Kubernetes Services
Services
A Service defines network access rules for Pods in a Kubernetes cluster. It selects Pods based on labels, allowing clients to reach these Pods via a fixed IP.
- Use services to access groups of Pods by label
- Clients connect through a fixed IP
- The service distributes incoming requests across Pods
To view services in all namespaces:
kubectl get svc -A
When creating EKS clusters, two services are deployed by default:
- kubernetes: allows communication with cluster nodes
- kube-dns: connects to various Pods
Service Discovery
Kubernetes uses two main methods for service discovery:
-
Environment Variables
- Automatically injected by Kubernetes into containers
- Uses a naming convention based on the service name
-
DNS
- Creates DNS records for services automatically
- Allows containers to discover services by querying cluster DNS
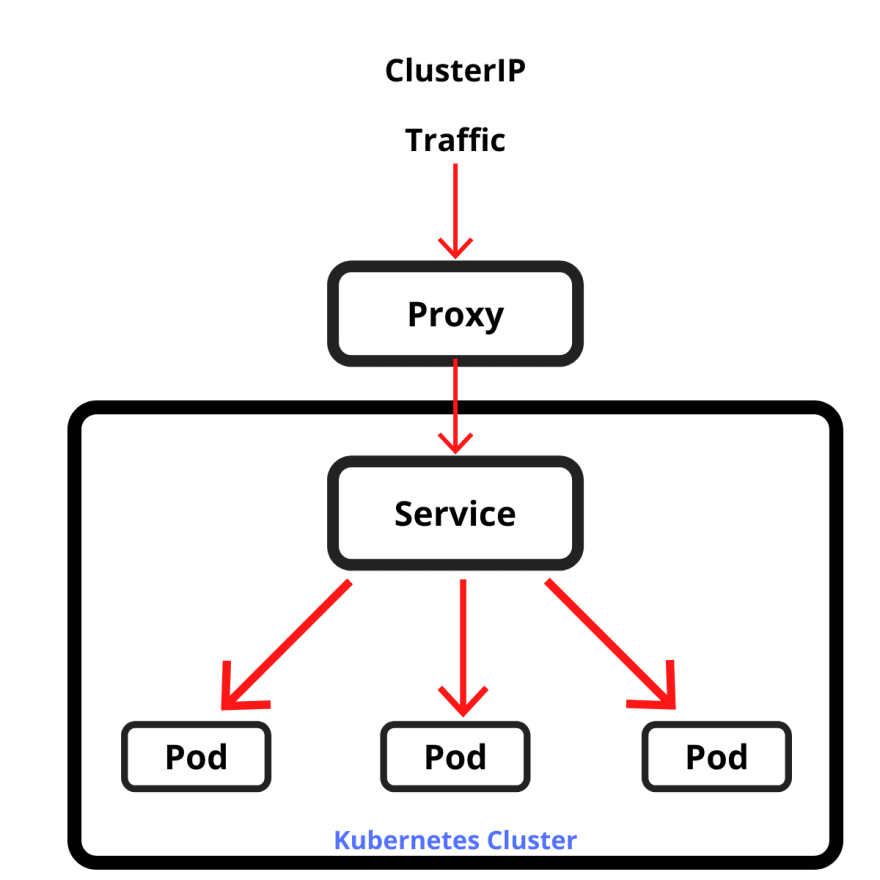
ClusterIP
ClusterIP assigns an internal IP to a service, making it accessible only within the cluster. The kube-proxy component on each node routes requests to the service's endpoints.
- Used for internal services, like databases or internal APIs
- Provides a stable internal network identity for pods
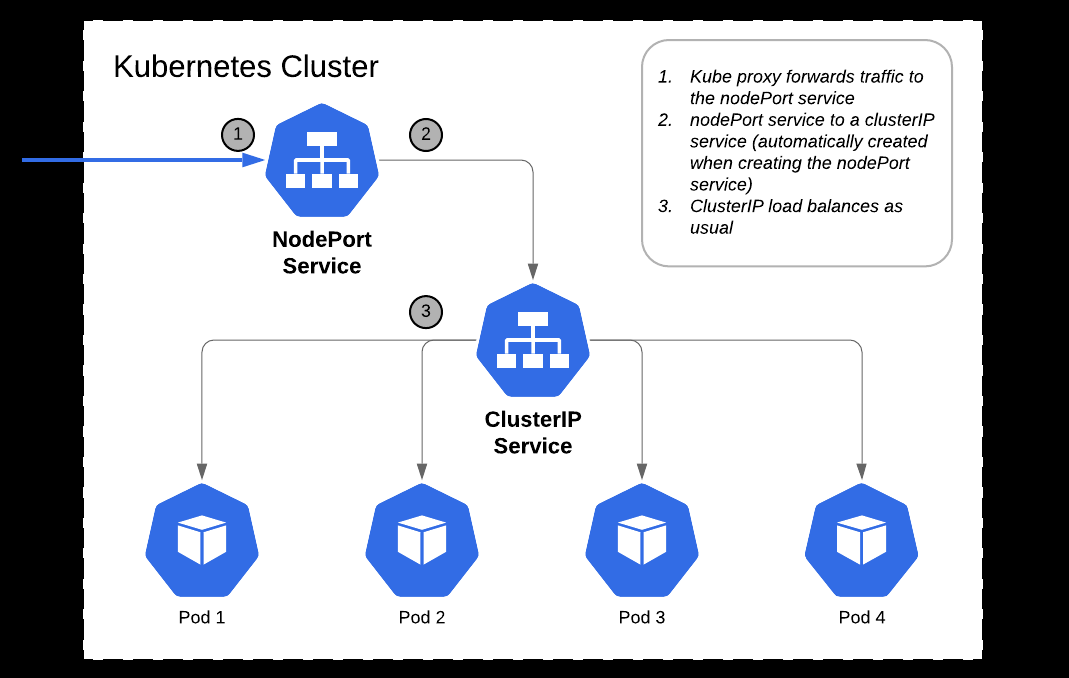
NodePort
NodePort exposes a service externally by opening a specific port on each node. Requests sent to this port route to the service’s cluster IP.
