EC2 Storage
This is not an exhaustive documentation of all the existing AWS Services. These are summarized notes that I used for the AWS Certifications.
To see the complete documentation, please go to: AWS documentation
Instance Store
Instance store provides temporary block-level storage for your instance. This storage is located on disks that are physically attached to the host computer.
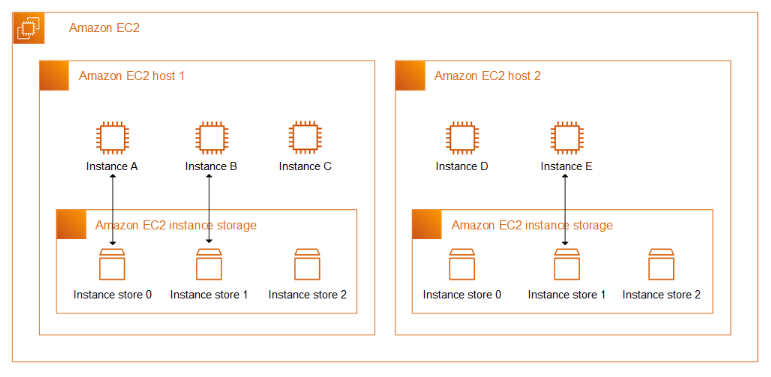
Table:
| Operation | Description |
|---|---|
| Reboot | Rebooting an instance does not shut down the instance; if an instance reboots (intentionally or unintentionally), data on the instance store persists. |
| Stop/Terminate | The data in an instance store persists only during the lifetime of its associated instance. If an instance is stopped or terminated, then the instance store does not persist |
To learn more, please see Amazon EC2 instance store.
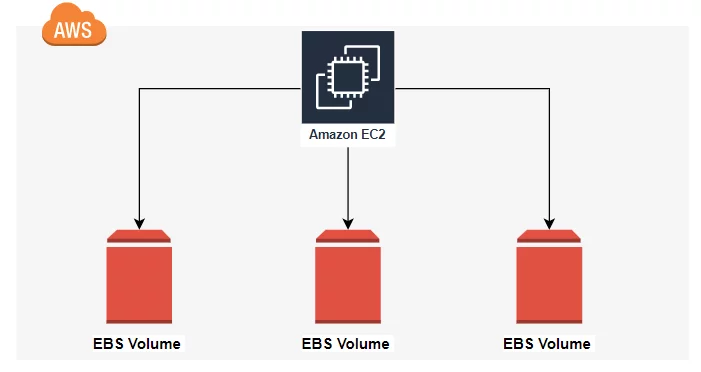
Amazon Elastic Block Storage (EBS)
Persistent block storage volumes. You can attach multiiple Ebs volumes to a single instance.
To learn more, please see Amazon EBS volumes.
EBS Types
- Magnetic
- General Purpose (SSD)
- Provisioned IOPS (SSD)
EBS Encryption
- Use AWS KMS master keys or use a customer master key (CMK)
- Creating your own CMK gives you more control on the key.
EBS Snapshot
- Point-in-time backup copy of an EBS volume that is stored in Amazon S3.
- Incremental, which means only the blocks that have changed after your most recent snapshot is saved.
- When snapshot is deleted, only data exclusive to that snapshot is deleted.
- Can be shared across AWS accounts or copied across regions
EBS Migration
- EBS volumes are locked to a specific availability zone.
- To migrate an EBS volume to a different AZ or region:
- Snapshot the volume
- Copy the volume to a different region (optional)
- Create a volume from the snapshot.
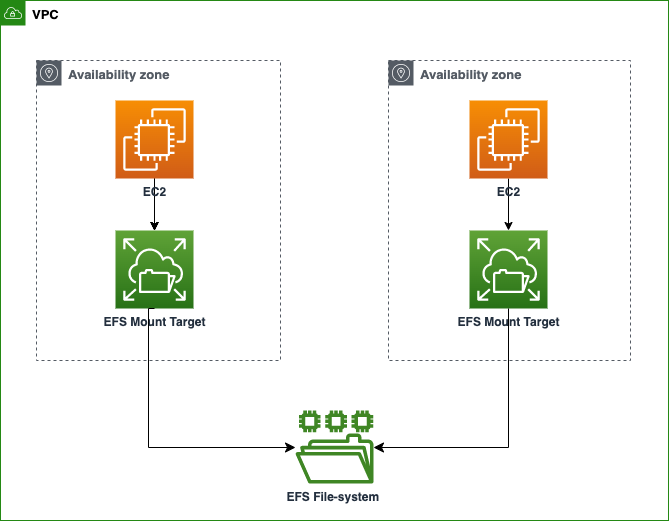
Amazon Elastic Filesystem (EFS)
Amazon EFS provides scalable file storage for use with Amazon EC2. You can use an EFS file system as a common data source for workloads and applications running on multiple instances.
To learn more, please see Amazon EFS.