Restrict Network Access
Network-wide Security
We can apply network-wide security using external appliances like Cisco, Fortinet, etc.
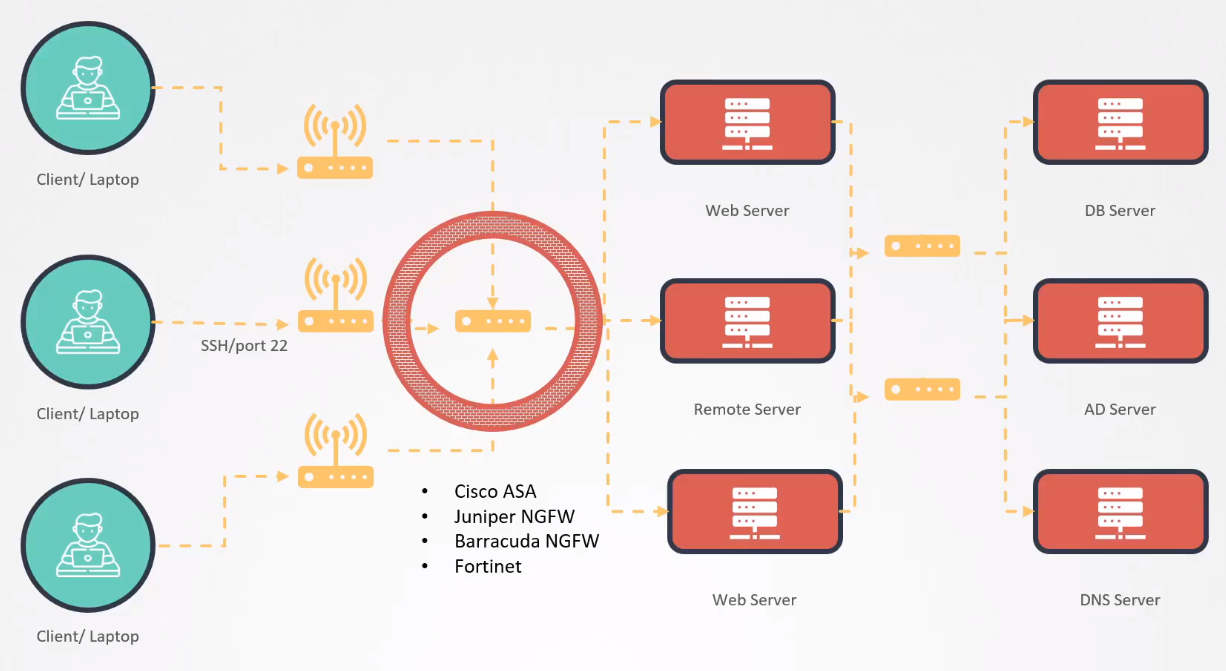
Server-Level Security
In addition to network security, server-level security can be enforced using tools like:
iptablesufw
Uncomplicated Firewall (UFW)
UFW is a simple command-line interface for managing iptables, Linux's default firewall tool.
- Integrates with system applications.
- Supports logging to monitor and detect firewall activity.
- Default
DENY ALLfor incoming connections unless explicitly allowed.
Basic UFW Commands
-
Enable UFW:
sudo ufw enable -
Disable UFW:
sudo ufw disable -
Check Status:
sudo ufw status -
Allow Traffic to a Specific Port:
sudo ufw allow 22/tcp # Allow SSH traffic -
Deny Traffic to a Specific Port:
sudo ufw deny 80/tcp # Deny HTTP traffic -
Allow Traffic from Specific IP Address:
sudo ufw allow from 192.168.1.2 -
Delete a Rule:
sudo ufw delete allow 80/tcp
Usage Examples
-
Allow SSH and deny everything else:
sudo ufw default deny incoming
sudo ufw allow ssh -
Allow HTTP and HTTPS traffic:
sudo ufw allow 80/tcp
sudo ufw allow 443/tcp -
Enable UFW logging:
sudo ufw logging on
Installing UFW
Installing and setting up UFW is simple:
-
1. Check UFW Availability
UFW is typically pre-installed on Debian-based systems. Check if it's already installed:
sudo ufw statusIf UFW is not installed, proceed to the next step.
