ADF Elements
Overview
Azure Data Factory (ADF) is made up of small pieces that work together to move and process data.
-
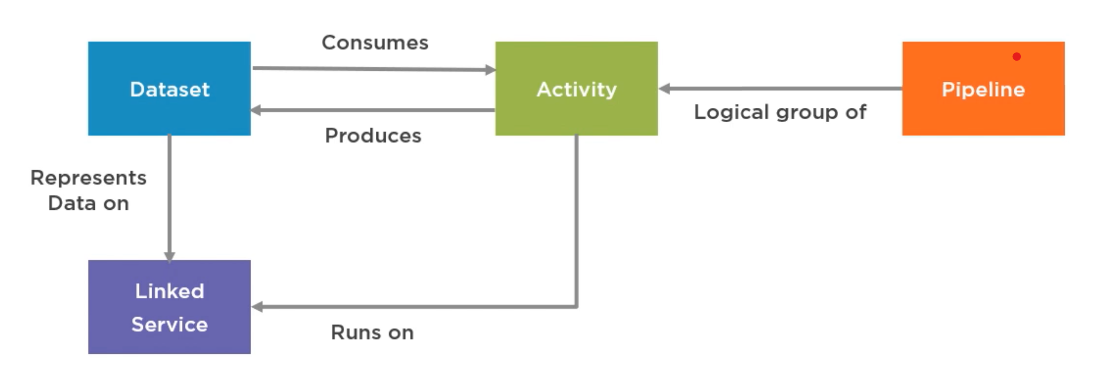
Pipeline
- A group of steps or actions
- Pipelines group
activitiestogether - Holds and organizes tasks
-
Activity
- A single task that does something
- Can copy, move, change, or control data
-
Dataset
- Describes the data you're working with
- Can point to files or database tables
- Helps activities know what data to use
-
Linked Service
- Connects ADF to data sources
- Works like a connection string
- Needed for every dataset
-
Trigger
- Starts a pipeline
- Can run on schedule or based on an event
-
Integration Runtime
- The engine that runs the tasks
- Provide the compute power for ADF
- Can be in the cloud or on your own machine
- Needed for every activity
Each of these elements works with the others to create a full pipeline. ADF uses them to control data in a reliable and repeatable way. An example flow:
- Copying data from one place to another is an activity.
- The trigger can run that task every morning at 8 AM.
- The integration runtime handles the actual work behind the scenes.
All these pieces work together. Pipelines organize everything, activities do the actual work, and the rest help define how, when, and where things happen.
Pipelines vs SSIS
If you're used to SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS), here’s how they match:
| ADF | SSIS |
|---|---|
| Pipeline | Package |
| Activity | Task |
| Linked Service | Connection Manager |
| Dataset | Source/Destination |
| JSON format | XML (.dtsx) |
If you're already familiar with SSIS, the concepts in ADF will feel very similar, but ADF is cloud-first and more scalable.
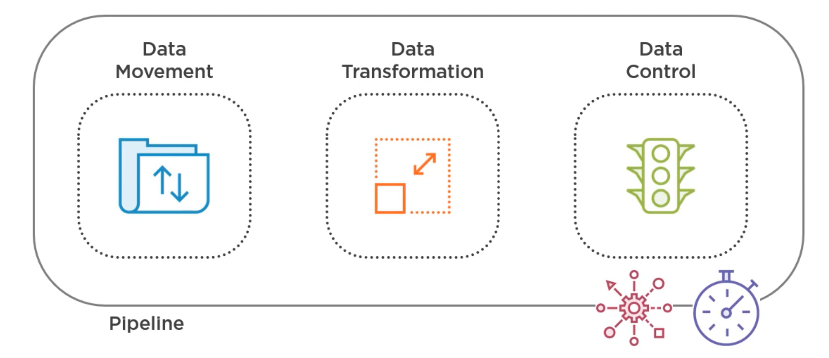
Types of Activities
There are different types of activities in ADF, depending on what you want to do with the data.
-
Movement (copy activity)
- Copy activity moves data from one place to another
- There's no
moveactivity in ADF - Combined
copyanddeleteactivities does the move
-
Transformation (modify the data)
- Transformations change or clean up data.
-
Control (manage flow and logic)
- Control activities like “If”, “ForEach”, or “Wait”
- Helps manage pipeline logic.
Data Movement
This is the most common task. It moves data between different sources.
- Supports over 80 data stores
- Can use common file formats like CSV or JSON
If your system doesn’t have a direct connector, you can still use basic protocols (like ODBC or HTTP) or export data to CSV or JSON before using ADF.
{
"name": "CopyFromBlobToSQL",
"type": "Copy",
"inputs": [ { "referenceName": "InputDataset", "type": "DatasetReference" } ],
"outputs": [ { "referenceName": "OutputDataset", "type": "DatasetReference" } ]
}
This JSON sample shows a simple copy task from one dataset to another.
Data Transformation
You can change or clean data using ADF itself or by using other services.
- ADF Data Flow for basic transformation
- Use built-in or advanced options depending on needs
You can also use external services like:
- Spark
- Azure Functions
- Databricks
- SQL procedures
Data Control
These activities let your pipeline make decisions or wait for something to happen.
ForEach,If,Wait,SetVariable,ExecutePipeline- Helps manage the order and logic of activities
These actions are useful when building more complex pipelines where things depend on each other.
Dataset and Linked Service
These two help ADF understand what and where the data is.
- Dataset points to the data (e.g., a file or table)
- Linked service provides the connection info
A dataset without a linked service won’t work. They always go together.
Integration runtime
This is what runs your tasks. You choose which runtime to use depending on where your data lives or how secure it needs to be.
- Can be hosted by Microsoft, on-prem, or self-hosted
- Required for every activity in ADF