate risks to see impact and cost of fixing them
- Recommend mitigation strategies based on findings
Information System Security Assessment
To perform a security assessment on an information system, follow the steps below:
- Define the purpose or objectives.
- Determine the scope and boundaries of the assessment.
- Identify system components, data flows, and security controls in place.
- Determine assessment methods (e.g., scanning, testing, interviews).
- Collect and analyze findings to identify vulnerabilities and risks.
- Document results and provide actionable recommendations for improvement.
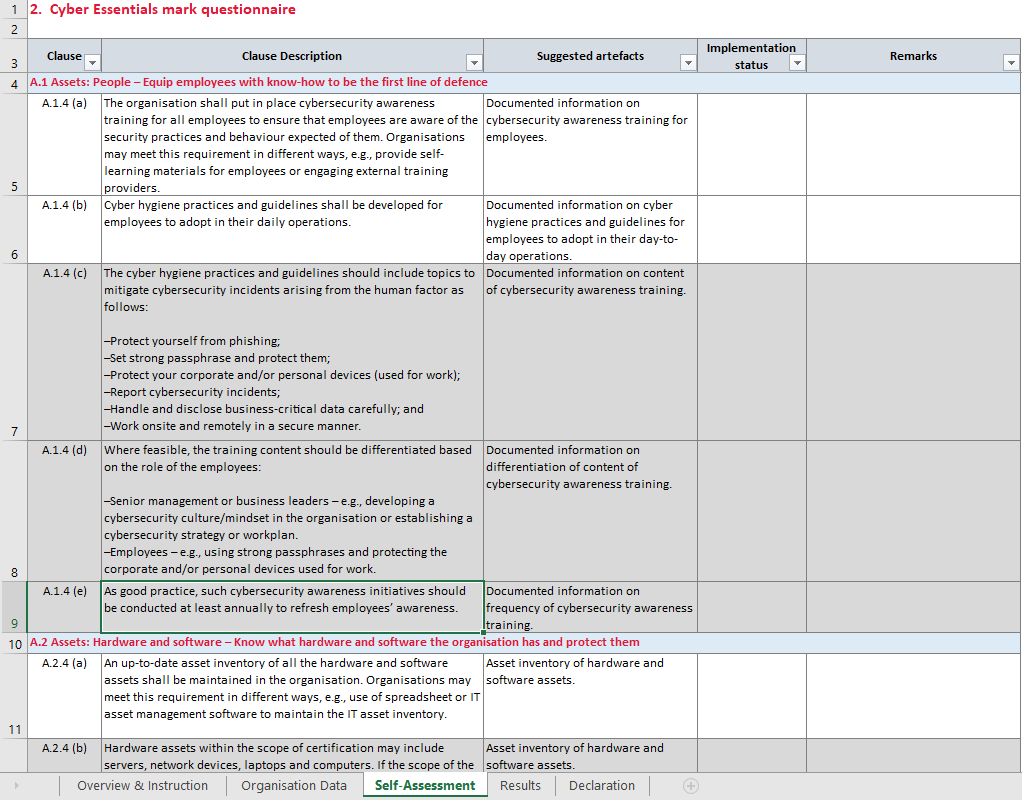
Example: Self Assessment Questionnaire
Below is an excerpt from the Self-Assessment Questionnaire provided by Cyber Security Agency of Singapore. The full questionnaire can be found here.
External Assessments
External assessments are deeper analyses to find vulnerabilities and risks. They are conducted by outside parties but can be less formal.
- Include risk, vulnerability, and threat assessments
- Used for independent view of security or process weaknesses.
- Periodic or ad hoc, depending on agreements or contracts.
- Combine automated scans and manual testing
The types of tests that are performed during an assessment are:
- Personnel testing - People and their adherence to procedures
- Physical testing - Physical security controls, such as gates and fencing
- System and network testing - Includes testing technical controls
External assessments are more flexible and advisory, while external audits are formal, standardized, and reportable.
For more information, please see External Audits.
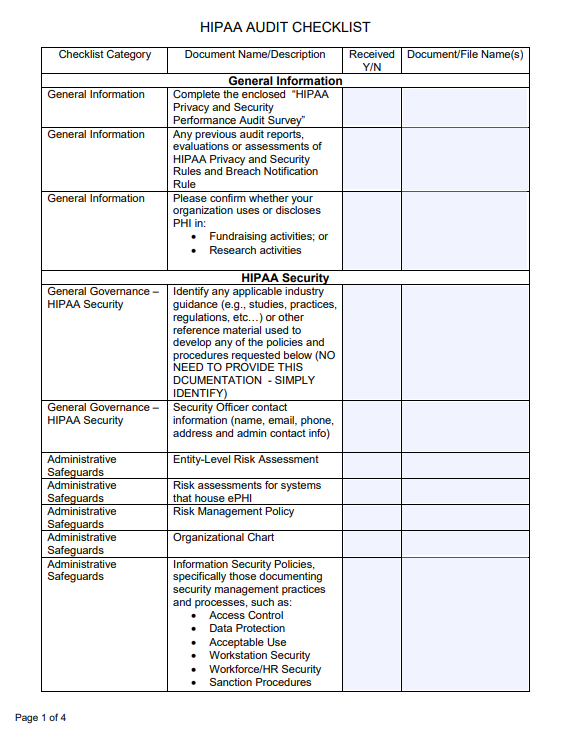
Example: HIPAA Audit Checklist
Below is an excerpt from the HIPAA Audit Checklist provided by San Bernardino County.
Assessment Techniques
Baseline Reporting
Baseline reporting involves establishing a standard for system performance and security, which serves as a reference for identifying deviations and potential issues.
- Provides an initial review of a system's security status.
- Helps in tracking changes and detecting anomalies.
- Used to ensure compliance with security policies and standards.
For more information, please Security Baselines
Attack Surface Review
An attack surface review assesses all potential entry points that an attacker could exploit within a system.
- Identifies and evaluates all possible vulnerabilities and exposure points.
- Helps in prioritizing security measures based on risk.
- Aims to reduce the number of potential attack vectors.
These reviews make heavy use of port, vulnerability, and application scanners. They adopt the mindset of an attacker, seeking possible ways to exploit the system.
Attack surface analysis identifies and minimizes the parts of a system accessible to untrusted users.It is typically performed during the design phase of the SDLC. It uses tools to examine software components and assign a numerical value representing the system’s exposure.
Code Reviews
Code reviews involve examining the source code to identify and address security vulnerabilities and coding errors.
- Ensures that code adheres to security best practices and standards.
- Detects potential vulnerabilities before the code is deployed.
- Improves code quality and reduces the risk of security flaws.
For more information, please see Code Reviews
Architecture Reviews
Architecture reviews assess the design and structure of a system to identify potential security weaknesses.
- Evaluates the overall system design for security gaps and risks.
- Ensures that security principles are integrated into the architecture.
- Helps in identifying and addressing potential issues early in the design phase.
Password Cracking
Password cracking is a technique used during security assessments to test the strength and resilience of user credentials.
- Used in internal or external assessments
- Helps identify weak, reused, or default passwords.
- Includes brute force, dictionary, and rainbow table attacks.