Data Modelling
Data Models
Data models define how data is structured in a database. Two common models for data warehouses are star schema and snowflake schema. These models help organize data for analysis by separating it into fact tables and dimension tables.
Fact Table
A fact table stores measurements or metrics about business processes.
- Each row represents a transaction.
- Contains numeric values like sales quantity and tax.
- Includes foreign keys linking to dimension tables.
Example: ABC Enterprise, a home office furniture company, tracks sales orders in a fact table:
Sales_Order_Fact table:
| CustomerID | ProductID | DateID | UnitSold | SalesAmount | Tax |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 101 | 501 | 202401 | 2 | 500 | 25 |
| 102 | 305 | 202402 | 1 | 200 | 10 |
| 103 | 701 | 202403 | 3 | 750 | 37.5 |
| 104 | 202 | 202404 | 5 | 1200 | 60 |
| 105 | 608 | 202405 | 4 | 800 | 40 |
Dimension Table
Dimension tables store descriptive attributes related to the fact table.
- Provide details like customer name, location, or product type.
- Help categorize and analyze data.
- Are linked to the fact table through foreign keys.
Example: Customer dimension table:
Product_Dim table:
| ProductID | LotCode | Color | Description | Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 202 | L100 | Black | Office Chair | X1 |
| 305 | L200 | White | Desk Lamp | Y2 |
| 501 | L300 | Gray | Standing Desk | Z3 |
| 608 | L400 | Silver | Monitor | A4 |
| 701 | L500 | Brown | Bookshelf | B5 |
Customer_Dim table:
| CustomerID | Name | AccountNum | LoyaltyID | Country | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 101 | John | ACC1001 | L001 | USA | john@email.com |
| 102 | Lisa | ACC1002 | L002 | UK | lisa@email.com |
| 103 | Alex | ACC1003 | L003 | USA | alex@email.com |
| 104 | Emma | ACC1004 | L004 | Canada | emma@email.com |
| 105 | Ryan | ACC1005 | L005 | Germany | ryan@email.com |
Time_Dim table:
| DateID | Year | Quarter | Month | DayOfWeek |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 202401 | 2024 | Q1 | Jan | Monday |
| 202402 | 2024 | Q1 | Feb | Tuesday |
| 202403 | 2024 | Q1 | Mar | Wednesday |
| 202404 | 2024 | Q2 | Apr | Thursday |
| 202405 | 2024 | Q2 | May | Friday |
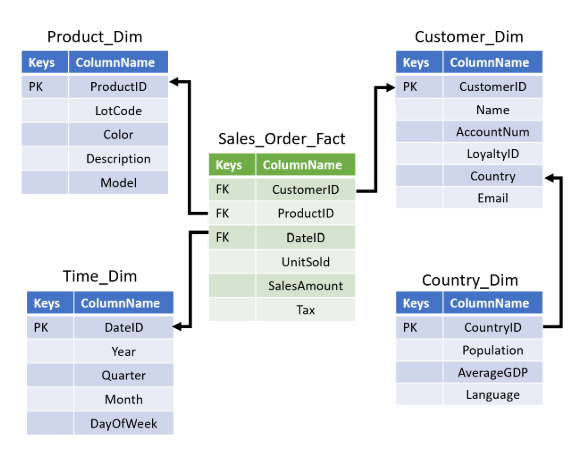
Star Schema
A star schema has a single fact table linked to multiple dimension tables.
- Simple structure, fast queries.
- Easy to understand and use.
This layout makes queries fast and efficient.
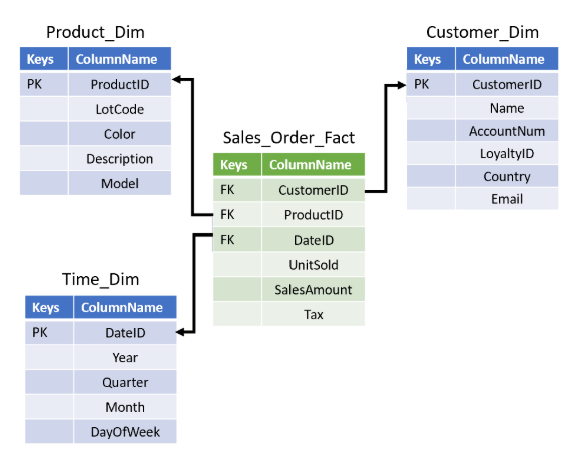
Snowflake Schema
A snowflake schema is an extension of the star schema where some dimensions are further normalized.
- At least one dimension table is split into smaller tables.
- Requires more joins but reduces redundancy.
This structure provides more flexibility but may slow down queries due to extra joins.
Example: Instead of storing customer country in the Customer table, we create a separate Country table.