Common Tenets of DevOps
Overview
The community around DevOps have coalesced around a set of generally agreed upon tenets that support the philosophy. Three of the most commonly accepted tenets are:
- Culture
- Automation
- Measurement
The essence of DevOps lies in its philosophy of efficiently developing, deploying, and operating top-quality software.
Break Down the Silos
The term "DevOps" is derived from the fusion of "development" and "operations." Originally, it emerged to dismantle silos, and foster collaboration among engineers to achieve a balance between speed and stability.

DevOps aims to eliminate inefficiencies within the development, deployment, and operations pipeline while emphasizing enhanced quality. Traditional approaches to developing, deploying, and operating software often struggle to adapt to the continual changes inherent in modern software systems.
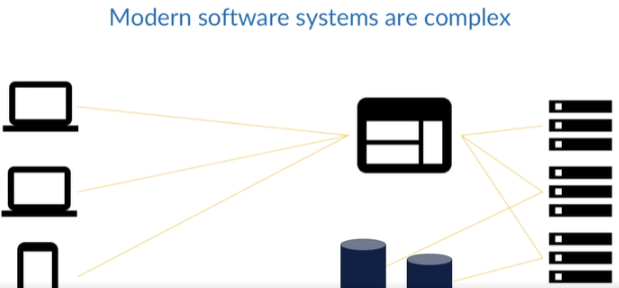
Complex Systems
The complexity of systems, with numerous interacting components, increases the likelihood of issues arising when introducing changes, whether in code, configuration, or infrastructure.
Remain Stable or Go Fast
The goals of developers and operations often conflict to some extent. Developers focus on making changes and adding features.
- It's the developer's job to implement changes
- But every change can cause problems like bugs or outages.
On the other hand, operations focus on keeping systems stable.
- They manage deploying new code to production.
- Each deployment can disrupt system stability.
In the past, teams thought they had to choose between moving fast or staying stable, but it’s possible to do both.
For example, companies like Etsy are able to deploy new code into production dozens of times every day, while keeping their site's availability high.
Automation and Measurement
DevOps improves the development, deployment, and operations pipeline by encouraging teamwork and automating tasks that add value.
- Automation reduces manual errors and speeds up processes
- Collaboration breaks down barriers between teams for smoother workflows
DevOps also emphasizes collecting and measuring useful data to guide improvements.
- Tracking metrics helps identify bottlenecks and issues
- Data-driven decisions improve efficiency and quality
- Continuous measurement supports ongoing process refinement
User Expectations and Quality
Users expect software to work smoothly without interruptions, even when many people use it at once. For example, can your system handle 10 million new users without manual fixes or server issues?
Quality matters too. If customers lose data after an update, how quickly can your team fix the problem? How did a serious bug get released, and how long does it take to build and launch new features: days, weeks, or months?
DevOps helps by improving how development, deployment, and operations teams work together. It focuses on finding and fixing issues quickly while boosting quality.
- Keeps software stable during heavy use
- Speeds up fixing bugs and releasing updates
- Investigates why problems happen in production
- Reduces time needed to deliver new features
- Improves efficiency and quality through teamwork
Not any one thing
DevOps is a mindset that guides how to build, deploy, and manage modern software efficiently.
- It is not a product or tool
- It is not a brand or a specific job title
- It is not a single team or role
- It is a set of principles and practices
Remember, DevOps exists to solve the challenge of managing complex software systems effectively. This focus is key to understanding its true purpose.
Culture
Culture means the shared beliefs, values, and behaviors of a group or company. It is deep-rooted and hard to change. DevOps requires cultural shifts that focus on automation and measurement.
DevOps Cultural Values
- Automation and measurement are key DevOps values
- Lack of automation adds extra work for engineers
- Poor measurement limits data for smart decisions
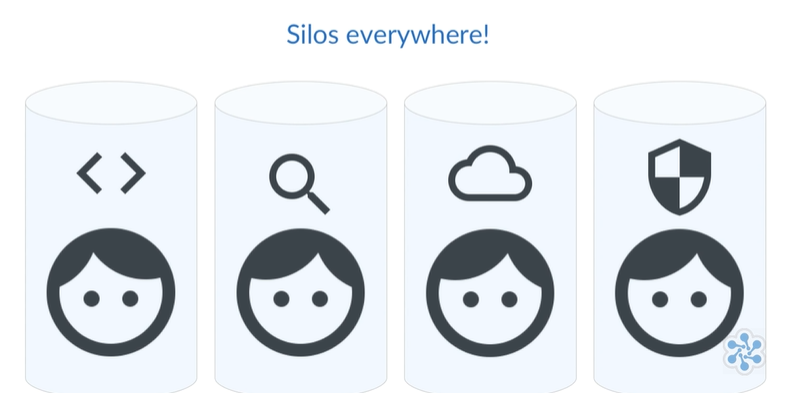
Silos in Traditional Companies
- Teams like development, QA, security, and operations often work separately
- These silos can have conflicting goals, causing delays and problems
Challenges of Silos
- Conflicting goals reduce teamwork and slow progress
- For example, developers want fast feature releases, while QA blocks bugs
Shift to Collaboration
- DevOps pushes breaking silos and encouraging teamwork
- This change can be uncomfortable as roles become less fixed
- Shared responsibility improves ongoing cooperation
Cross-Functional Teams
- Teams include developers, QA, security, and operations working together
- They handle the full product lifecycle to boost quality and stability
Beware of DevOps Teams
- Creating a separate "DevOps team" can form a new silo
- This limits collaboration and frustrates engineers
In silo models, blame often happens when problems arise, creating friction. DevOps promotes a blameless culture where mistakes are owned and used for learning. This builds trust, reduces negativity, and supports continuous improvement.
