Cryptography Basics
Cryptography
Cryptography is the practice of securing information and communication by converting it into a protected form, so only authorized users can access it. Its main goals are to keep data private, accurate, and trustworthy.
- Encryption - Transforming plaintext into ciphertext using an algorithm and a key.
- Decryption - Converting ciphertext back to plaintext with the appropriate key.
Other important terms:
- Cryptanalysis - Techniques used to break or weaken cryptographic protections.
- Cryptosystem - A system or tool that enables encryption and decryption processes.
- Cryptology - The broader field that encompasses both cryptography and cryptanalysis.
Obfuscation
Data Masking or Obfuscation
Obfuscation is a technique to make code, data, or communications harder to understand or analyze.
- Protect intellectual property, sensitive information.
- Protect sensitive data from being easily understood or extracted.
- Prevent unauthorized reverse engineering or tampering with software.
In obfuscated, the code or data is transformed into a form that is functionally equivalent but difficult for humans to read or interpret. Common methods include:
- Renaming variables and functions with meaningless names
- Removing comments
- Reordering code structures.
There are a few considerations:
- Obfuscation is not foolproof.
- Skilled attackers can often reverse-engineer obfuscated code.
- Over-obfuscation can complicate legitimate debugging and maintenance.
- Not a replacement for proper encryption and other security practices.
Steganography
Steganography and obfuscation are techniques used to conceal information, but they differ in their methods and objectives.
- Steganography hides a message within another medium to keep its existence secret.
- Obfuscation makes code or information difficult to understand
Derived from Greek word, meaning "covered writing", Steganography hides secret data within ordinary, non-secret files or messages. Its purpose is not to prevent unauthorized access, but to avoid suspicions.
We can try this at Steganography Online.. We'll use the sample photo below:

The message that we want to hide in the image:
All right men, commence Operation: Special Delivery!
Upload the photo and enter the message in the field. Click Encode.
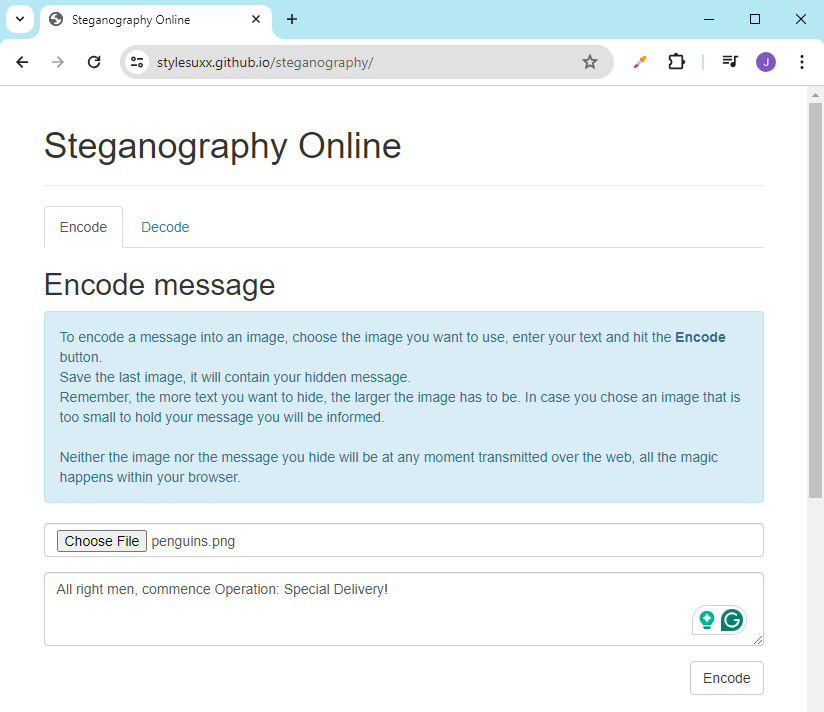
It will generate the encoded image.
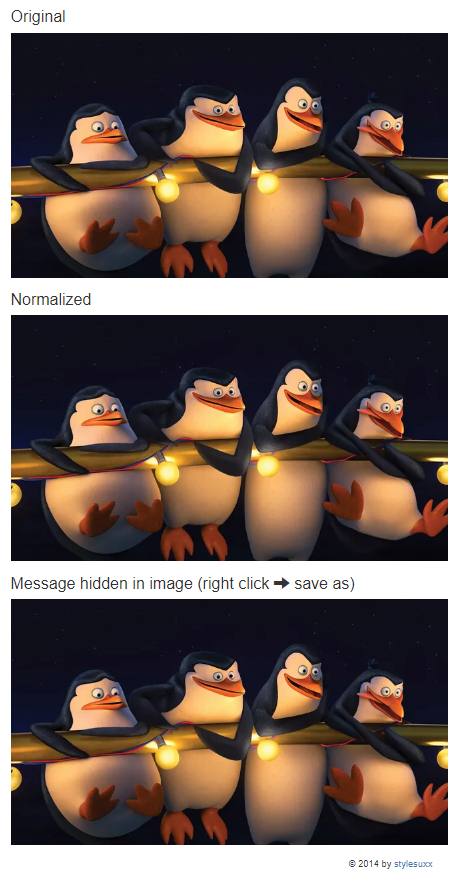

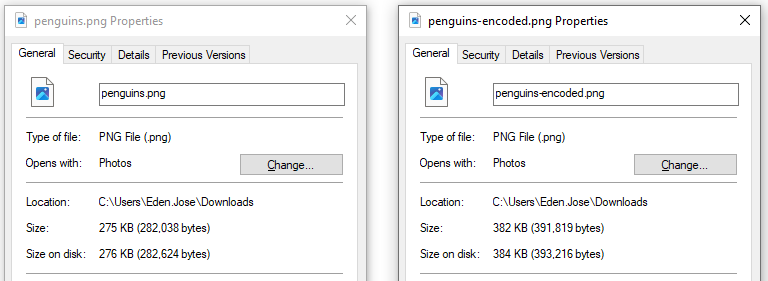
Right-click on the third image > Save as. Then check the properties of the original photo and the encoded photo. We can see that the size changed.
