Protecting Data
Data Security Controls
Data security controls are measures used to protect data from unauthorized access, modification, or destruction. They help maintain confidentiality, integrity, and availability, while supporting compliance with regulations.
- Use encryption to protect sensitive information
- Implement access controls for stored data
- Monitor and audit data activity to detect unauthorized access
Anonymization
Anonymization of data is the process of removing or altering personally identifiable information (PII) to ensure that the data cannot be traced back to specific individuals.
- Anonymized data has limited marketing value
- GDPR allows anonymized data collection and use without user consent
- Randomized masking can be effective in anonymizing data
Pseudo-Anonymization
Pseudo-anonymization replaces unique identifiers (like PII) with artificial identifiers (or "pseudonyms") to protect privacy.
- Keeps data useful for analysis while protecting identities.
- Useful for collaboration without exposing sensitive personal data.
- Information can also be selectively removed.
Unlike full anonymization, pseudo-nonymization can be reversed if needed under controlled conditions.
Tokenization
Tokenization replaces sensitive data with unique tokens that allow access without revealing the original information.
- Tokens are useless outside the system, reducing theft risk
- Common in payments, authentication, and APIs
- Helps meet compliance by limiting exposure of sensitive data
- Can be combined with encryption for extra security
Data Minimization
Data minimization means collecting and keeping only the data necessary for a specific purpose.
- Merchants should not store full credit card details unnecessarily.
- Retain only what is required by law or regulations.
- Example: compliance with PCI DSS standards.
Data Masking
Data masking hides sensitive information from unauthorized users while keeping it usable for authorized purposes.
- Allows safe use of data for testing, analytics, or training
- Can be done by changing stored data (static)
- Another way is to hide it during use (dynamic)
- Example: Showing only the last 4 digits of a credit card on receipts
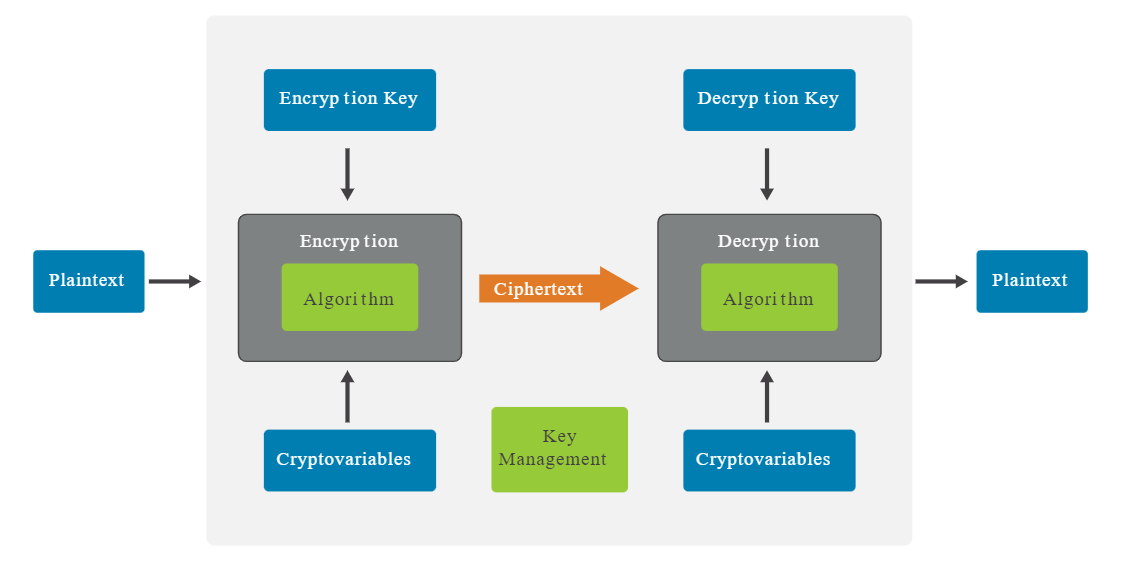
Encryption
Encryption keeps sensitive information secure and unreadable to unauthorized users, whether stored or in transit.
