Updates and Patches
Patch Management
Patch Management involves updating software to address vulnerabilities and improve security.
- Ensures systems are protected against known threats.
- Key for maintaining a secure and resilient IT infrastructure.
Update New Device Firmware First
New network devices may sit in storage for months before being used. During that time, several firmware updates might be released. To fix any known security issues, the first thing an IT admin should do is update the device's firmware.
Terms
-
Software Patch
- A software patch is a quick-repair solution for programming issues.
- Designed to address functionality problems, enhance security.
- Introduces new functionalities to improve user experience.
-
Hotfix
- Also known as "Quick-Fix", it solves a security issue.
- Cumulative package addressing specific issues in a software product.
- Should be applied immediately after being tested in a lab environment.
-
Updates
- An update provides the system with additional functionality,
- It does not usually provide any patching of security related issues.
- Often introduce new security vulnerabilities, which may require another hotfix.
-
Service Pack
- Updates, fixes, or enhancements bundled into a single installable package.
- Provides comprehensive improvements to a software program.
Centralized Patching
Centralized patching uses a single management system to deploy updates across all devices, ensuring consistency and control.
- Simplifies tracking and reporting of patch status.
- Ensures timely and uniform deployment of updates.
- Reduces security risks from unpatched systems.
Decentralized Patching
Decentralized patching distributes the responsibility of applying updates across multiple devices or teams rather than relying on a central system.
- Allows teams to apply patches independently.
- Helps maintain security when devices are offline or not centrally managed.
Issues with decentralized patching:
- Inconsistent patching, creating security gaps
- Risk of missed or delayed updates
- Hard to track patch status across devices
- Admin credentials are often needed to install patches
- Apps downloading patches independently can cause network congestion
