Kubernetes Cluster
Overview
A Cluster is a collection of distributed physical or virtual servers or nodes, which is used to host and manage workloads.
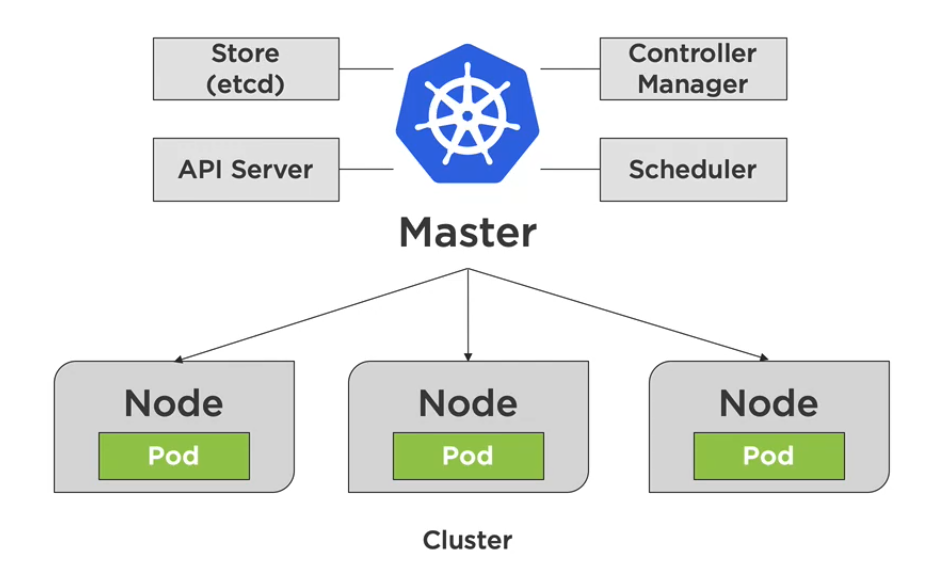
It has two types nodes:
-
Master Node (Control Plane)
- Manages the cluster, making global decisions.
- Components:
- kube-apiserver – Exposes Kubernetes API
- kube-scheduler – Assigns workloads to nodes
- kube-controller-manager – Keeps resources current
- etcd – Stores cluster data and configurations
-
Worker Nodes (Data Plane)
- Host application workloads.
- Components running on all nodes (master and worker):
- kubelet – Agent on each node, registers it with the cluster
- kube-proxy – Network proxy ensuring workload reachability
Master Node (Control Plane)
The master node manages core control functions of the cluster.
- Primary access point for administration
- Coordinates cluster operations
- Manages monitoring and scheduling
- Runs system Pods (API server, Cluster Store, Scheduler, Control Manager)
- Forwards workloads to worker node Pods
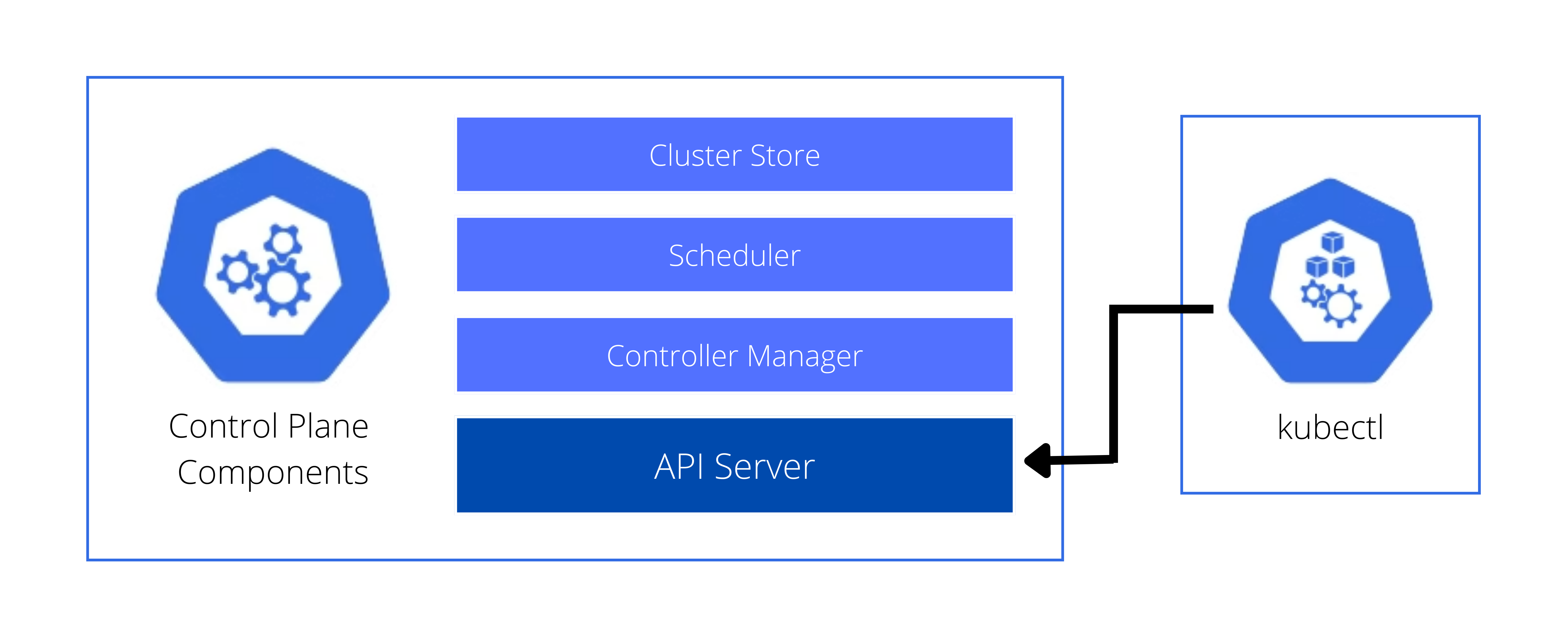
API Server
The API Server is the central hub for all Kubernetes communication and operations.
- Acts as a REST API interface
- Routes all configuration changes
- Verifies operations and updates etcd
etcd (Cluster store)
etcd is the persistent storage for the Kubernetes cluster.
- Saves Kubernetes object states in key-value pairs
- Monitors object state with watches on keys
- Stateless services retrieve data via the API server
Scheduler
The Scheduler assigns Pods to Nodes based on resource needs.
- Monitors API server for unscheduled Pods
- Matches Pods to Nodes based on resource constraints
Scheduling process:
- Filtering – Finds Nodes with required resources
- Scoring – Ranks Nodes to pick the best match for each Pod
Controller Manager
The Controller Manager maintains system state via Controllers.
- Runs controller loops to monitor
- Update system state based on desired configurations
Controller types:
- Node Controller – Manages node availability
- Replication Controller – Maintains correct Pod counts
- Endpoints Controller – Links services and Pods
- Service Account and Token Controllers – Manages default accounts and tokens for namespaces
Cloud Controller Manager (for EKS Setup only)
The Cloud Controller Manager manages cloud-based resources for AWS EKS.
- Manages autoscaling and cloud integrations
- Provisions EBS volumes and load balancers
Additionally, kubectl is essential for interacting with the API Server, though it is not part of the control plane itself.
Worker Node
A worker node starts and maintains Pods, ensuring they run smoothly. It manages networking and operates within a cluster of multiple nodes.