Focusing on learning instead of blame, DevOps culture values transparency, teamwork, and breaking down barriers. Changing culture is hard but essential for real DevOps success. Without it, DevOps is just a buzzword that frustrates engineers.
Automation
The definition of automation involves operating or controlling a process with minimal human intervention.
- Ensures tasks are done consistently and without mistakes
- Reduces problems caused by distractions or errors
- Helps scale work, keep it predictable, and improve quality
Like following a complex recipe, human errors can happen when done manually. Automation helps by taking over repetitive and detailed tasks, reducing mistakes and saving time.
Automation in the Pipeline
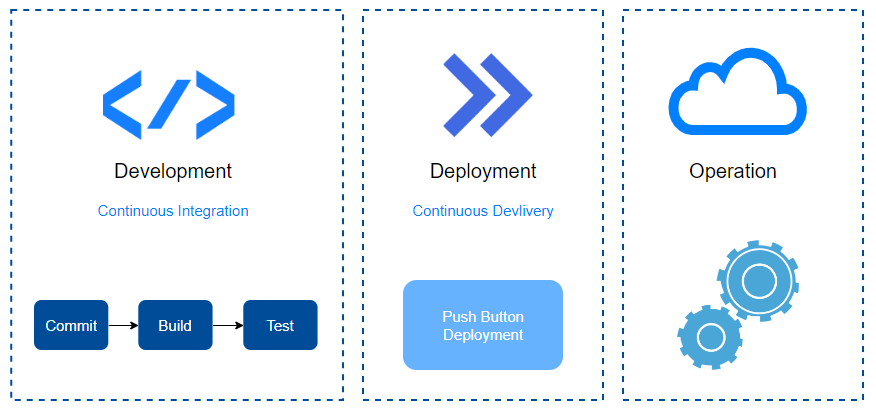
Automation plays a big role in software development and delivery.
-
Continuous Integration (CI):
- Automatically builds and tests code after each change
- Keeps code ready for production
-
Continuous Delivery (CD):
- Enables easy, quick software releases
- Supports push-button deployments
-
Infrastructure as Code (IaC):
- Lets engineers set up infrastructure with code
- Ensures consistent, scalable setups
- Uses tools like Chef, Ansible, Puppet, SaltStack
Role of Automation in DevOps
Automation solves pipeline bottlenecks and improves workflow.
- Boosts efficiency and quality
- Core part of DevOps culture
- Helps companies customize their processes
- Speeds up and stabilizes software delivery
It supports faster and more reliable software development and deployment.
Operations also will want to automate things like log aggregation and log management.
- Centralized logs make analysis easier
- Automated monitoring gathers useful data for decisions
Automation's Impact on Efficiency
Automation creates a steady, reliable process that saves time and keeps quality high.
- Not a full list, but a good start for pipeline automation
- Makes workflows consistent and predictable
- Maintains stability and quality through the pipeline
Getting Started with Automation
Start small and build up.
- Use tools like Jenkins to automate code builds
- Look for simple improvements in your current process
Addressing Automation Concerns
Starting automation can feel overwhelming, but it’s best to begin with simple, manageable tasks.
- Focus on easy tasks like compiling code or installing dependencies
- The key is to begin, not to wait for perfection
Key Questions Answered
Automation reduces manual work, making pipelines faster and more scalable.
- Speeds up development and deployment
- Helps deliver better-quality software consistently
Metrics
Metrics help measure how well DevOps practices improve the pipeline’s efficiency and software quality.
- Aims for fast, reliable development, deployment, and operation
- Metrics are needed to track efficiency and quality progress
To learn more about metrics, please see Measuring Metrics