AAA of Security
The AAA
Authentication
When a person’s identity is established with proof and confirmed by a system.
- Something you know
- Something you have
- Something you are
Authorization
Occurs when a user is given access to a certain piece of data or certain areas of a building
Accounting
Often called auditing, it involves tracking of data, computer usage, and network resources.
-
Non-repudiation - proof that someone has taken an action
-
Types of auditing:
- Resource access
- Failed login attempts
- Changes to files/records
-
In Windows, we can see audit logs in the Event viewer.
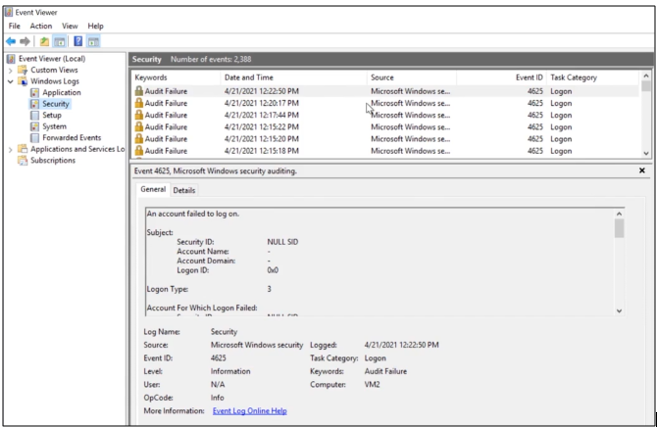
Authentication
This is the process of verifying the identity of a user who has stated their identity.
- Proving the identity of the requestor.
- Enhances security by ensuring authorized access.
Ther are two common methods of authentication:
-
Single-Factor Authentication (SFA)
- Relies on only one method of authentication.
-
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
- Requires successful demonstration of two or more authentication methods.
Common Authentication Techniques
Knowledge-based
Knowledge-based authentication uses a passphrase or secret code. It is vulnerable to attacks and often requires additional authentication methods for better security.
-
One-time Password (OTP)
- Unique password code generated for single use
- Static code sent by email or SMS
-
HMAC-based OTP
- Uses a shared secret and an incremented counter to generate the code
- HMAC encrypts a hash to ensure authenticity
- In hardware token devices, the code changes whenever the button is pushed
- The code is valid until it is used.
-
Time-based OTP
- Instead of using a counter, it uses the time of day in conjunction with the shared secret
- Code is only valid for a short period of time, until a new code is generated
- Token device and authentication system must have synchronized clocks
- Google Authenticator uses TOTP
In addition to OTPs, there are Knowledge-based authentication can also be in the following forms:
-
Push Notifications
- Phone call, SMS, or email
-
Password Managers
-
Also called "password vaults"
-
a master key protects the vault - DON'T FORGET IT!
-
Examples: LastPass, cloud-based vaults to store password keys
-
For Windows, we can use Credentials Manager - NOT RECOMMENDED
-
Certificate-based
Certificate-based authentication relies on Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) certificates, which are issued by a trusted Certificate Authority (CA) to verify the identity of an individual or device. These certificates ensure secure communication and authentication.
- Certificates are typically stored on devices like smart cards or in secure storage.
- Certificate are validated against a trusted CA and ensuring it hasn’t been revoked.
- Used for secure access to systems, encrypted communication, and digital signatures.
- Common Access Card – A widely used smart card that can authenticate a user to multiple systems and services, providing both identification and authentication.
Token-based
Token-based authentication uses physical devices like tokens, memory cards, or smart cards to verify a user's identity.
- Tokens generate a temporary code that users enter to authenticate.
- Memory and smart cards can store user credentials and cryptographic data.
- Offers a more secure alternative to password-based systems, as physical possession is required.
Token-based Authentication has two types:
-
Synchronous
- Generates codes at fixed intervals without a server challenge.
- Security token produces a new code every 30 seconds.
- Server and token stay synchronized for code expectations.
-
Asynchronous
- Does not generate codes at fixed intervals.
- Requires a server challenge for each code.
SSH Public Keys
SSH public key authentication secures remote access by using a cryptographic key pair.
- Sign-in requires a username, private key, and passphrase for the private key.
- The private key is not a password for the user but is used to decrypt the authentication process.
- The public key is stored on the server, and the private key is stored on the admin device.
- Commonly used in Linux servers for secure, passwordless login.
Characteristic-based
Characteristic-based authentication relies on unique, measurable physical or behavioral traits for identity verification.
- Fingerprint
- Retina
- Iris
- Facial
- Voice
- Vein
- Gait analysis (how you walk)
It also has the following efficacy rates:
- False acceptance rate (incorrectly accepting an unauthorized user).
- False rejection rate (incorrectly rejecting an authorized user).
- Crossover error rate (the point where false acceptance and false rejection rates are equal).
Multi-Factor Authentication
Multifactor Authentication (MFA) is a security system that requires more than one method of a authentication from independent categories of credentials to verify the user's identity.
Factors:
-
Knowledge-based
- Something you know
- Examples: Passwords or passphrases.
-
Possession-based
- Something you have
- Examples: Tokens, memory cards, smart cards, keyfob
-
Inherence-based
- Something you are
- Measurable characteristics.
- Examples: Biometrics, facial, fingerprint, voice
-
Behavior-based
- Something you do
- Recognizing patterns associated with a user
- Examples: Mouse movement, keystroke pattern, how they walk
-
Location-based
- Somewhere you are
- IP address verification, geolocation, GPS tracking
- Access can be restricted based on a user's location
Types of MFA:
-
Single-Factor Authentication
- Using a single authentication factor to access a user account
- Username + password
- Insecure, not recommended
-
Two-Factor Authentication
- Using two different authentication factors
- Username-password + SMS or email or push notifications
-
Multi-Factor Authentication
- Using two or more factors for authentication
- The more factors used, the safer it is, but the more complex it becomes
When implementing MFA, make sure that the factors used are not the same. Prompting the user to enter a password and a passphrase are both something you know.
Password-less Authentication
Provides improved security and a more user-friendly experience.
-
Biometrics
- Unique characteristics
- Fingerprint, facial, voice
-
Hardware Tokens
- Uses physical device that generate short-lived and ever-changing login code
- Security key
-
One-time Passwords
- Sent via SMS or email
- Code is only valid for a short period of time
- Code can only be used once, new code is generated after given time.
-
Magic Links
- Email link that automatically logs in user
- Sent via email, user just needs to click
- Can be accessed only once, new link is needed for each login
-
Passkeys
- Integrates with browser or OS
- Can also user biometrics as login method
Best Practices
Implement at least two of the three common authentication techniques for better security.
-
Challenges with Knowledge-based Authentication
- Vulnerable to attacks; password resets may pose risks.
- Better security often requires additional forms of authentication, like tokens or characteristics.
-
User ID and Password Combination
- Not considered MFA as it involves two things that are known.
- MFA requires two or more authentication methods, not simply two known elements.