Patching unmanaged devices may be the only advantage to using decentralized patching, as these devices might not always be on the network or cannot be patched using centralized methods (e.g., personal devices).
Applying Patches
Windows
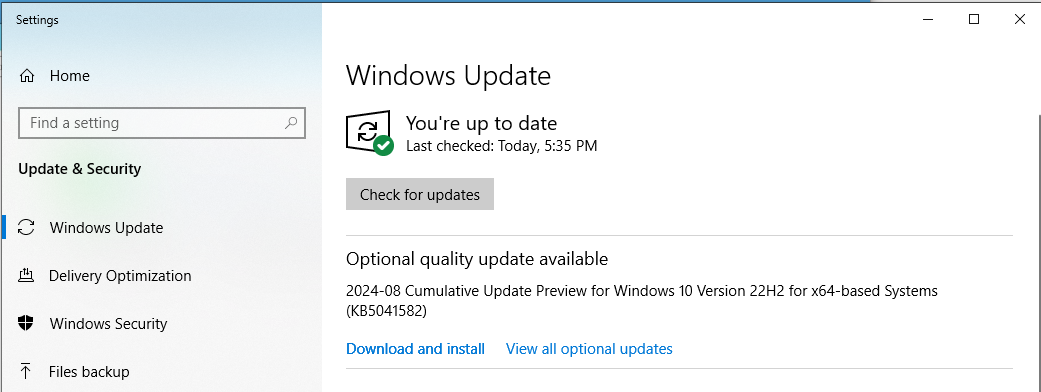
In a Windows environment, the Windows Update is the simplest way to apply security patches as soon as they are released. To enable the windows update:
Settings > Windows Update > Check for updates
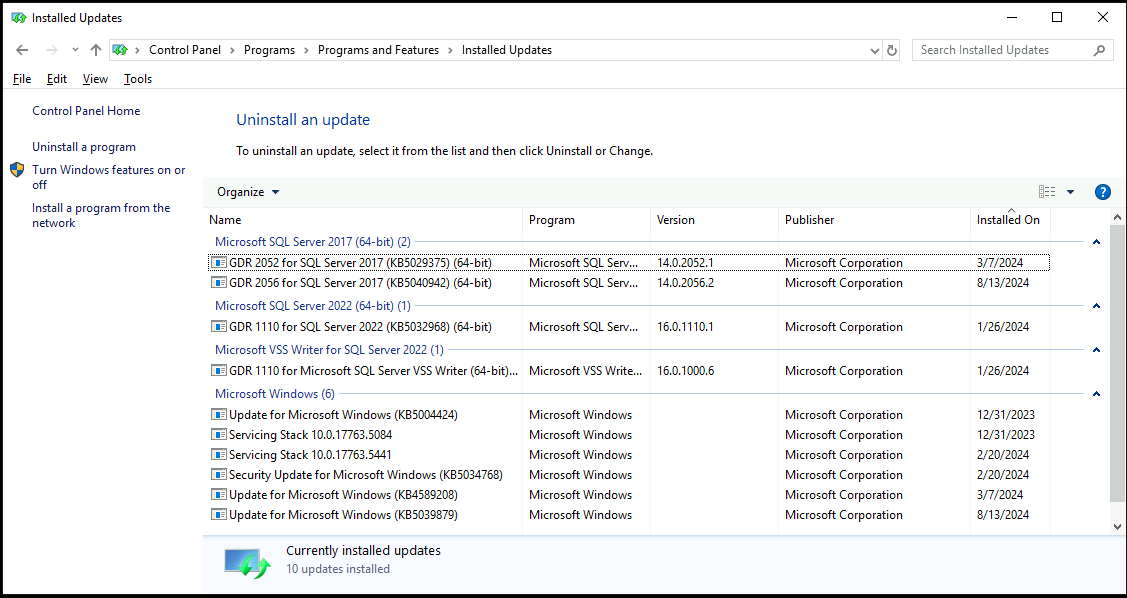
To see all the installed updates:
Control Panel > Programs > Programs and Features > View installed updates
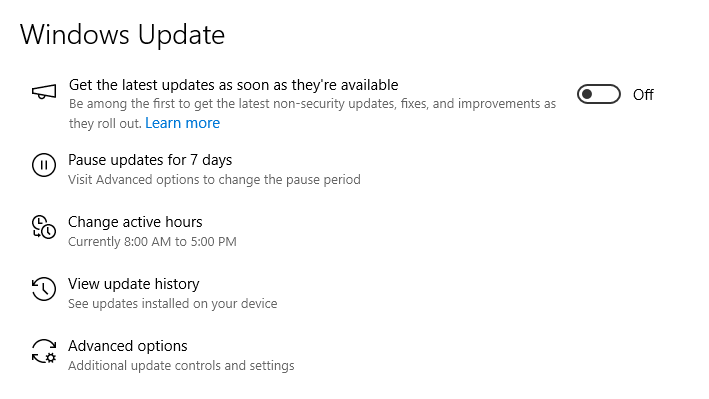
To enable automatic updates, toggle the Get the latest updates as soon as possible:
Linux
Ubuntu/Debian:
## Update package lists
sudo apt update
## Upgrade packages
sudo apt upgrade
## Upgrade the entire system, including kernel and distribution-specific packages
sudo apt full-upgrade
CentOS/RHEL:
## Update package lists and apply all available updates
sudo yum update
## Upgrade specific packages
sudo yum upgrade [package_name]
Fedora:
## Update package lists and apply updates
sudo dnf update
Arch Linux:
## Synchronize package databases and update packages
sudo pacman -Syu
Challenges and Best Practices
Applying patches improves security, but it also comes with challenges.
- Patches can sometimes affect system stability.
- It's important to balance quick patching with reliability.
- Always test patches in a staging or test environment first.
- Don't rely only on vendor trust, verify patches yourself.
- Applying patches on a fixed schedule doesn't guarantee system stability afterward.
Recommendations
- Designate a team to monitor vendor security patches.
- Implement automated system-wide patching for OS and apps.
- Extend patch management to cover cloud resources.
- Prioritize patches as urgent, important, or non-critical.
- Validate critical patches in test environments before deployment.
- Keep detailed patching logs for evaluation and monitoring.
- Define a process for assessing, testing, and applying firmware updates.
- Establish a technical procedure for deploying urgent patches.
- Regularly review non-critical patches for combined deployment.