Physical Access
Physical Access Controls
Physical access controls are tangible measures that prevent, detect, or monitor direct contact with systems and secure areas.
- Protect people first, then assets
- Range from deterrents to detection and response tools
- Each area needs tailored controls and monitoring
Badge Systems and Gate Entry
Badge systems control who can enter a space.
- Use turnstiles, mantraps, or controlled doors
- Compare badges to a verified access database
- Biometrics added for high-security zones
For card types:
- Barcode
- Magnetic stripe
- Proximity
- Smart
- Hybrid
Environmental Design
Design spaces to reduce crime by shaping visibility and flow.
- Apply Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design (CPTED)
- Direct traffic and highlight authorized areas
- Improve natural surveillance and reduce hiding spots
Biometrics
Biometrics use physical or behavioral traits to identify people.
- Store a template for comparison or on a smart card
- High accuracy but can be costly and raise privacy concerns
Types:
- Physiological: fingerprint, iris, retina, palm, vein
- Behavioral: voice, signature dynamics, keystroke
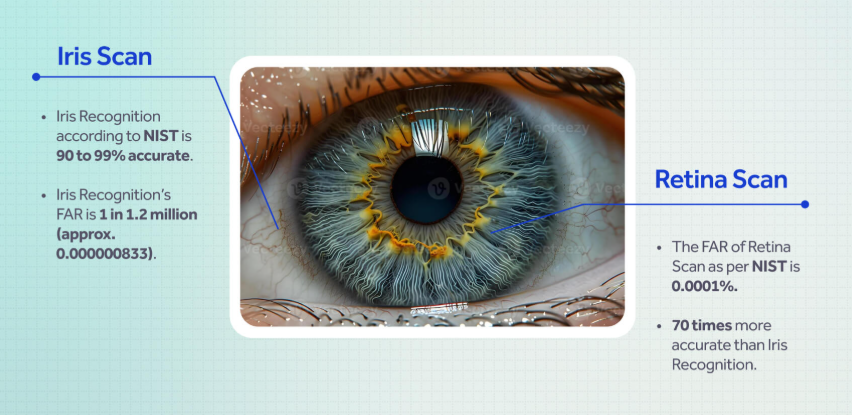
Iris Scans and Retina Scans
An iris scan uses a camera to take a picture of the colored part of the eye from a distance, making it non-invasive and fast, and is widely used for security and identification.
- Iris patterns remain stable throughout a person's life
- This makes it a reliable biometric authentication method
- Has a very low false acceptance rate, making it a highly accurate
- Iris patterns can be recognized from a distance (nonintrusive)
- Disadvantage: Scanners can be fooled by high-quality images of a person's face.
A retina scan requires a close-up, invasive process that uses a beam of light to map the blood vessels on the back of the eye and is now primarily used for medical diagnostics.
Fences, Bollards, and Mantraps
-
Fences
-
Encloses an area using interconnected panels or posts.
-
Visual deterrent, shows where property starts and ends.
-
Made with materials such as wood, metal, wiremesh, concrete, etc.
-
Delays intruders, provides security personnel longer time to react.

-
-
Bollards
-
A bollard is a short post embedded into a street or sidewalk.
-
These posts are common in city and building designs.
-
Boundary markings or protective barriers.

