Start here
Database
A Database is a software that is used to store data - basically any piece of information that we may need at a later time. A lot of data that'll be stored in databases are used for data analytics. Organization use these data to predict patterns, find ways to utilize and improve them, and then determine strategies to best serve the customers
There are two main types of databases:
- Relational Databases
- Non-Relational Databases
Relational Databases
These databases store data in tables that are related to each other. Each table has rows (representing records) and columns (representing attributes). The relationships between tables are based on common data (keys).
Common relational databases(SQL):
- MySQL
- SQL Server
- Oracle
- DB2
- PostgreSQL
Non-Relational Databases
Also known as NoSQL databases, these databases store data in a variety of ways that are not table-based, such as key-value pairs, documents, graphs, or wide-column stores. They are often used when dealing with large volumes of varied data types.
Common non-relatonal databases(NoSQL):
- MongoDB
- Cassandra
- SQLite
- Redis
- Couchbase
Basic Concepts
-
Database
- A database is a collection of structured data.
- Think of it as a big box where you store all the information for later retrieval.
-
Database Management System (DBMS)
- A DBMS is the software that interacts with end users, applications, and the database itself to capture and analyze the data.
- Examples include Oracle, SQL Server, MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQLite.
-
Table
- A table is a structured list of data of a specific type in a database.
- It's comprised of rows and columns. It's similar to a spreadsheet in Excel.
-
Column
- A column (or field) is a set of data values of a particular type.
- For example, a column named "FirstName" in a table "Customers" might be of type "VARCHAR" (variable character length), and hold customers' first names.
-
Row
- A row (or record) in a table represents a single, implicitly structured data item.
- For example, a row in a "Customers" table might represent a single customer, with columns for first name, last name, phone number, etc.
-
Primary Key
- A primary key is a column (or set of columns) whose values uniquely identify every row in a table.
- No two rows can have the same primary key value.
-
Foreign Key
- A foreign key is a set of one or more columns in a table that refers to the primary key in another table.
- It's used to link two tables together.
-
Index
- An index is a data structure that improves the speed of data retrieval operations on a database table.
- It works in a way similar to an index at the back of a book.
-
SQL
- SQL (Structured Query Language) is the standard language for dealing with Relational Databases.
- SQL can be used to insert, search, update, delete database records.
-
Relational Database
- Sstores and provides access to data points that are related to one another.
- Organizes data into tables which can be linked or related, based on data common to each.
Where does the database fit in an application?
An application consist of two main components: the frontend and the backend.
-
Frontend is what the users see when they access a website or open the application in their devices. The user are able to see details through the frontend, as well as input information but they don't have access to the backend, where the database lies.
-
Backend is where the details are received, processed, and stored. This is where the server-side processing occurs.
Databases are part of the backend of an application. They enable the application to "remember" any information by storing and organizing them.

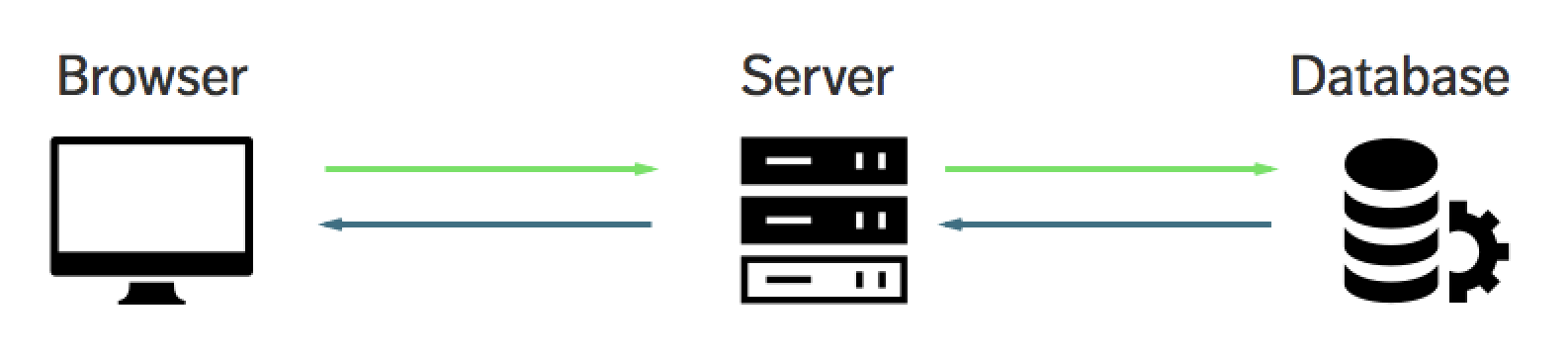
How Data is Obtained
An applications's structure can vary from application to application and different organizations will have different ways of building applications, but in general, this is how data is obtained.