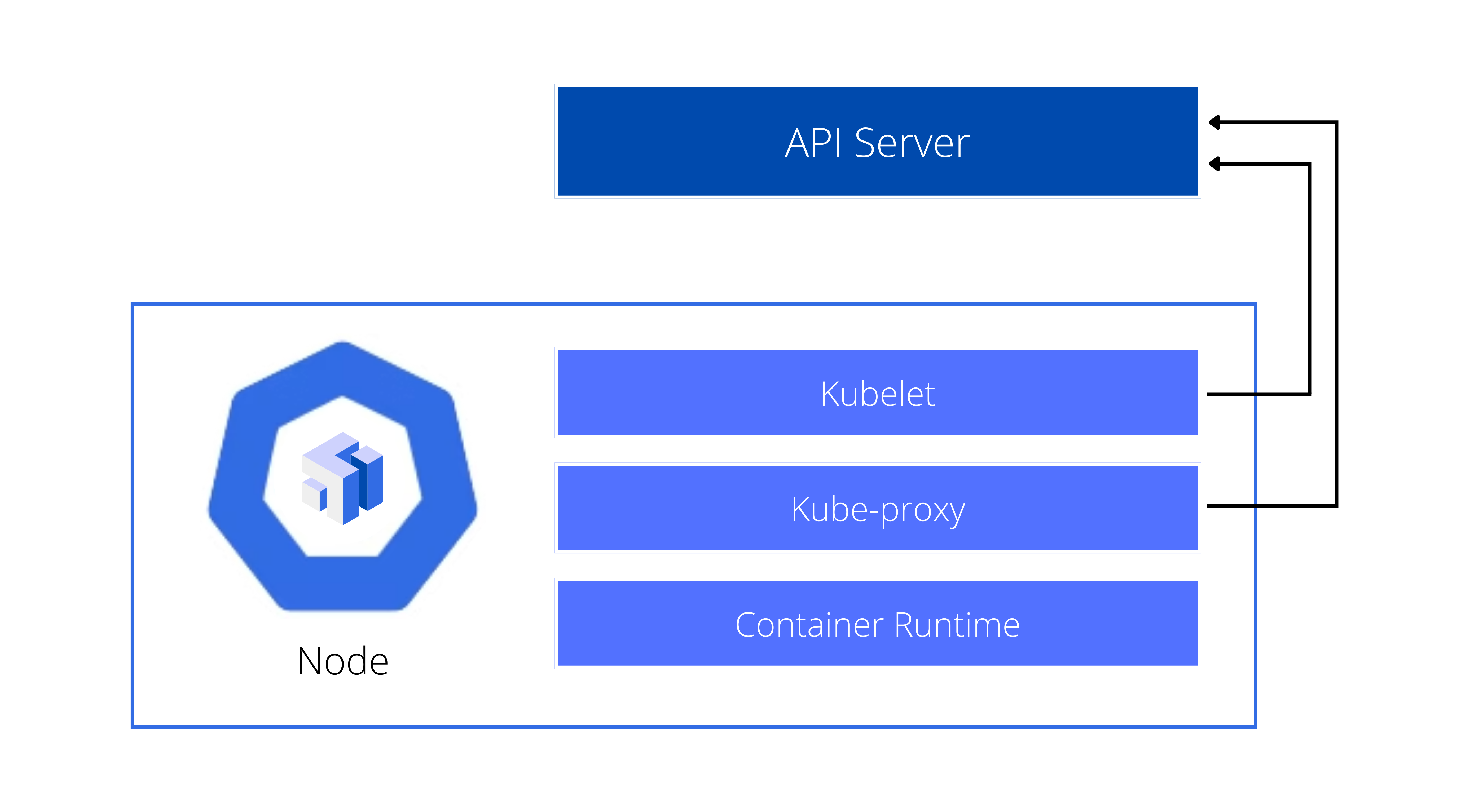
Kubelet
The Kubelet is the node agent that communicates with the Kubernetes API server.
- Starts and stops Pods as directed by the API server
- Monitors Pod and node status; reports back to API server
- Liveness probes - for health check of Pods and applications
Kube-proxy
The Kube-proxy is a network proxy that runs on each node to manage network traffic.
- Provides rules for cluster IPs and Pod networking
- Talks to the API server for networking information
- Handles service abstraction and load balancing
- Routes traffic to Pods
Container Runtime
The Container Runtime is the environment where the container image runs.
- Pulls images from the registry
- Provides the execution environment
- Default runtime is Docker, though others are supported
Scheduled/Add-Ons
Add-ons are specialized Pods offering extra cluster services.
-
DNS Pod – Manages DNS and service discovery within the cluster
-
Ingress controllers and dashboards – Provide web-based administration