Attack Frameworks
Cyber Kill Chain
A model developed that describes the stages by which a threat actor progresses a network intrusion.
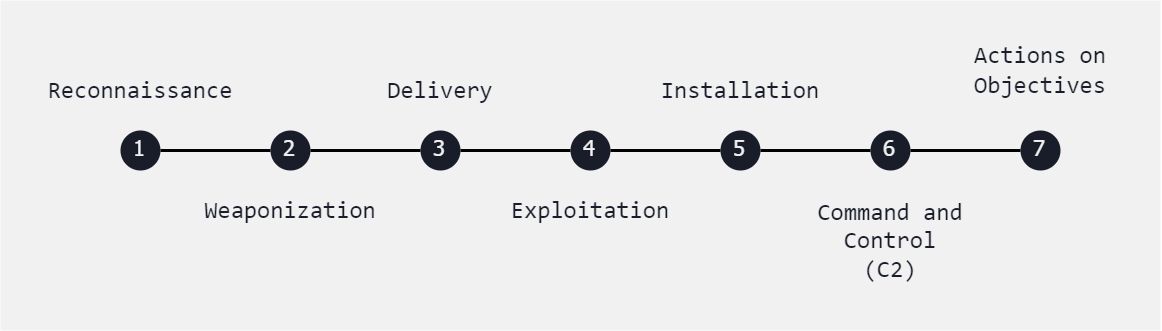
These are the generic stages of Cyber Kill Chain Analysis.
Below is another variation of the Cyber Kill Chain which focuses on a detailed range of stages.
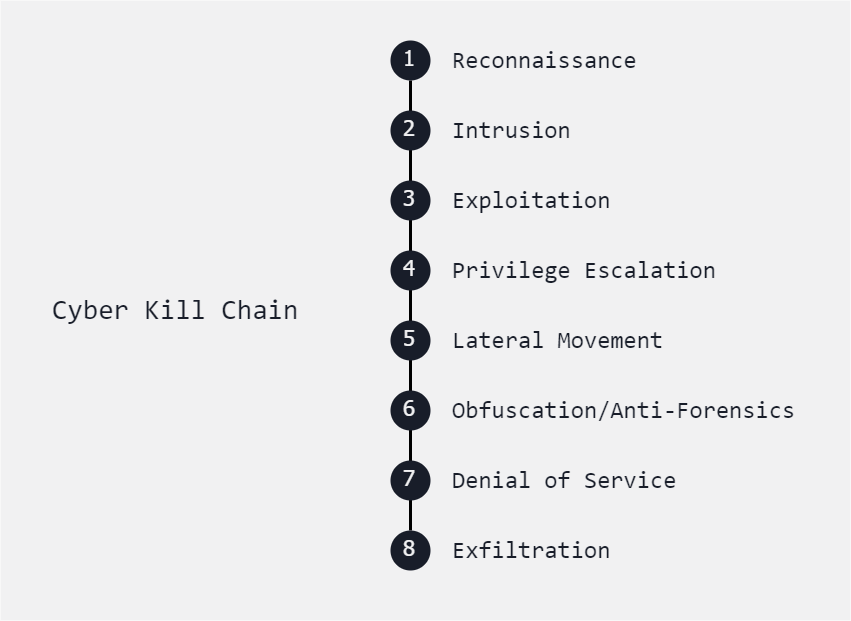
Reconnaissance
Reconnaissance involves gathering information about the target, such as identifying vulnerabilities and system configurations.
- Conducting port scans
- network mapping
- OS fingerprinting
Intrusion
Intrusion is all about gaining unauthorized access to the target system or network, offten done through exploitation of vulnerabilities.
- Exploiting a known software vulnerability to access a web server
- Exploiting weak credentials to log in to a database.
Exploitation
Exploitation requires the use of identified vulnerabilities to compromise the target system or gain control.
- Exploiting a buffer overflow vulnerability in a web application
- Execute arbitrary code or deploying malware through a phishing email.
Privilege Escalation
Privilege Escalation involves elevating privileges to gain deeper access and control over the compromised system or network.
- Exploiting a misconfigured service to gain root access on a Linux server
- Exploiting a Windows privilege escalation vulnerability to gain administrative privileges.
For more information, please see Privilege Escalation.
Lateral Movement
Exploitation can also be done by moving laterally within the network to expand access and compromise additional systems or resources.
- Using compromised credentials to pivot from one system to another within the network
- Exploiting trust relationships between systems to gain access to sensitive data.
- For more information, please see Pivoting
Obfuscation/Anti-forensics
Obfuscation refers to concealment of malicious activities and evasion of detection through the use of security tools and forensic analysis.
- Encrypting malware payloads to evade antivirus detection
- Using steganography to hide malicious code within image files
Denial of Service
Denial of Service (DoS) involves disrupting the availability of services or resources to legitimate users. This can be achieved by overwhelming systems with excessive traffic or resource requests.
- Launching a distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack against a web server.
- Flooding a network with malformed packets to degrade performance.
- This makes it unavailable to legitimate users
Exfiltration
With exfiltration, sensitive data are stolen from the compromised system to external servers controlled by attackers.
- Extracting customer credit card information from a compromised database
- Then transferring it to a remote server under the attacker's control
- Exfiltrating proprietary company documents via encrypted communication channels.
MITRE ATT&CK Framework
A knowledge base maintained by the MITRE Corporation for listing and explaining specific adversary tactics, techniques, and common knowledge (ATT&CK) or procedures (attack.mitre.org).
- The pre-ATT&CK tactics matrix aligns to the reconnaissance and weaponization phases of the kill chain.
- Used for post-compromise analysis to identify attacker techniques:
- What was done?
- How was it done?
Mitigation techniques:
- Modify existing firewall or IDS/IPS alert rules
- Deploy honeypot traps
Diamond Model of Intrusion Analysis
A framework for analyzing cybersecurity incidents and intrusions by exploring the relationships between four core features:
- Adversary
- Infrastructure
- Victim
- Capability
It shows how malicious actors use exploit capabilities over an infrastructure againsts victims.
- Use data from honeypots