Reducing Costs
This is not an exhaustive documentation of all the existing Azure Services. These are summarized notes for the Azure Certifications.
To see the complete documentation, please go to: Azure documentation
Overview
Understanding the key factors that influence Azure costs is crucial for effective budgeting and cost management. Additionally, adopting cost-saving strategies can optimize expenses. Here are some significant factors and strategies related to Azure costs:
1. Region Selection
-
The region where Azure resources are hosted impacts costs.
-
Some regions may have higher costs than others for the same services.
-
Consider cost differences when choosing a region, especially if data residency or latency is not a primary concern.
2. Data Transfer Costs
-
Data transfer into Azure resources (ingress) is typically free.
-
Data transfer out of Azure resources (egress) may incur costs, especially if transferred across regions or outside the Azure network.
-
Minimize egress costs by keeping resources within the same region unless specific reasons justify cross-region deployment.

3. Resource Groups and Regions
-
Resource group location is irrelevant for costs; the contained resources incur charges.
-
Placing resources in different regions within a resource group does not cause additional charges.
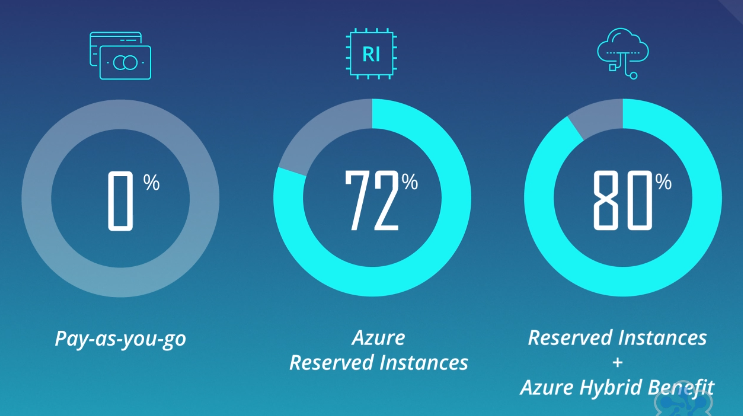
4. Reserved Capacity
-
Reserved Instances involve committing to a long-term contract (1 or 3 years) for specific Azure services.
-
Offers potential cost savings (up to 72%) compared to pay-as-you-go pricing.
-
Available for select services, and the VM region is chosen during reservation.
-
Exchanging reservations is possible, but a new reservation must be made.

5. Azure Hybrid Benefit
-
Utilize existing Windows Server or SQL Server licenses covered by Microsoft Software Assurance on Azure.
-
Applicable to Azure VMs, Azure SQL Database, or Azure SQL Managed Instance.
-
Helps reduce costs by leveraging existing licenses.
6. Azure Spot Virtual Machines
-
Utilizing unused compute capacity, saves virtual machine costs.
-
Significant cost savings (up to 90%) but may be preempted with short notice (30 seconds).
-
Suitable for non-critical workloads like batch processing, testing, or rendering.
-
Ideal for workloads that can tolerate interruptions and don't require completion within a specific time frame.
7. Right-Sizing Virtual Machines
-
Resize underutilized VMs to a more cost-effective option.
-
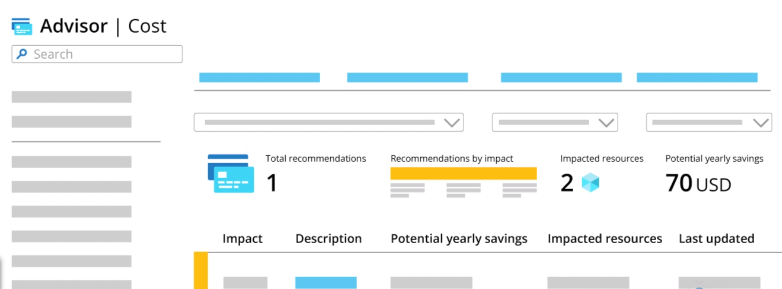
Azure Advisor provides insights into underutilized VMs and potential cost savings.
-
Consider downsizing or shutting down VMs based on usage patterns.
8. VM Deallocation and Resource Cleanup
-
Stopped (deallocated) VMs may still incur charges for associated resources like data disks and static public IP addresses.
-
Deleting a VM might not remove all associated resources; clean up data disks and public IP addresses separately.
-
Azure Advisor assists in identifying unused resources, including public IP addresses.