Tokenization
Tokenization replaces sensitive information with non-sensitive tokens, enhancing data security by removing direct exposure to confidential data.
How It Works
- Sensitive data is swapped for unique tokens stored in a secure vault.
- The original data is stored somewehere.
- Original data can only be retrieved through secure processes.
- If data breach occurs, attackers will only find the useless tokens.
Applications
- Used in payment systems for credit card security.
- Applied in healthcare to protect patient information.
- Employed in databases to secure sensitive data.
- Supports compliance with data protection regulations.
Considerations
- The token vault must be securely protected.
- Tokenization should be part of a comprehensive security strategy.
Diffusion
Diffusion spreads the influence of one part of the input across many parts of the output, making hidden patterns harder to detect.
- Makes data appear more random and less predictable
- Commonly used in block ciphers through mixing or permutation steps
- A small change in input causes large changes in output
Example: Changing one letter in the plaintext completely alters the ciphertext.
Confusion
Confusion makes the link between the key and ciphertext complex, hiding how the key affects the output.
- Alters data to make the relationship between input and key unclear
- Commonly achieved through substitution tables or nonlinear functions
- Works with diffusion to build stronger encryption
Example: Substituting letters or bits so the original data looks entirely different.
Confusion is carried out through transposition and diffusion is carried out through substitution.
Types of Encryption
These types of encryption play critical roles in modern cybersecurity, often used together to achieve a balance of speed and security.
Symmetric Encryption
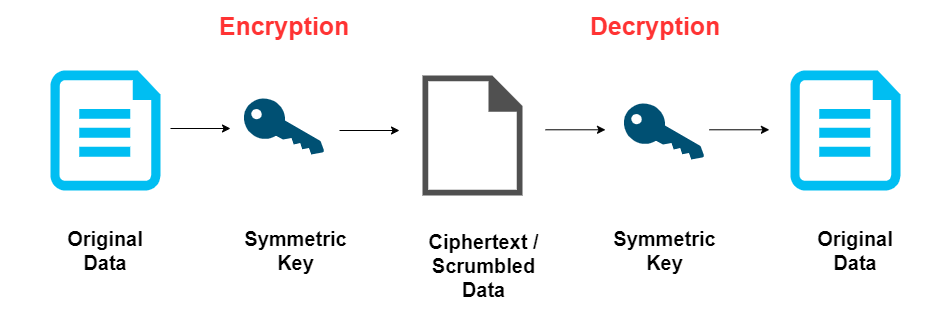
Symmetric cryptography uses the same key for both encryption and decryption. The sender and receiver must share this key, keeping it secret from others.
- Session key - single key is used for data encryption only one time
- Both parties must have this key.
Symmetric encryption is generally faster and less computationally intensive compared to asymmetric cryptography. It is also effective for encrypting large volumes of data.
For more information, please see Symmetric Encryption.
Asymmetric Encryption
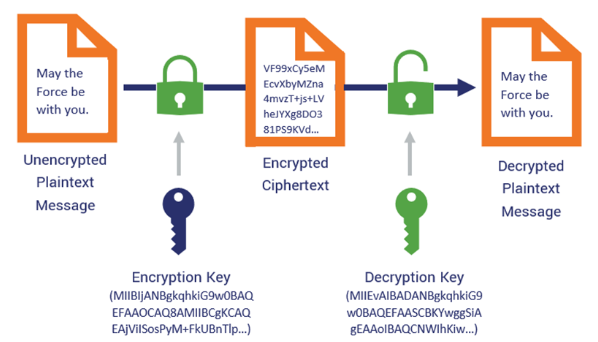
Asymmetric cryptography uses a pair of keys:
- a public key for encryption
- a private key for decryption.
The public key can be shared openly, but the private key must remain confidential.
For more information, please see Asymmetric Encryption.
Hybrid Implementation
Utilizes asymmetric encryption to securely transfer a private key, which can then be used with symmetric encryption.
Homomorphic Encryption
Homomorphic encryption is a cryptographic technique that allows computation on encrypted data without decrypting it. The result of the computation, once decrypted, is the same as if it had been performed on the plaintext.
This makes it ideal for:
- Cloud environments, where sensitive data must remain encrypted
- Financial institutions or any organization that needs to preserve data confidentiality
- When data privacy is critical and trust in the cloud provider is limited
While homomorphic encryption is computationally intensive and slower, this is acceptable for organizations prioritizing security over speed, such as banks, government agencies, and healthcare providers.
Storing Keys
Best practices:
- Store keys in secure hardwared modules
- Encrypt keys when at rest
- Transmit keys securely when used
- Limit key access to regular audits and monitoring
Insecure key storage
Insecure key storage refers to improper handling of cryptographic keys and certificates, which can expose sensitive data to attackers. This includes:
- Storing private keys in plaintext
- Leaving certificates in publicly accessible locations
- Failing to protect certificates with strong permissions
- Not using hardware security modules (HSMs) or secure key vaults
Such practices compromise the confidentiality and integrity of encrypted communications or data, and are a common vulnerability in systems that rely on cryptographic certificates.