AWS Compute
This is not an exhaustive documentation of all the existing AWS Services. These are summarized notes that I used for the AWS Certifications.
To see the complete documentation, please go to: AWS documentation
Compute
Compute resources can be considered the brains and processing power required by applications and systems to carry out computational tasks via a series of instructions. They are closely related to common server components such as CPUs and RAMs.
A physical server within a data center would be considered a Compute resource, as it may have multiple CPUs and many gigs of RAM to process instructions given by the operating system and applications
Commonly used compute services:
- EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud)
- ECS (Elastic Container Service)
- ECR (Elastic Container Registry)
- EKS (Elastic Container Service for Kubernetes)
- AWS Elastic Beanstalk
- AWS Lambda
- AWS Batch
- Amazon Lightsail
To learn more, check out the following links:
Amazon Machine Images (AMIs)
An AMI provides the information required to launch an instance. These are basically "disk images" which is used to spin up the instances.
Main categories:
- Community AMIs
- AWS Marketplace AMIs
- Custom AMIs
Default Limits
Below are some limitations for EC2. Note that these may change. For more information, see Amazon EC2 service quotas.
| Resource | Limits |
|---|---|
| Instance | 20 instances per region |
| Snapshots | 10000 snapshots per region |
| EC2 Auto Scaling Groups | 200 per region |
| Scaling policies per Auto Scaling group | 50 |
| Scheduled actions per Auto Scaling group | 125 |
| Lifecycle hooks per Auto Scaling group | 50 |
| SNS topics per Auto Scaling group | 10 |
| Classic Load Balancers per Auto Scaling group | 50 |
| Target groups per Auto Scaling group | 50 |
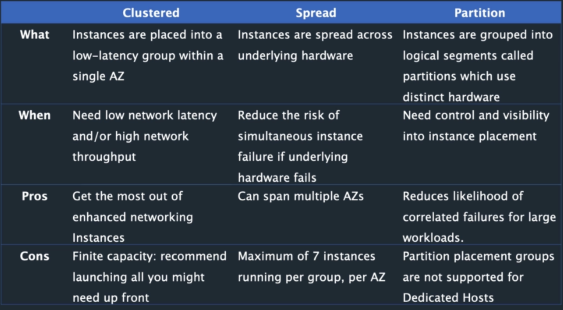
Placement Groups
Placement groups are a logical grouping of instances in one of the following configurations:
-
Cluster Placement Group (single-az+single-rack)
- A cluster placement group is a logical grouping of instances within a single Availability Zone.
- Recommended for applications that benefit from low network latency, high network throughput, or both, and if the majority of the network traffic is between the instances in the group.
-
Partition Placement Group (multi-az+separate racks)
- Spread on logical partition
-
Spread Placement Group (multi-az+separate rack+1 instance per rack)
- A spread placement group is a group of instances that are each placed on distinct underlying hardware
- Recommended for applications that have a small number of critical instances that should be kept separate from each other
Table:
Status Checks
-
System Status Checks
- Problem with your instance that may require AWS involvement repair.
- AWS needs to t-shoot
-
Instance Status Checks
- Problems that may involve the OS
- USER needs to t-shoot
VM Import/Export
Easily import virtual machine images from your existing environment to Amazon EC2 instances and export them back to your on-premises environment.
To learn more, please see VM Import/Export.
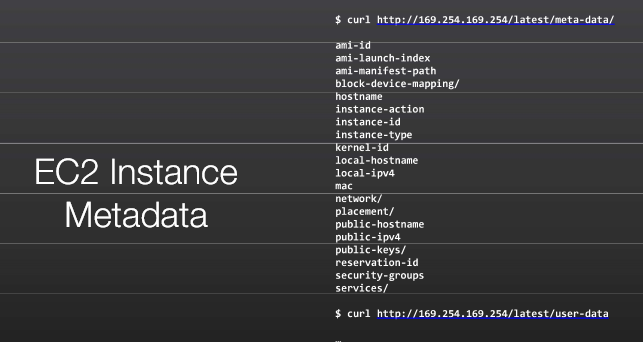
User Data and Metadata
Instance Metadata
These are the data about your instance that you can use to configure or manage the running instance.
User Data
EC2 User data is supplied by the user at instance launch in the form of a script.
- Limited to 16KB
- Can be used to bootstrap the instance.
Bootstrapping runs the provided script, so anything you can accomplish in a script you can accomplish during bootstrapping:
-
Install the most current security updates.
-
Install the current version of the application.
-
Configure Operating System (OS) services.