- User opens the application through a browser/device.
- Application reach outs to API or backend server.
- Backend server talks to the data layer, including the database.
- Database receives the request and checks the collection or tables.
- The database then passes the details back to API server, all the way to the application being accessed by the user.
Types of Data
Data can come in different forms, each with its own characteristics and uses.
-
Structured Data
- Easily searchable and organized, like a spreadsheet with set columns.
- Relational databases, queried using SQL (Structured Query Language).
- About 20% of data is structured.
- Example: Employee tables, where each row represents an employee and columns hold specific information.
-
Semi-Structured Data
- Resembles structured data but allows more flexibility, often stored in NoSQL databases.
- Formats include JSON, XML, YAML.
- NoSQL databases as storage
- Example:JSON file of users’ favorite artists, where each user ID contains varied numbers of favorite artists.
-
Unstructured Data
- Data that doesn’t follow a model, making it hard to search and organize.
- Typically found in data lakes, sometimes in data warehouses or databases.
- Extremely valuable but requires machine learning and AI for effective extraction.
- Example: Lyrics, songs, album pictures, artist profile pictures, music videos.
SQL versus NoSQL
There's no one-size-fits-all database solution. Each type has its own use case, so it's important to understand when to use which.

SQL or Standard Query Language Databases refers to structured, relational databases. With structure data, we have:
- The more tables, the more inserts are required
- Joins are required to retrieve data
- Structure is hard to break
- Organized data reduces redundant information
- Data model cannot change easily
- Data model needs to be thought of upfront to ensure consistency
- Requires more work for developers
NoSQL, on the other hand, refers to unstructured, non-relational databases. With NoSQL, we can:
-
Easily next data, allowing related details to be in one spot
-
Nested files solves the issue of needing to join documents
-
Flexible structure allows for easy iterations
-
Structure can change
-
Could use structured on unstructured data
-
Less time focusing on the database, more time to code

Benefits of SQL
SQL (Structured Query Language) plays a vital role in both Data Analysis and Data Engineering due to its versatility, wide acceptance, and powerful capabilities in handling data. Here are some of the reasons why SQL is important in these fields:
-
Universal Language for Managing Data
- SQL is a standard language for managing and manipulating data held in relational database management systems (RDBMS).
- It allows for the creation, querying, updating, and management of databases, making it fundamental to both data analysis and data engineering.
-
Efficient Data Manipulation
- SQL makes it easy to retrieve, insert, update, and delete data in a database.
- It supports complex queries to fetch data based on various conditions, making it a powerful tool for data analysis.
-
Complex Analytical Operations
- SQL provides functions and capabilities to perform complex analytical operations, such as aggregations, calculations, transformations, and others, directly on the database.
- This can dramatically improve the efficiency of data analysis tasks.
-
Data Structure and Integrity
- SQL helps enforce data structure and integrity, which is a critical aspect of data engineering.
- It allows the definition of constraints that help maintain data accuracy and consistency.
-
Scalability
- SQL can handle large volumes of data, which makes it an important tool for data engineering tasks, such as constructing and managing large databases and data warehouses.
-
Integration with Other Technologies
- SQL integrates well with other technologies, including data visualization tools, statistical software, and various programming languages.
- This compatibility extends its utility in the broader data ecosystem.
-
Popularity and Community Support
- SQL is widely used across industries, and there is a vast community of users and experts who can provide support.
- This broad adoption also means that SQL skills are highly sought after by employers.
SQL Implementations
There are several SQL versions with small differences. Switching between them is like switching keyboard layouts or English dialects. They are mostly similar with some changes.