-
Transaction Protection
- Secures personal and business transactions
- Data is unreadable without proper decryption
-
Digital Signatures
- Confirms authenticity of software updates and sources
- Ensures integrity and legitimacy of digital content
-
Secure Email
- Protects digitally signed contracts
- Verifies authenticity and binding nature of agreements
For more details, see Data Encryption.
Cryptography
Cryptography protects information and ensures secure communication by providing confidentiality and integrity.
-
Confidentiality
- Keeps messages hidden from unauthorized users
- Ensures only authorized parties can access the information
-
Integrity
- Uses hash functions and digital signatures
- Detects changes and verifies that data remains unaltered
For more information, please see Cryptography Basics.
Cryptographic Hash Function
A hash function is a mathematical process that converts an input (message) into a fixed-size output (hash value).
- The output is usually much smaller than the original message
- It produces a unique representation of the data
- Commonly used to check data integrity
- Plays a key role in many cryptographic systems
For more information, please see Hashing
Message Digests
Message digests help verify data integrity and ensure that the information remains accurate and unchanged.
- Use cryptographic hash functions like MD5 or SHA-256
- Generate a unique, fixed-length digest of the original data
- Websites may provide a hash value for downloaded files
- Users can compute the hash of the file to compare with the provided value
- Matching digests confirm the file was not altered during transfer
In some resources, message digests are interchangeable with hashes or hash value.
Digital Signatures
A digital signature uses assymetric cryptography to transform data to achieve:
- Data origin authentication
- Data integrity
- Non-repudiation of the signer
However, digital signatures cannot guarantee confidentiality (i.e. the property of data or information not being made available or disclosed).
For more information, please see Digital Signatures in Asymmetric Encryption.
Message Authentication Code
A Message Authentication Code (MAC) does not guarantee anonymity. MAC is a cryptographic function that guarantees a message's:
- Integrity
- Authenticity
- Non-repudiation
On the other hand, anonymity is not a guaranteed by a MAC.
Digital Rights Management (DRM)
DRM technologies are designed to prevent unauthorized use of digital content, protecting intellectual property from theft and piracy.
- Protect content through encryption to prevent unauthorized access.
- Used in music, movies, books, video games, and other digital media.
Example: Apple initially used FairPlay DRM for music on iTunes but later switched to DRM-free music. Now, DRM is used to control access in subscription-based services, allowing revocation if the subscription is canceled.
Some methods associated with DRM solutions:
-
DRM License
- Grants authorized access to content.
- Defines usage rights, such as viewing, copying, or printing.
- Can be tied to a specific device or user.
-
Persistent Online Authentication
- Requires users to verify identity periodically.
- Ensures only authorized users can access content.
- Prevents sharing of credentials across multiple devices.
-
Continuous Audit Trail
- Tracks who accesses content and when.
- Logs all actions, including copying or printing.
- Helps detect and respond to unauthorized use.
-
Automatic Expiration
- Limits access to content after a set time.
- Licenses remain valid only for their intended period.
- Reduces risk of long-term unauthorized access.
Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB)
A Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB) is software placed between users and cloud services to monitor activity and enforce security controls.
- Enforces security policies for cloud access.
- Provides authentication and authorization for users.
- Detects shadow IT by analyzing usage logs and activity patterns.
Mishandling Data
Cybersquatting
Cybersquatting is the practice of registering domain names to profit from someone else's trademark.
- Done to sell the domain to the trademark owner for a profit.
- Example: Registering "mycompany.com" to resell it.
- Can confuse customers and harm the brand.
- Considered unethical and deceptive.
Cybersquatting is illegal under the U.S. Anticybersquatting Consumer Protection Act (ACPA) and similar laws worldwide.