Query Optimization
Overview
Longer queries use more resources, increasing costs. Optimizing queries helps run them faster and more cost-effectively.
- Faster queries save time.
- Optimized queries reduce costs.
Schema diagram for the Pizza dataset:

Common Query Problems
-
Exploding joins: Missing join conditions lead to large results.
Incorrect:
SELECT *
FROM order_details AS od
JOIN pizzas AS pz
Correct:
SELECT *
FROM order_details AS od
JOIN pizzas AS pz
ON od.pizza_id = pz.pizza_id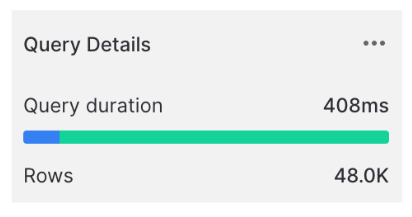
-
Using
UNIONinstead ofUNION ALL: Knowing when to use.UNIONremoves duplicates, costing extra time, slows down queryUNION ALLis faster if no duplicates
Optimize Queries
-
Use
LIMIT: Limiting the number of rows returned helps save time.Longer query:
SELECT *
FROM sample_data.table.orders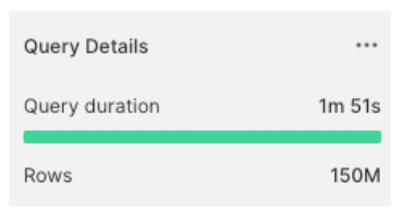
Shorter query:
SELECT *
FROM sample_data.table.orders
LIMIT 10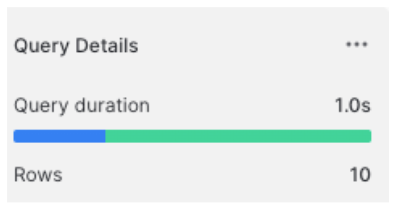
-
Avoid
SELECT *: Ensures only necessary columns are retrieved, which speeds up queries.Longer query:
SELECT *
FROM sample_data.table.orders
Shorter query:
SELECT
order_date,
order_status
FROM sample_data.table.orders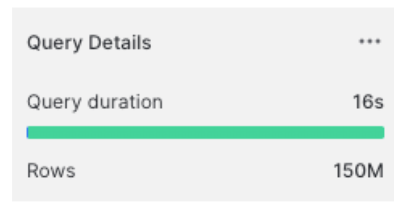
Early Filtering
Filtering rows before performing joins minimizes the data processed during joins, making the operation faster.
Example:
WITH filtered_orders AS (
SELECT order_id, order_date, order_status
FROM orders
WHERE order_date = '2024-01-01'
)
SELECT o.order_id, o.order_date, o.order_status, od.product_id
FROM filtered_orders o
JOIN order_details od ON o.order_id = od.order_id;
This approach filters the orders first, reducing the amount of data processed by the join.
Query History
The query_history view helps track query performance and find which ones need optimization based on execution times.
- Find long-running queries via Snowflake's
query_historyview - Filter by execution time.
Example:
SELECT *
FROM snowflake.account_usage.query_history
WHERE query_text ILIKE '%order_details%'
AND execution_time > 5000; -- Execution time greater than 5000 milliseconds
This query filters the query history to show only those with long execution times, helping you pinpoint queries that need optimization.

The ILIKE keyword is a case-insensitive way to match strings.
To spot slow or frequently running queries:
SELECT
query_text,
end_time,
execution_time
FROM snowflake.account_usage.query_history
WHERE execution_time > 5000;
