VPN
VPN Gateway
A VPN Gateway is a specialized virtual network gateway used for encrypted network traffic over the public internet, connecting:
- Azure virtual network to on-premises network
- Azure virtual network to another Azure virtual network
Note that oly one VPN gateway can be defined per virtual network, but it can support multiple connections.
How it works
- Azure deploys at least two hidden VMs in a specified gateway subnet.
- Hidden VMs contain routing tables and gateway services.
- VMs are not visible or configurable by users.
- Deployment of VPN gateways can take up to 45 minutes to complete.
Gateway Types
- "VPN" type for typical VPN connections.
- "ExpressRoute" for configuring an ExpressRoute connection.
After Deployment
- Create an IPSec or IKE VPN tunnel between the newly deployed vNet gateway and other gateways.
- vNet-to-vNet connection to another VPN gateway in Azure.
- Site-to-site connection to an on-premises VPN device.
- Point-to-site connection for remote location access.
For more information, please see Azure VPN Gateway Documentation
Point-to-Site VPNs
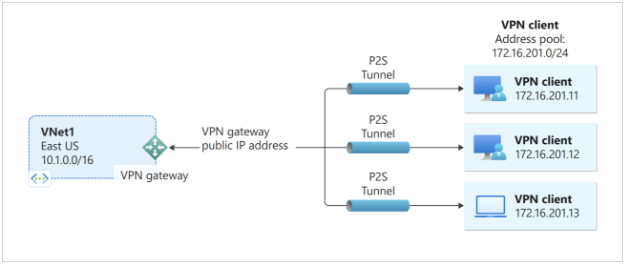
A Point-to-Site (P2S) VPN gateway connection securely links a single client computer to an Azure virtual network, often used by remote workers.
Protocols
-
OpenVPN Protocol
- SSL/TLS-based, traverses firewalls through TCP port 443 outbound.
- Compatible with Android, Windows, Linux, and Mac OSX.
-
Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol (SSTP)
- Proprietary VPN protocol leveraging TLS.
- Penetrates firewalls, but supports only Windows devices.
-
IKEv2 VPN
- Standards-based IPSec VPN solution.
- Suitable for connecting from Mac OSX devices.
Authentication Methods
-
Azure Certificate Authentication
- Requires a client certificate on the device, validated by the VPN gateway during the connection handshake.
-
Azure AD Authentication
- Users connect using Azure AD credentials, supported only for OpenVPN protocol.
- Windows 10 necessitates the Azure VPN Client for compatibility.
-
Traditional AD Domain Authentication
- Users in a traditional AD domain are authenticated via a RADIUS server integrated with the domain controller.
Gateway SKUs Supporting P2S VPNs
For more information, please see official documentation.
| Gateway SKU | P2S VPN Support |
|---|---|
| Standard | Yes |
| HighPerformance | Yes |
| VpnGw1 | Yes |
| VpnGw2 | Yes |
| VpnGw3 | Yes |
Site-to-Site VPNs
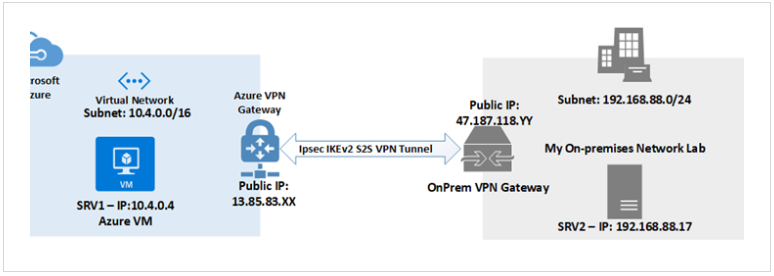
Site-to-Site VPN gateways bridge on-premises networks to Azure virtual networks, establishing a secure IPSec or IKE VPN tunnel.
Creating the Connection
-
Azure Virtual Network Setup
- Create the Azure virtual network that will connect to your on-prem network.
-
Gateway Subnet and VPN Gateway Creation
- Establish a gateway subnet within your virtual network.
- Create the VPN gateway (may take up to 45 minutes).
-
Local Network Gateway Setup
- Set up the local network gateway, symbolizing the on-premises endpoint.
-
Configuration of On-Prem VPN Device
- Customize the on-premises VPN device configuration.
-
Azure VPN Connection Deployment
- Deploy the VPN connection in Azure.
-
Verification of Connection
- Verify the connection to ensure a seamless and secure link.
Routing Options for VPNs
Two types of routing:
-
Policy-based
- Route-based is more robust and the only supported option for point-to-site connections.
-
Route-based
- Does not support point-to-site connections from the same VPN Gateway.
- Only one VPN Gateway is allowed per virtual network; creating another virtual network may be necessary.
For a direct connection without internet flow and more bandwidth, use Azure ExpressRoute.