Elastic Load Balancer
This is not an exhaustive documentation of all the existing AWS Services. These are summarized notes that I used for the AWS Certifications.
To see the complete documentation, please go to: AWS documentation
Overview
Elastic Load Balancers(ELB) automatically distribute incoming application traffic across multiple targets and virtual appliances in one or more Availability Zones (AZs).
How Elastic Load Balancing works
Please see How Elastic Load Balancing works.
Types
Health Checks
- Ping
- Connection attempt
- Page request
Listeners
A listener is a process that checks for connection requests, using the protocol and port that you configure. The rules that you define for a listener determine how the load balancer routes requests to the targets in one or more target groups
Rule conditions
There are two types of rule conditions.Each rule can have up to one host condition and up to one path condition
- host
- path
Stickiness
Stickiness ensures that the same client is always redirected to the same instance behind the loadbalancer.
- The cookie used for stickiness has an expiration date which you can control
- Useful if you want your user to not lose session data
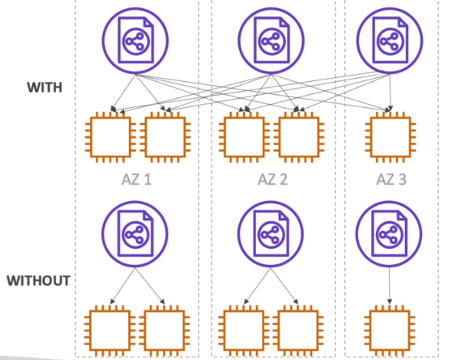
Cross-Zone Loadbalancing
Load is distribtued evenly across all registered instances in all availability zone.
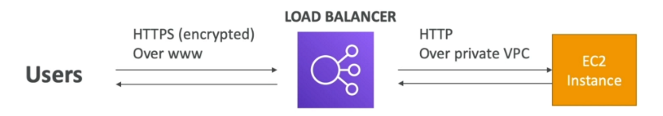
SSL Certificates
SSL certificates can be used to encrypt the traffic between clients and the loadbalancer.
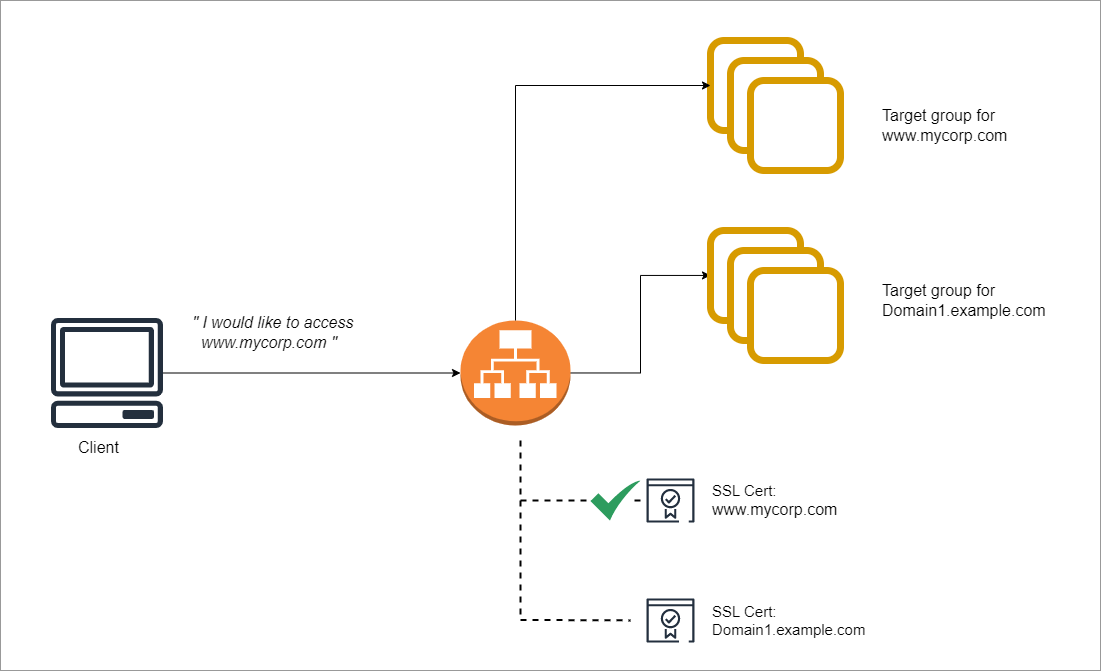
The loadbalancer uses an X.509 certificate and can eb managed using AWS Certificate Manager (ACM).
- Need to specify an HTTPS listener.
- Specify a default certificate
- Clients can then use SNI to specify the hostname they are trying to reach.
Server Name Indication (SNI)
SNI solves the problem of lading multiple SSL certificates onto one web server. By using SNI, clients can indicate the hostname to connect to. It supports multiple secure websites using a single secure listener.
Connection Draining
Refers to the time to complete "in-flight requests" while the instance is de-registering or unhealthy.
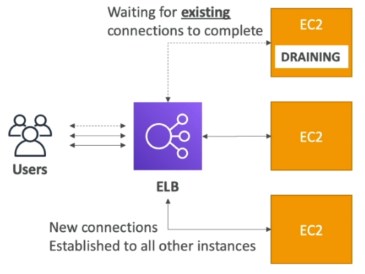
When enabled, new requests will not being sent to the intance being de-registered.
- Can be disabled by setting value to 0.
- default is 300 seconds
Server Order Preference
Ensures that load balancer determines which cipher to use for SSL connection. Elastic Load Balancing supports the Server Order Preference option for negotiating connections between a client and a load balancer.
-
During the SSL connection negotiation process, the client and the load balancer present a list of ciphers and protocols that they each support, in order of preference.
-
By default, the first cipher on the client’s list that matches any one of the load balancer’s ciphers is selected for the SSL connection.
-
If the load balancer is configured to support Server Order Preference, then the load balancer selects the first cipher in its list that is in the client’s list of ciphers.
-
This ensures that the load balancer determines which cipher is used for SSL connection.
-
If you do not enable Server Order Preference, the order of ciphers presented by the client is used to negotiate connections between the client and the load balancer.