-
-
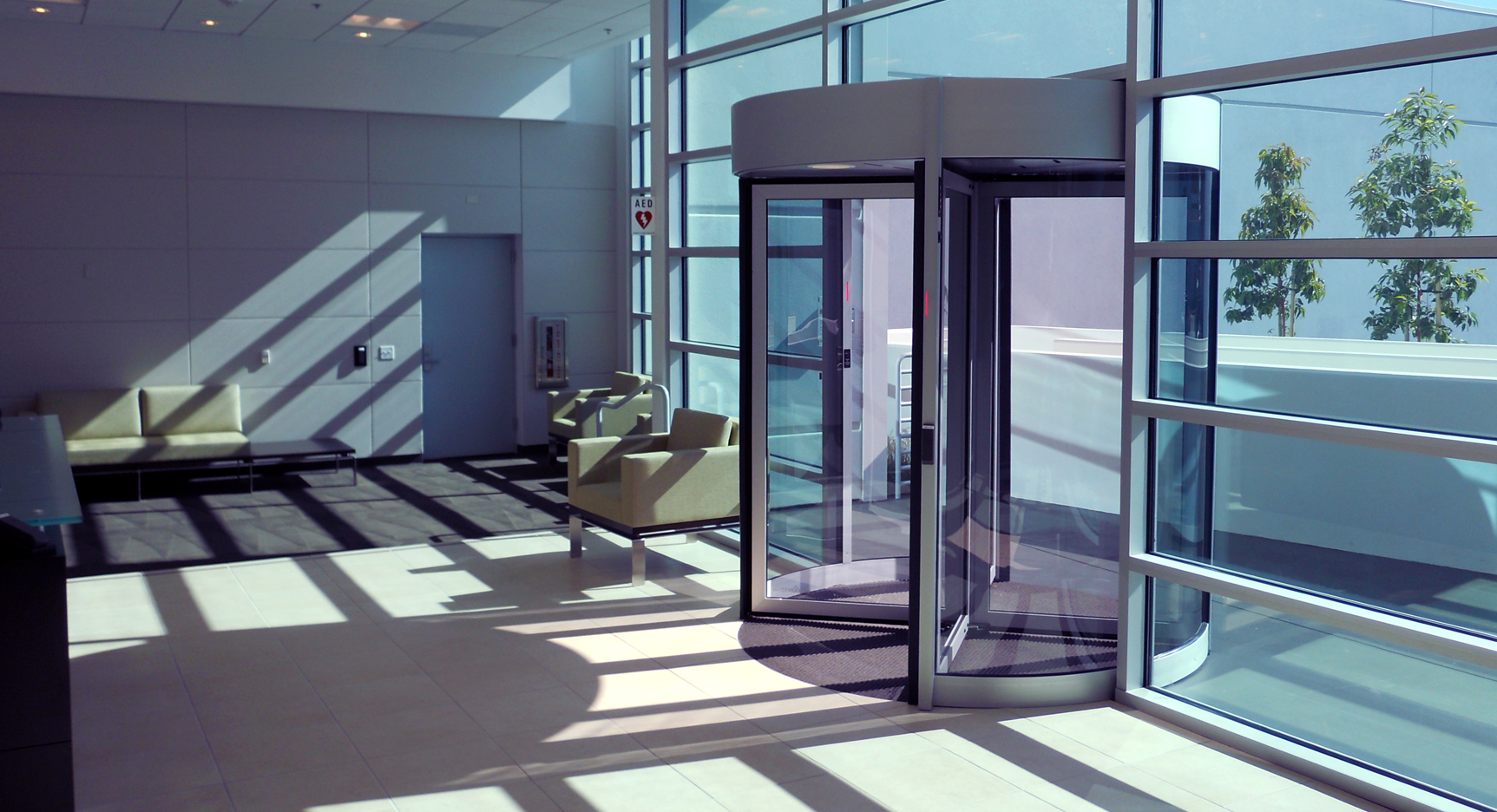
Mantrap
-
Small room with an entry door and exit door.
-
One door stays locked until the other closes.
-
Separates secure and non-secure areas to prevent unauthorized access.

-
Access Control Vestibules
Small controlled spaces to prevent unauthorized entry.
- System with two electronically-controlled doors
- Ensures only one door is open at any given time.
- Can control foot traffic and reduce drafts or noise
Like a mantrap, a security vestibule consists of a small space between two sets of doors but the space may be larger and more open. It can prevent the following:
-
Piggybacking
- Two people, with and without access, entering a secure area.
- Intentionally allowing the second person to enter.
-
Tailgating
- Unauthorized person closely follows someone with access without their knowledge and consent.

Door Locks
Common lock types used in facilities:
-
Padlocks
- Portable locks for doors, gates, lockers, or storage.
- Can be key-operated or combination-based
- Made of brass, steel, or laminated metal.
-
Pin tumbler locks
- Most commonly used tumbler lock.
- Require the key to have just the right grooves.
- The key align spring-loaded pins to lock or unlock.
-
Wafer tumbler locks
- Also called disc tumbler locks.
- Small, round locks usually seen on file cabinets.
- Uses flat discs (wafers) instead of pins inside the locks.
- Easy to bypass because it can be easily circumvented.
-
Cipher locks
- Also known as programmable locks
- keyless and use keypads to control access into an area.
- Requires a specific combination and possibly a swipe card.
- Cost more, but their combinations can be changed.
- Specific combination sequence values can be locked out
- Supports duress code which opens the door and initiate a remote alarm.
-
Combination locks
- Unlocks with a number sequence, not a key.
- User spins the lock interface left and right by so many clicks
- When the internal wheels must aligned, the door is opened.
-
Biometric locks
- Use fingerprints, iris, face, or hand geometry.
