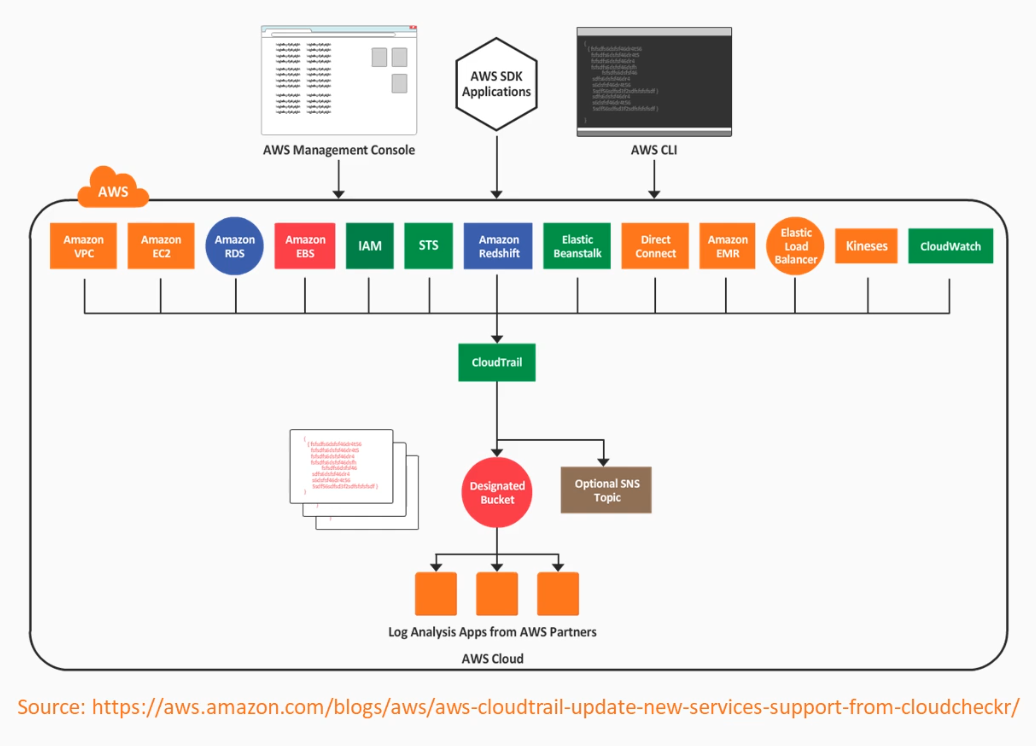
CloudTrail
This is not an exhaustive documentation of all the existing AWS Services. These are summarized notes that I used for the AWS Certifications.
To see the complete documentation, please go to: AWS documentation
Overview
CloudTrail automatically records user activity and deliver those logs for you.
- Enable auditing, incident investigation, intrusion detection, and compliance.
- Almost all AWS services are supported, except AWS Sumerian.
- Can be enabled for the entire account.
- Aggregation is possible across regions and accounts.
- Usual S3 functionalities are possible:
- Notifications
- Server Side Encryption (SSE)
- Bucket Policies
- Lifecycle
Who did what and when
- Records metadata around API calls
- Identifying the caller (user and source IP)
- Date and time of events
- Request/response data
Log File Integrity
We can verify that log files have remain unchanged since CloudTrail delivered them to the S3 bucket.
- Log file validation can be configured during the Trail creation.
- A hash value is created for each log file.
- Log files can be shipped with a digest file.
- Digest files contain details of all logs delivered within the last hour.
- Digest files can be used to validate the integrity of log file.
- Digest fiels are stored in the same bucket as log files.
- These digests are signed by private key of a public and private keypair.
Note that verification of the log file integrity can only be achieved via programmatic access and not through the console. This can be done through AWS CLI:
aws cloudtrail validate-logs --trail-arn <trailARN> --START-TIME <start-time>
We can also add additional parameters:
aws cloudtrail validate-logs --trail-arn <trailARN> --START-TIME <start-time> \
--end-time <end-time> \
--s3-bucket <bucket-name> \
--s3-prefix <prefix> \
--verbose
Digest file folder structure in the S3 bucket:
S3-bucket-name/AWSLogs/accounID/CloudTrail-Digest/Region/digest-end-year/digest-end-month/digest-end-date/
CloudTrail Process Flow
- Create a Trail.
- Specify an S3 bucket for log storage.
- (Optional) Encrypt log files with KMS.
- (Optional) Notifications of new log files via SNS.
- (Optional) Enable log file validation.
- Once trail is created, we can add configuration change.
- (Optional) Deliver CloudTrail logs to CloudWatch for monitoring.
- (Optional) Configure Event Selector for Management/Data
- (Optional) Add any required tags.
- Configuration is complete.
