Starter Notes
Overview
From the official Hashicorp documentation:
Terraform is an infrastructure as code (IaC) tool that allows you to build, change, and version infrastructure safely and efficiently. This includes both low-level components like compute instances, storage, and networking, as well as high-level components like DNS entries and SaaS features.
Terraform can be used to:
- Provision on-prem resources
- Provision multi-cloud deployments
- Has open-source but also has Terraform Cloud
- Codify infra into machine-readable executable documentation
- Repeatable infra builds
- Manage and maintain infra configuration drift
- Version-controll through git
- Integrate with CICD systems
Install Terraform
To use Terraform, it needs to be installed on your machine.
See: Install Terraform.
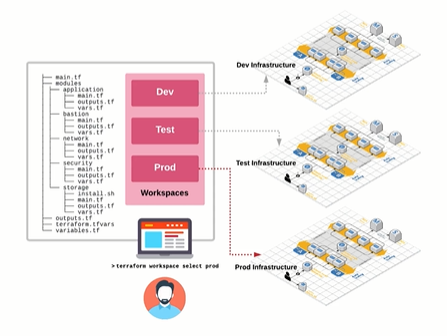
Workspaces
We can utilize workspaces to manage separate environments using the same set of configuration files.
terraform workspace
To create a new workspace,
terraform workpace new <name>
To select a workspace,
terraform workspace select <name>
Root Module
This is a directory on the local filesystem containing all the configuration files and code files. This is typically consists of three files:
main.tfvariables.tfoutputs.tfprovider.tf
This root directory may also contain:
terraform.stateterraform.state.backup
Providers
Terraform uses providers to interact with various cloud platforms and services. Some popular providers include:
- AWS
- Azure
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
- Kubernetes
For more information, please see Providers
Using Terraform with Git
Terraform configurations are often stored in Git for version control. Some files should never be committed because they contain local state or downloaded dependencies.
These files can be added to your .gitignore to prevent accidental commits. Sample .gitignore:
.terraform*
.terraform.tfstate*
*.tfstate.*
*.tfstate
.terraform.lock.hcl
linux_386
linux_amd64
Authentication
Before writing Terraform code, you need to make sure authentication with API keys is set up. Terraform reads credentials in the order specified below:
- API keys can be hardcoded in
main.tf(not recommended) - Environment variables to store keys securely
shared_credentials_filefor local credentials
Terraform CLI
Here is a summarized cheatsheet.

Provisioning Workflow
The typical workflow when using Terraform involves the following commands:
terraform initterraform validateterraform planterraform applyterraform destroy
Terraform HCL Language
Terraform uses the HashiCorp Configuration Language (HCL) to define and manage infrastructure.
- Defines the basic structure and grammar of Terraform code
- JSON syntax is available for systems that don’t use HCL directly
- Style conventions ensure consistent formatting across files
You can automatically apply formatting standards using terraform fmt.
Comments can be added using the # symbol:
# This is a comment
For multi-line comments, use /* */:
/* This is
a comment
spanning multiple lines
*/
Strings can be defined in different ways depending on their length and purpose:
"This is a single-line string"
For multi-line strings, use the EOF marker:
<<EOF
This message
is composed of
multiple lines.
EOF
For more details, refer to the official Terraform syntax documentation.