- Limited external access, for testing or non-production apps
- Accessible via
<NodeIP>:<NodePort>
Loadbalancer
A LoadBalancer service exposes the service to the internet using a cloud provider’s load balancer.
- Automatically provisions a load balancer with a public IP
- Configurable for SSL, health checks, and other features
External Name
ExternalName maps a service to an external DNS name instead of internal routing, useful for services outside the cluster.
- Returns a CNAME record for the external DNS name
- Often used for connecting to external databases or APIs
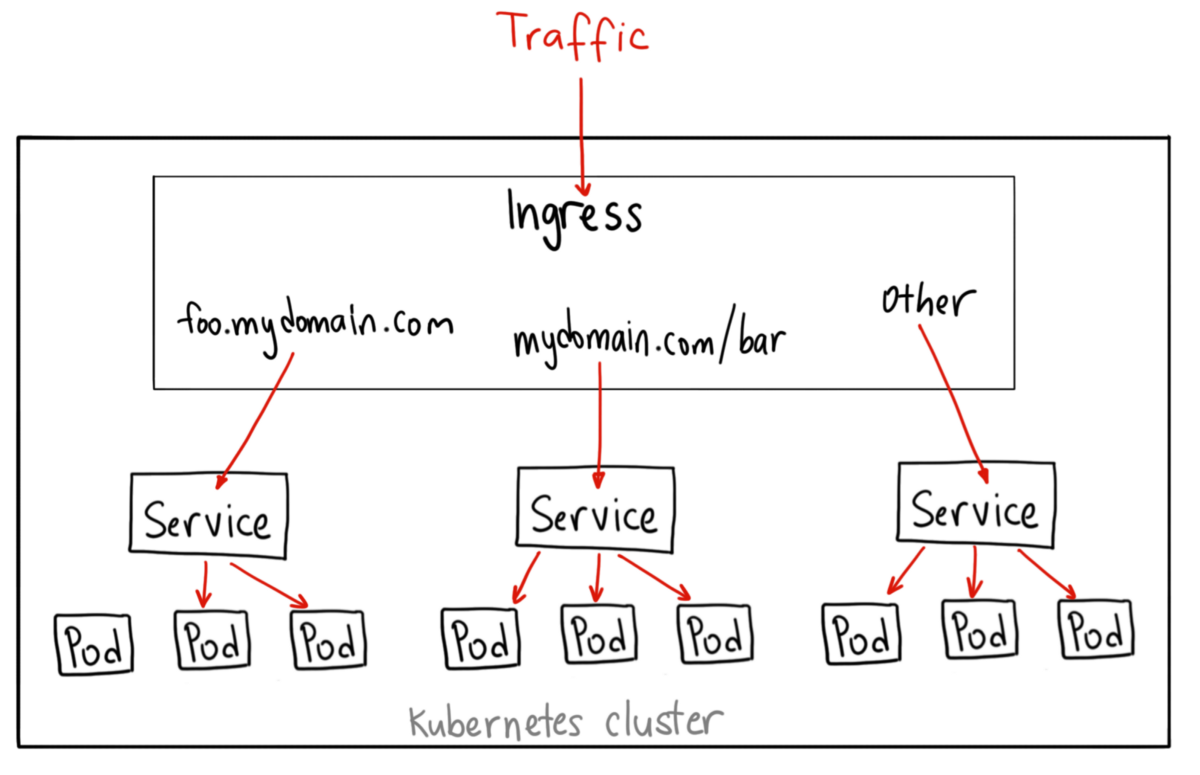
Kubernetes Ingress
Ingress Controller manages layer 7 traffic, supporting SSL, load balancing, and path-based routing.
- Routes external traffic based on domain and path
- Supports SSL termination and custom routing rules
Once we have an ingress controller in place, we can leverage the ingress to define rules for inbound connections to services.