Adopting DevSecOps
Accelerate Digital Transformation
As a refresher, the different phases of DevOps include:
-
Planning
- Business features are defined
- Backlogs are created and tasks are prioritized
- Impementing Scrum and Kanban
-
Coding
- Implementation of small chunks of software untis
- Automated builds are versioned and stored in repository
-
Testing
- Automation suites are used
- Perform code covergae and dynamic analysis
- Implement techniques such as Test-Driven Development (TDD)
-
Release
- CICD Pipeline is leveraged
- End-to-end testing, making software ready for deployment
-
Deployment
- Utilize tools such as Ansibel, uppet, and Chef for configuration management
-
Operate
- Monitor systems through metrics, alerts, and health checks
Avoid Late Security Checks
Avoiding security checks that are late in the release cycle prevents:
- Slower release cycles and slower throughput
- Higher cost
- Breakdown of Agile and DevOps practices
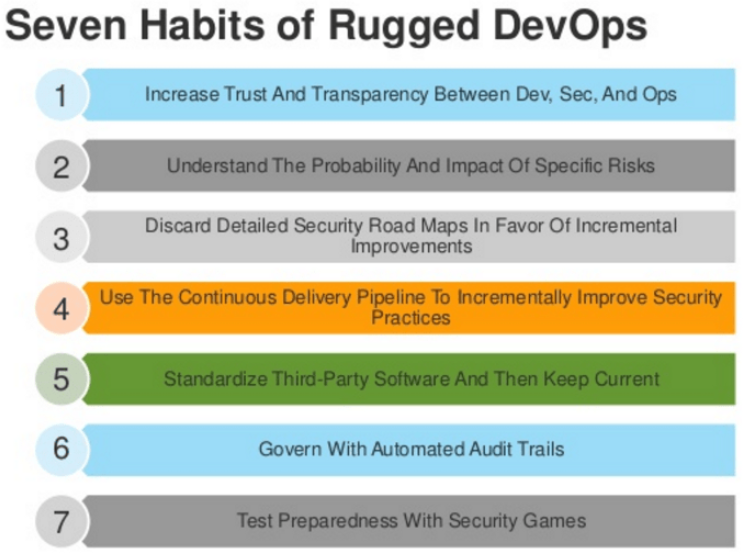
Security threats are constantly evolving and organizations require application with improved response to these threats. As a possible solution, we can follow the "Rugged Manifesto".
Enter the "Rugged Manifesto"
"Rugged" describes software development organizations that have culture of rapidly evolving their ability to create available, survivable, defensible, secure, and resilient software.
- Security as the primary consideraton at every phase
- Makes DevSecOps and DevOps are both critical in an environment
- Adds robust security methods to traditional DevOps practices
- Add increased trust, transparency, and clearer understanding of probable risk
- Adopt security measure into all stages of software design and requirements
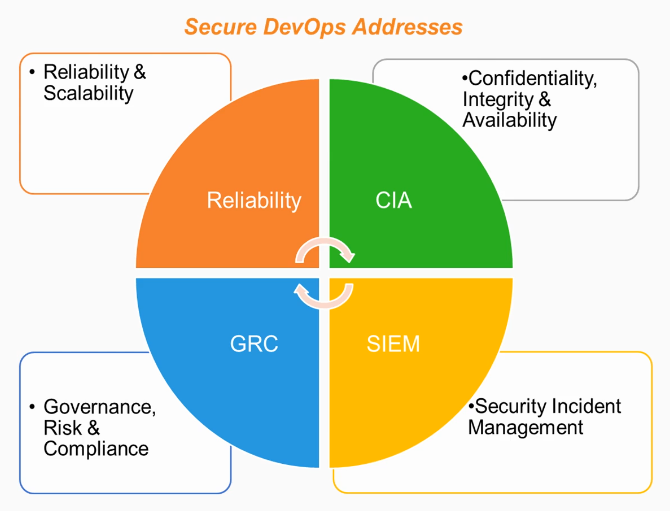
Secure Devops for Application Security
DevSecOps signifies a shift in security as it orchestrates and integrates config management.
Planning:
- Address security at planning stage
- Prepare threat modelling and data flow diagram
Coding:
- Security architecture should be done with code inspector and environment hardening
- Choose security tools and solutions that integrate within the development environment
Testing:
- Interactive applications can help in instrumenting the app from the inside
- Perform other activites such as protocol and input fuzzing, and application vulnrability correlation
Release Phase:
- Further security checks can be done, such as penetration testing
Deployment Phase:
- Harden the system
- Binary is signed and timestamped in the config phase
- Signatures are checked before deploying to the CICD pipeline
- Perform chaos testing to observe how application behaves in unsual circumstances
Operate:
- Check signature of binaries
- Focus on configuration assurance at instantiation by security controls
Monitor:
- Not all vulnerabilities will be identifies, and some may reach production
- Continuous monitoring can check for irregular behavior in production
Business-Driven Strategies
1. Build Security Champions in DevOps
- Promote respect between developers, security, and business.
- Include security experts in DevOps to balance priorities.
- Understand security concerns and learn product vulnerabilities.
2. Embed Security in DevOps Processes
- Align processes for quick delivery.
- Treat features and defects equally.
- Foster collaboration and prioritize incremental improvements.
3. Integrate Security Tools in DevOps
- "Shift-left" to consider security early.
- Use automatic audit trails and security gates.
- Utilize data from security tools and test readiness with security exercises.
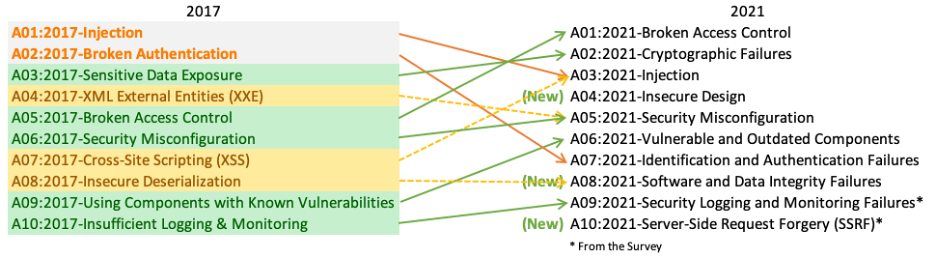
OWASP Security Guidelines
The Open Web Application Security Project® (OWASP) is a nonprofit focused on enhancing software security. It offers resources on security methodologies, tools, and technologies.
The OWASP Top 10 is a widely accepted resource for developers and security professionals. It highlights the most critical security risks facing web applications.