REST APIs
How API works
APIs as a way to serve your customers
Example scenario: Your small business’s website has a form used to sign clients up for appointments. You want to give your clients the ability to automatically create a Google calendar event with the details for that appointment.
API use: The idea is to have your website’s server talk directly to Google’s server with a request to create an event with the given details. Your server would then receive Google’s response, process it, and send back relevant information to the browser, such as a confirmation message to the user.
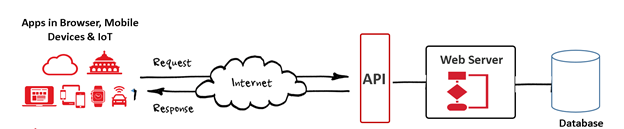
Alternatively, your browser can often send an API request directly to Google’s server bypassing your server.
Reference: What's an API
SOAP vs. REST
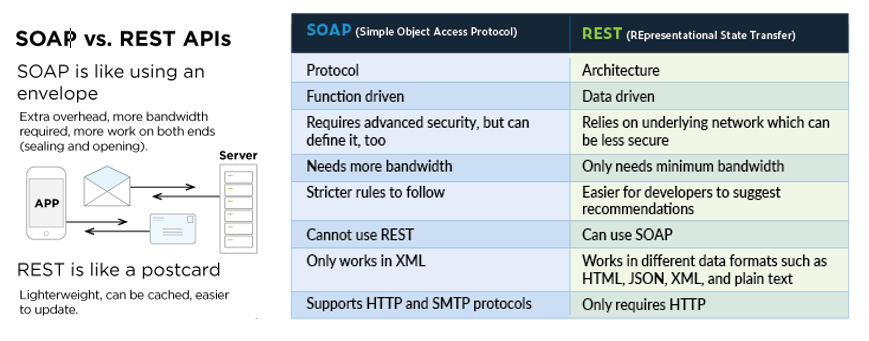
Representational State Transfer
REST (REpresentational State Transfer) is an architectural style that standardizes communication between web systems, facilitating easier interaction.
- Stateless design where each request contains all necessary information
- Separation of concerns between client and server roles
- RESTful systems promote interoperability and scalability
Reference: Codecademy's site
Resources and Representation
REST is about resource state manipulation through their representations on the top of stateless communication between client and server.
When designing REST over HTTP, URLs are used to locate the resources, HTTP methods are used to express the operations over the resources and representations such as JSON and/or XML documents are used to represent the state of the resource.
-
What is a resource? Understand resource as the concept of a user. Don't think about the table in your database, think about an abstraction of a user with their set of attributes.
-
What is a representation? A JSON document can be used to represent the state of a particular resource. A resource can have many representations, such as JSON and/or XML documents, and the client can use content negotiation to request different representations of the same resource.
-
What is a state transfer and when does this happens? The state of a given resource can be retrieved and manipulated using representations.
A GET request, for example, allows you to retrieve a representation of the state of a resource, sent in the response payload. A PUT request, for example, allows you to replace the state of a resource with the state defined by the representation enclosed in the request payload.
When the client and server exchange messages; the client server architectural style is the first of the architectural constraints in the REST architectural style.
Reference: StackOverflow discussion.
Data Format
Representational state that you may receive from a database could be in the form of a row from a database. You can then write a logic ot convert this row to another forms:
- XML
- JSON
- HTML
- JPEG, PDF, TXT, etc
When is API "RESTful"?
An API is RESTful when:
- It's built using the RESTful Architectural Style.
- It follows the set of principles for RESTful APIs
Types of API based on Consumers
Here's an excerpt from Stoplight's article on API:
-
Open APIs
- Publicly available with minimal restrictions.
- May require registration or an API key.
- Allows external developers to access data/services (e.g., UK government data).
-
Internal APIs
- Designed for internal use within a company.
- Shares resources between teams.
- Offers security, access control, and an audit trail.
-
Partner APIs
- Similar to open APIs but with restricted access.
- Often controlled via a third-party API gateway.
- Typically used for specific purposes, like paid services.