- Harder to duplicate; can log entries.
- Some combine biometrics with keypads or cards for extra security.
Surveillance System
Organized strategy or setup designed to observe and report activities in a given area.
- Security Guards act as visible deterrents
- Cameras deter crime and provide forensic evidence
- Lighting improves camera effectiveness and deters intruders
- Motion sensors trigger alerts and can integrate with lighting
Categories of motion sensors:
- Infrared Sensors
- Pressure sensors
- Microwave sensors
- Ultrasonic sensors
Integrated Sensors
Sensors embedded in doors, gates, and structures.
- Use strain-sensitive cables, vibration, pressure, or motion sensors
- Detect forced entry or tampering quickly
Logging
Record keeping for access and security events.
- Protect logs against tampering and unauthorized access
- Review logs regularly and keep retention policies documented
- Watch for log anomalies as an early warning sign
- Includes physical logs, e.g. sign-in sheets, electronic access logs.
Alarm Systems
Alarm systems aim to promptly notify relevant authorities in case of unexpected events.
-
Basic Functionality
- Commonly on doors/windows, designed to signal unexpected openings.
- Simplest form alerts appropriate personnel when unauthorized access occurs.
-
Access Control
- Authorized access (e.g., code/badge) does not trigger an alarm.
- Unauthorized access (e.g., forced entry) activates the alarm.
-
Fire Alarm Systems
- Activated by heat or smoke sensors.
- Audible warnings safeguard lives and notify local response teams.
-
Emergency Response
- Panic buttons serve as a quick alert mechanism.
- When activated, alerts police or security personnel for immediate response.
Visitor Management Policy
A visitor management policy helps organizations track and manage visitor access.
- Log visitor details and purpose of visit
- Visits should be logged, e.g. signing on record book or electroniccally
- Define who may escort visitors and who gets unescorted access
- Issue visible visitor badges and require them to be worn
Detectiom Systems
Perimeter Intrusion Detection System
Perimeter Intrusion Detection and Assessment System (PIDAS) detects anyone trying to cut, climb, or tamper with a fence.
- Sensors are installed on the fence and at the base
- Detects vibration or movement on the fence.
- Passive cable sensors trigger alarms
- Sends alerts to security or monitoring system
Electromechanical Detection System
Electromechanical systems reliably detect physical tampering using simple electrical and mechanical components.
- Contact switches detect forced openings on doors and gates
- Strain gauges sense pulling or impact on panels
- Control units map events to alarms
- Can route alerts to monitoring systems
Passive Infrared (PIR) System
PIR sensors detects human presence by sensing body heat and movement.
- Monitors infrared energy in a defined area
- Detects warm bodies moving through
- Can be used indoors or outdoors
- Integrates with alarms or lighting
Acoustical Detection System
Acoustical systems detects sounds of tampering like cutting, climbing, or breaking.
- Uses microphones or acoustic sensors near perimeters
- Filters background noise to identify suspicious sounds
- Can trigger cameras or alarms
Photometric System
Photometric detection uses light or image analysis to detect changes.
- Cameras or light sensors monitor for unusual activity
- Detect shadows, openings, or motion
- Supports image analysis for alerts
- Can verify alerts from other sensors
Choosing an Access Control System
The following are key factors when selecting controls.
- Performance is primary factor.
- Prioritize safety and reliability next
- Consider scalability, compatibility
- Balance cost and complexity with security needs
Example:
- Choosing a biometric system for higher security performance despite complexity.
- Simplicity and efficiency are secondary considerations.
- Aesthetic appeal is irrelevant to the primary function of access control.
Site Assessment
Decide controls based on site sensitivity and impact.
- Assess sensitivity of data and critical areas
- Choose higher security (e.g., biometrics) for server rooms and exec offices
- Avoid over-securing low-risk areas like supply closets
Example:
Biometric scanners installed based on sensitivity. They are needed for server rooms, executive offices, but not break rooms or supply closets.
Physical Attacks
-
Attacking with Brute Force
- Forcible entry like disabling locks
- Tampering with security devices
- Confronting or attacking the security personnel
- Ramming a barrier with a vehicle
-
Bypassing surveillance systems
- Visual obstructions
- Blinding sensors and Cameras
- Interfering with acoustics
- Electronic interference
- Physical environment attack, e.g. causing fire
-
Access badge cloning
- Refers to copying data from a badge to a blank device
- Cloned badge can then be used to trick the system
- How attackers clone badges:
- Scanning
- Data exfiltration
- Writing to a new card
- Using a cloned access badge