Telephony
Overview
Telephony refers to the technology that allows for voice communication over distances. It includes traditional landline systems, mobile networks, and modern digital methods like VoIP.
- Traditional telephony used circuit-switched networks/
- Evolved from analog to digital, now including mobile networks.
- Features include voicemail, conferencing, and call forwarding.
- Integration with digital and mobile systems.
VOIP
VOIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) enables voice communication over data networks, replacing traditional phone lines by leveraging internet protocols.
- Carries voice communication over data networks
- Converts voice from analog to digital form
- Transmits signals using the Internet Protocol
VOIP Devices
VoIP devices enable voice communication over IP networks, replacing traditional telephone hardware.
-
VoIP phones
- Look similar to traditional phones but connect directly to data networks.
- Convert voice into data packets for transmission over IP.
-
Softphones
-
Software-based solutions that enable VoIP calls on computers or mobile devices.

-
-
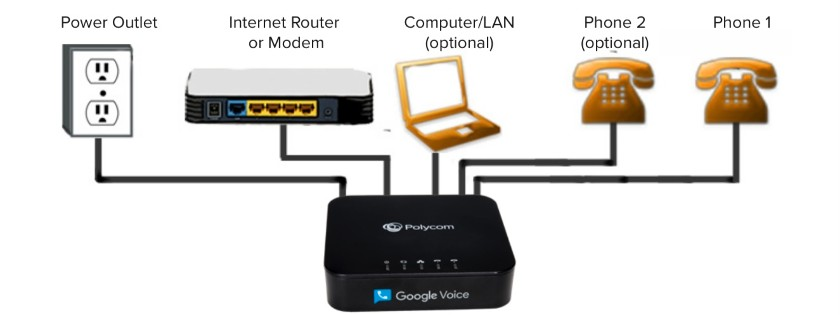
Analog Telephone Adapters (ATAs)
-
Allow traditional analog phones to connect to VoIP networks.
-
VOIP Security
Ensuring the security of VoIP communications is essential to preventing eavesdropping and unauthorized access.
-
Encryption
- Protects VoIP traffic by scrambling the data to prevent unauthorized access.
- Can impact voice quality due to increased processing requirements.
-
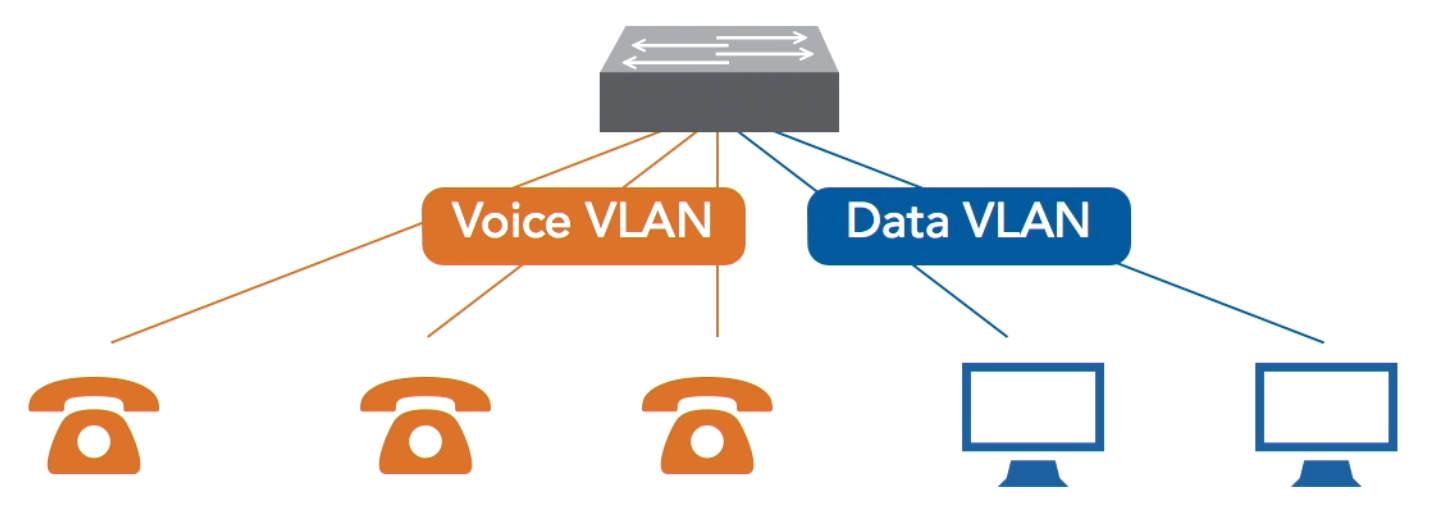
VLAN segmentation
- Separates VoIP traffic from other network traffic using Virtual LANs (VLANs).
- Helps protect voice communication and improves network performance.
-
Firewalls and intrusion detection
- Firewalls block unauthorized access to the VoIP network.
- Intrusion detection systems (IDS) monitor for suspicious activity and security threats.
How VoiP VLAN Segmentation looks like: