MPLS
Overview
MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching) is a high-performance method for directing data through a network. Instead of relying on traditional IP routing, MPLS uses labels to create predetermined paths for data packets, improving speed and efficiency.
- Efficiently routes traffic by avoiding complex lookups at every router.
- Used widely in service provider networks for delivering voice, video, etc.
- Supports Quality of Service (QoS); allows prioritization of certain traffic.
MPLS uses fixed paths determined by the first router in the path. The first MPLS router that encounters a packet attaches a label to the packet corresponding to a fixed path to the final destination. Subsequent routers read the label and forward the packet without performing additional lookups.
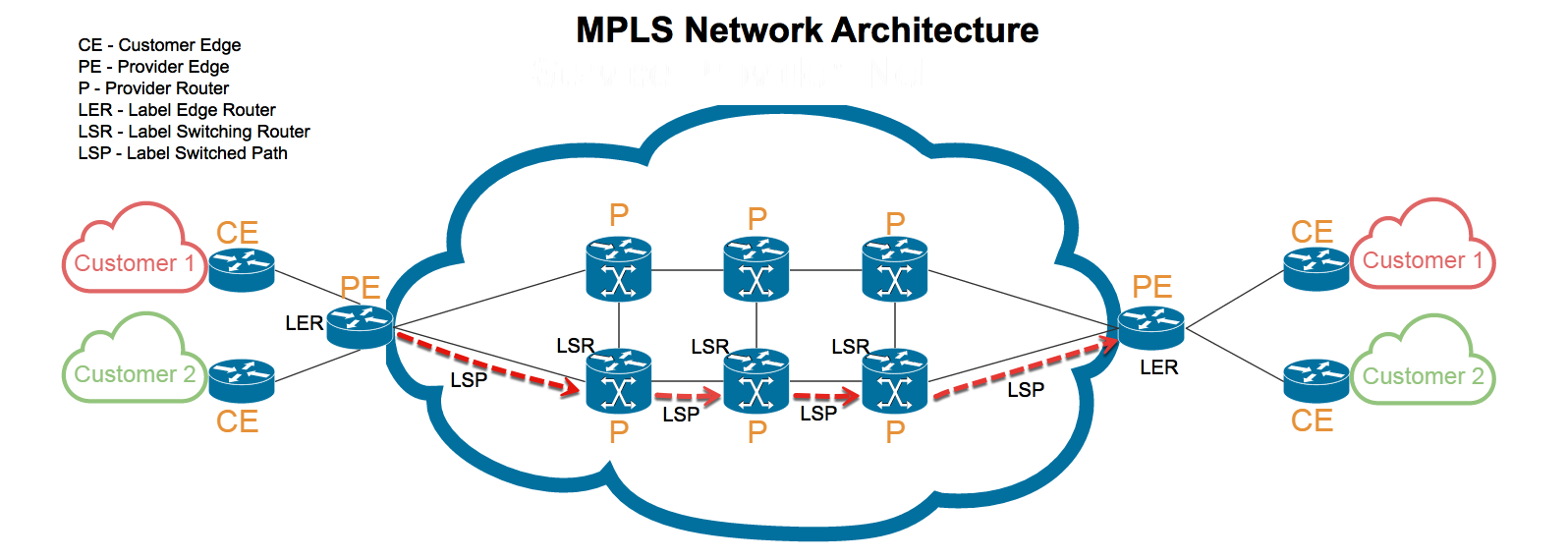
MPLS Tunnels
MPLS can be viewed as creating virtual tunnels between points in the network, using labels to guide traffic.
-
Label Edge Router (LER)
- The first router in the MPLS path
- Responsible for determining the path and attaching a label to the packet
-
Label Switching Router (LSR)
- Routers along the MPLS path that simply read the label
- Then forwards the packet to the next LSR
-
Egress Node
- The final destination router
- Removes the label once the packet has reached its destination.
The MPLS tunnel between the LER and the Egress Node may pass through several LSRs. These intermediate routers do not need to perform complex lookups, as they only need to read the label and forward the packet to the next router, ensuring a faster and more efficient data flow.
MPLS Routing Protocols
MPLS relies on specific routing protocols to manage label distribution and ensure efficient data flow. There are two primary MPLS routing protocols:
-
Label Distribution Protocol (LDP)
- Responsible for distributing labels between routers.
- Ensures routers along the path have the correct labels for packet forwarding.
- Commonly used for standard deployments where traffic engineering is not required.
-
Reservation Resource Protocol - Traffic Engineering (RSVP-TE)
- Advanced traffic engineering, reservES resources along the MPLS path.
- Ensures specific paths are available for critical traffic
- Optimizes bandwidth usage
- Used in scenarios where Quality of Service (QoS) and traffic prioritization are important.