-
2. Install UFW
Install UFW using your package manager. For Ubuntu/Debian, use:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install ufw -
3. Enable UFW
After installation, enable UFW:
sudo ufw enableConfirm the action, as enabling UFW may interrupt existing SSH connections.
-
4. Check UFW Status
Verify if UFW is active:
sudo ufw statusYou should see that the firewall is active.
-
5. Basic UFW Configuration
Set basic rules, like allowing SSH and HTTP:
sudo ufw allow 22/tcp # Allow SSH
sudo ufw allow 80/tcp # Allow HTTP -
6. Enable Logging (Optional)
To enable logging, use:
sudo ufw logging on -
7. Adjust Default Policies (Optional)
Set default policies for incoming and outgoing traffic. For example, to deny incoming traffic:
sudo ufw default deny incoming
sudo ufw default allow outgoing -
8. Verify UFW Configuration
Check your current rules:
sudo ufw status -
9. Restart Services (If Needed)
Restart affected services after significant changes.
-
10. Additional Configuration
Continue to configure UFW based on your needs, such as adding rules for other services or IP addresses.
Sample UFW Rules
-
Default rules:
sudo ufw default allow outgoing
sudo ufw default deny incoming -
Allow inbound connections to port 22 from a specific source IP 10.1.2.3.
ufw allow fromn 10.1.2.3 to any port 22 proto tcp -
Allow inbound connections to port 80 from a specific source CIDR 10.1.2.3/24.
ufw allow fromn 10.1.2.3/24 to any port 80 proto tcp -
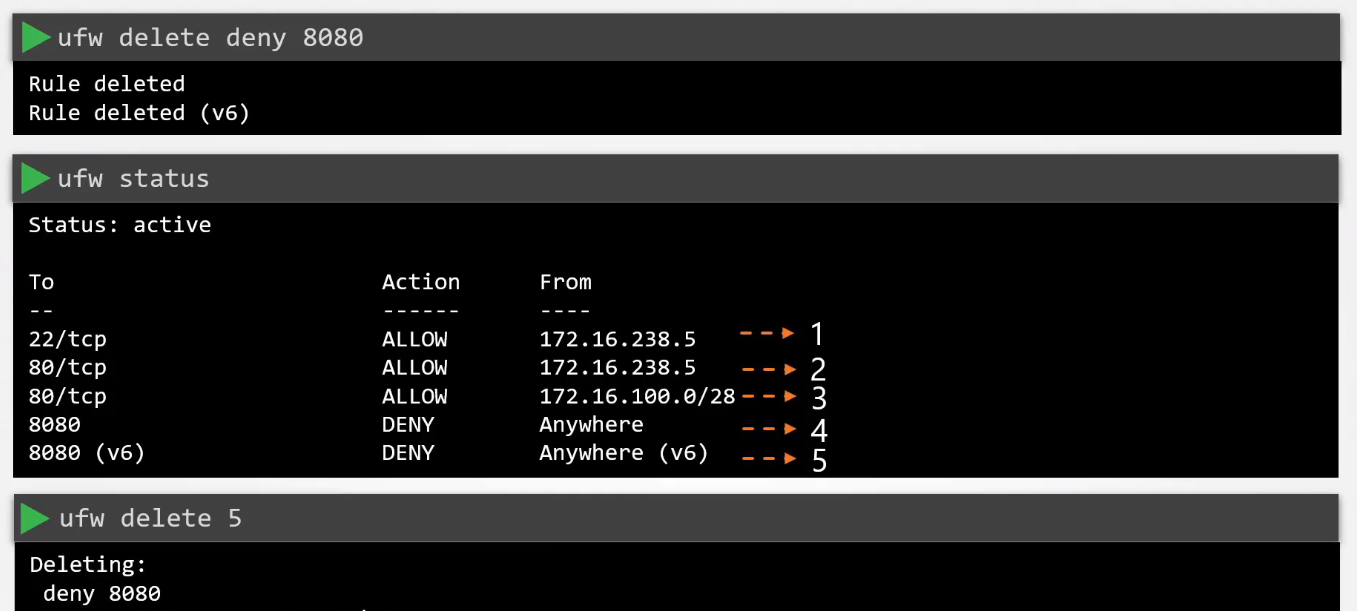
Deny port 8080.
ufw deny 8080
Deleting UFW Rules
We can use the delete command to remove a rule, or we can also specify the rule number.