Schemas
Database Schema
Databases consist of multiple related tables. The schema defines relationships between these tables.
As an example, here is a common database schema is music streaming platforms:
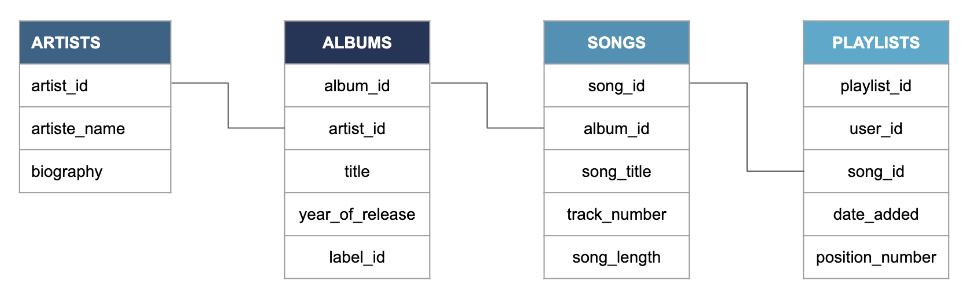
Lab 1 - Schema
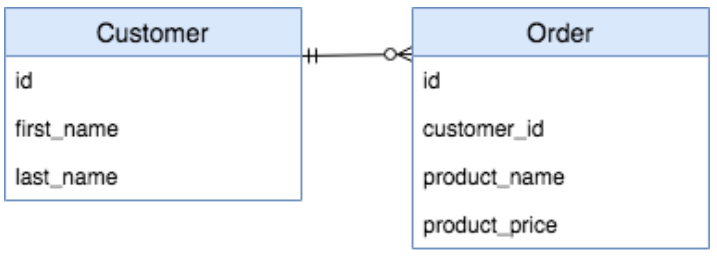
A PostgreSQL database is set up locally, containing the schema below. Use pandas to query the database using the read_sql() function and db_engine.
The pandas package imported as pd will store the query result into a DataFrame object, so you can use any DataFrame functionality on it after fetching the results from the database.
- Select the first_name and last_name from the "Customer" table, ordered by last name and then first name.
- Show the first 3 rows of data using
.head(). - Show general information using
.info().
Given SQL Statement:
# Complete the SELECT statement
data = pd.read_sql("""
Answer:
# Complete the SELECT statement
data = pd.read_sql("""
SELECT first_name, last_name FROM "Customer"
ORDER BY last_name, first_name
""", db_engine)
# Show the first 3 rows of the DataFrame
print(data.head(3))
# Show the info of the DataFrame
print(data.info())
Output:
first_name last_name
0 Connagh Bailey
1 Brook Bloom
2 Ann Dalton
Lab 2 - Joining on Relations
The power of SQL lies in joining information from multiple tables. Use the JOIN statement to combine the "Customer" and "Order" tables.
- Create the SELECT statement to join the "Customer" with the "Order" table.
- Print the id column of the resulting data.
Answer:
-
Write the SQL command to join the tables and select relevant columns:
SELECT Customer.CustomerID, Customer.FirstName, Customer.LastName, Orders.OrderID, Orders.OrderDate, Orders.TotalAmount
FROM Customer
INNER JOIN Orders ON Customer.CustomerID = Orders.CustomerID; -
Using pandas to run the SQL query and fetch the data:
import pandas as pd
# Assuming db_engine is already defined and connected to your PostgreSQL database
data = pd.read_sql("""
SELECT Customer.CustomerID, Customer.FirstName, Customer.LastName, Orders.OrderID, Orders.OrderDate, Orders.TotalAmount
FROM Customer
INNER JOIN Orders ON Customer.CustomerID = Orders.CustomerID;
""", db_engine)
# Display the data
print(data) -
The output will display the joined data from the "Customer" and "Order" tables:
CustomerID FirstName LastName OrderID OrderDate TotalAmount
0 1 Connagh Bailey 10 2023-07-01 99.99
1 2 Brook Bloom 11 2023-07-02 149.99
2 3 Ann Dalton 12 2023-07-03 79.99