Once data is captured, we can find particular events quickly through the use of API Activity Filters.
Lifecycle of an API call in CloudTrail
- IAM user or service calls an API.
- CloudTrails checks if the API call matches any configured trail.
- If a match is found, API call is recorded as an event on the log file.
- Event on log file can be delivered to an S3 bucket or CloudWatch Logs.
- In the 3 bucket, log files are sotred and encrypted by default by SS3 unless KMS is configured.
- If lifecycle rules are configured, log files may be stored on a different storage class or AWS Glacier.
CloudTrail Permissions
Currently there are two AWS Managed policies for CloudTrail:
AWSCloudTrailFullAccessAWSCloudTrailReadOnlyAccess
Custom permissions can be created by creating a new IAM policy and applying some of the permissions instead fo providing full access to CloudTrail.
KMS adds another layer of ecnryption to Log files, in addition to the default encryption that uses SS3-S3 encryption. If the logs in the S3 bucket have been encrypted using KMS, specific permissions are needed to decrypt the logs:
- Decrypt permissions must be given to the CMK policy
- S3 read permissions
Note that the KMS key and bucket needs to be in the same region.
CloudTrail Logs
- Logs all API Calls as "event".
- Logs can be delivered to an S3 bucket.
- Requests can be initiated from:
- Software Development Kits (SDKs)
- AWS CLI
- AWS Management Console
- Another AWS service
- New log files are created every 5 mins.
- Log files can be stored for as long as required.
- Log files can also be delivered to CloudWatch Logs for metric monitoring and alerting via SNS.
CloudTrail Trails
Without a Trail, AWS CloudTrail is unable to capture API calls.
- Trails hold the config information for capturing API calls.
- Can be created through the AWS Management console.
CloudTrail Log Files
Log Files are written in JSON format and new log files are created every 5 mins.
- Everytime a new event is captured, it is recorded to the log file.
- A new event is written for each API call.
- Logs are delivered approximately after API was initiated.
- Log files are held in CloudTrail for processing and then delivered to the S3 bucket.
Log file naming convention:
AccountID_CloudTrail_RegionName_YYYYMMDDTHHmmZ_UniqueString.FilenameFormat
Notes:
- The
THHmmZis the time and theZmeans the time is in UTC. - The
UniqueStringis a random 16-digit alphanumeric character as identifier. - Default format is json.gz.
As for the S3 bucket where the log files are stored, it also follows an S3 Bucket structure:
BucketName/prefix/AWSLogs/AccountID/CloudTrail/RegionName/YYYY/MM/DD
Log Aggregation to a Single Account
Logs from multiple accounts can be aggregated to a single S3 bucket in one of the accounts.
-
Configure a new Trail in your primary AWS account.
-
Apply permissions to S3 bucket allowing cross-account access.
-
Edit the resource attribute of bucket policy and add the accounts that need access to the bucket.
"Resource": {
"arn:aws:s3:::bucket-name/[optional]logFilePrefix/AWSLogs/111111111111",
"arn:aws:s3:::bucket-name/[optional]logFilePrefix/AWSLogs/222222222222",
"arn:aws:s3:::bucket-name/[optional]logFilePrefix/AWSLogs/333333333333"
} -
Create a new trail in the secondary AWS account and use a bucket from a different account.
-
Once trail is created, logs will now be delivered to the same S3 bucket in your primary account.
Accessing Cross-Account Log Files
For users/administrators in the secondary accounts to access the log files that are aggregated to the S3 bucket in the primary account, we need to configure a few elements in IAM:
- In the primary account. create IAM roles for each of the AWS account.
- Assign access policy to each Role that allows only a specific Account access.
- Users in the requesting account will need to assume one of these Roles for their corresponding AWS account log files.
Monitoring
Common monitoring use-cases:
- Starting, stopping, rebooting, and terminating EC2 instances.
- Changes to security policies within IAM and S3.
- Failed login attempts to the Management Console.
- API calls that result in failed authorization.
CloudTrail + CloudWatch Process:
- Log file sent to S3 and CloudWatch log group (if configured).
- CloudTrail assumes Role with permission to run two CloudWatch APIs:
- CreateLogStream
- PutLogEvents
Default IAM role created by cloudtrail:
CloudTrail_CloudWatchLogs_Rule
CloudWatch Configuration:
- CloudWatch Log Events have a size limitation of 256KB.
- Metric Filters can be added to allow search of the logs.
- Each metric filter requires customizable Filter pattern.
- Filter patters determines what data is monitored by CloudWatch.
Similarities with other AWS services
- CloudTrail, Config, and VPC flow logs are AWS managed services.
- All can be delivered to an S3 bucket.
- Their differences:
- AWS CloudTrail - User activity and API calls
- AWS Config - Configuration of your environment
- AWS VPC Flow Logs - Network traffic in VPCs