-
MS SQL Server (Microsoft SQL Server)
- Developed by Microsoft for enterprise use
- Handles many data types and offers strong performance and security
- Integrates well with other Microsoft tools
-
MySQL
- Open-source and owned by Oracle Corporation
- Common in web apps and part of the LAMP stack
- Known for speed, reliability, and ease of use
- Runs on Linux, Windows, and MacOS
-
PostgreSQL
- Powerful, open-source object-relational database
- Supports complex data and advanced features
- Features like MVCC and point-in-time recovery
- Highly customizable with extensions and libraries
-
Oracle SQL (Oracle Database)
- Multi-model system from Oracle Corporation
- Supports huge databases with billions of records
- Handles high transaction loads
- Feauters resource costing, data warehousing
- Also supports availability, scalability, and security
Terminologies
SQL syntax refers to the set of rules that define how SQL commands are structured. These rules dictate how to write, structure, and sequence SQL statements and clauses. Here are the fundamental components of SQL syntax:
1. SQL Statements
-
The fundamental form of SQL instruction is called a statement.
-
It's a command that performs a specific task. Examples include:
-
SELECT: Retrieves data from a database. -
INSERT INTO: Inserts new data into a database. -
UPDATE: Modifies existing data in a database. -
DELETE FROM: Deletes data from a database. -
CREATE DATABASE, CREATE TABLE: Creates a new database or table, respectively.
-
2. SQL Clauses
-
Clauses are components of a SQL statement.
-
They refine SQL statements by providing additional parameters or conditions.
-
For example, in the statement:
SELECT * FROM Employees WHERE Age > 30;WHEREis a clause that restricts the data returned.
3. SQL Expressions
- An expression is a combination of one or more values, operators, or SQL functions that result in a value.
- Expressions can be used in various parts of SQL statements, such as in the WHERE clause to filter data.
4. SQL Predicates
- Predicates specify conditions that can be evaluated to true, false, or unknown.
- They're used in SQL statements to limit the scope of data on which the SQL statement operates.
5. SQL Identifiers
- Identifiers are the names of database objects like tables, columns, and schemas.
- They must follow certain rules, such as starting with a letter and being unique within their scope.
6. SQL Operators
- Operators are symbols that specify an operation to be performed on the data.
- SQL includes various types of operators such as:
-
Arithmetic operators
+, -, *, / -
Comparison operators
>, <, =, <=, >=, <> -
Logical operators (AND, OR, NOT).
AND, OR, NOT
-
An example SQL query using these components might look like this:
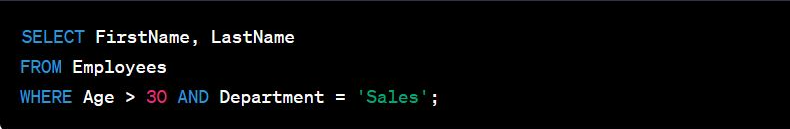
In this example:
SELECTandFROMare SQL statements,WHEREis a clause,Age > 30 AND Department = 'Sales'is an expression containing predicates and operators, andFirstName,LastName,Employees,Age, andDepartmentare identifiers.
SQL Expressions
SQL expressions are combinations of symbols and operators that the SQL database engine can evaluate to obtain a single data value. These expressions can involve the use of constants, variables, scalar functions, and column names that are combined using mathematical or logical operators. SQL expressions can be used in select lists, WHERE clauses, ORDER BY clauses, and other parts of SQL statements.
Here are some types of SQL expressions:
1. Arithmetic Expressions
- These are mathematical expressions involving operators such as +, -, *, and /.
- For example, if you have a table named Orders with a column Price and Quantity, you can calculate the total price for each item with the following arithmetic expression: Price * Quantity.
2. Comparison Expressions
-
Comparison expressions result in a value of
TRUE,FALSE, orUNKNOWN. -
They involve comparison operators like:
=, <>, >, <, >=, <=. -
For example, a comparison expression:
Salary > 50000
3. Logical Expressions
- Logical expressions combine boolean values (
TRUE,FALSE, andUNKNOWN) and yield a result of the same type. - They involve logical operators like AND, OR, and NOT.
- For example, (Salary > 50000 AND Department = 'Sales') is a logical expression.
4. Concatenation Expressions
- In SQL, the || operator is used to concatenate two or more strings.
- For example, to combine first name and last name in a Employees table, you could use: FirstName || ' ' || LastName.
5. Date Expressions
-
Date expressions manipulate date values.
-
For example, to extract the year from a date column:
EXTRACT(YEAR FROM OrderDate)
6. Case Expressions
-
Case expressions implement conditional logic by executing different expressions based on a condition.
-
The syntax is:
CASE WHEN condition THEN result [WHEN ...] [ELSE result] END -
For example, to categorize employees by salary:
CASE WHEN Salary > 50000 THEN 'High' ELSE 'Low' END