Motherboard
Overview
When you select your CPU, you need to make sure it's compatible with your motherboard - the circuit board that connects all your components together.
The motherboard is the main circuit board that connects all the components of the computer. It houses the CPU, RAM, and storage devices, and provides connectors for other peripherals. The motherboard includes a chipset that manages data flow between the CPU, memory, and peripheral devices, ensuring efficient communication and operation.
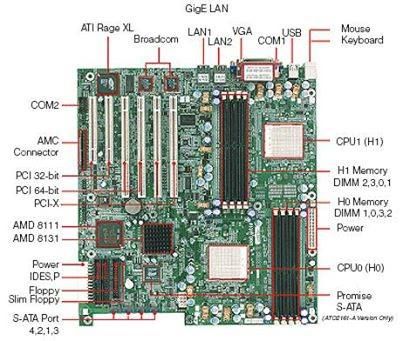
It's important to note that you can't simply purchase a collection of parts and expect them to work together seamlessly. CPUs are designed to fit into motherboards using specific socket types, and these sockets can vary. Some CPUs have numerous small pins that protrude, while others have contact points that resemble dots.
Expansion Cards
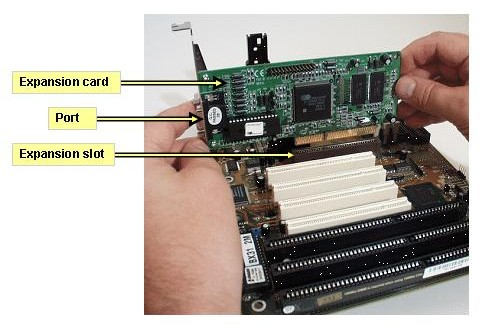
Motherboards enable us to enhance our computer's capabilities by adding expansion cards. They distribute power from the power supply and facilitate communication between various computer components.
Chipsets
Motherboards have several essential features, one of which is the chipset. The chipset determines how the components interact with each other within the system. It typically comprises two main chips:
- Northbridge chip: Connects high-speed components such as RAM and video cards.
- Southbridge chip: Manages input/output (IO) controllers, including hard drives and USB devices.
In many modern CPUs, the Northbridge is integrated directly into the CPU, eliminating the need for a separate Northbridge chip.
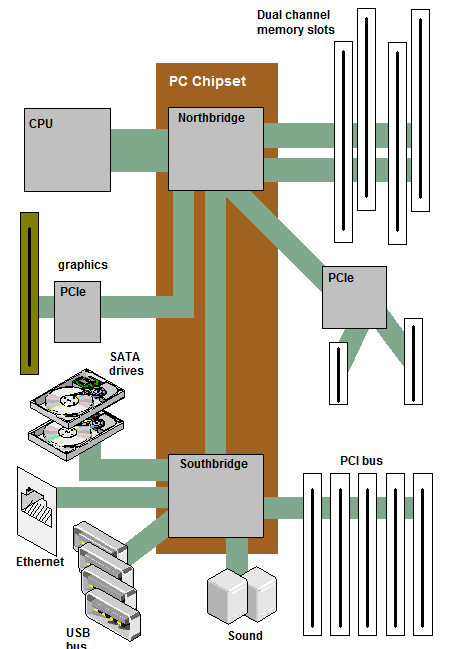
The chipset is crucial for managing data flow between the CPU, RAM, and peripherals. Peripherals are external devices like a mouse, keyboard, and monitor that connect to the computer.
Expansion Slots
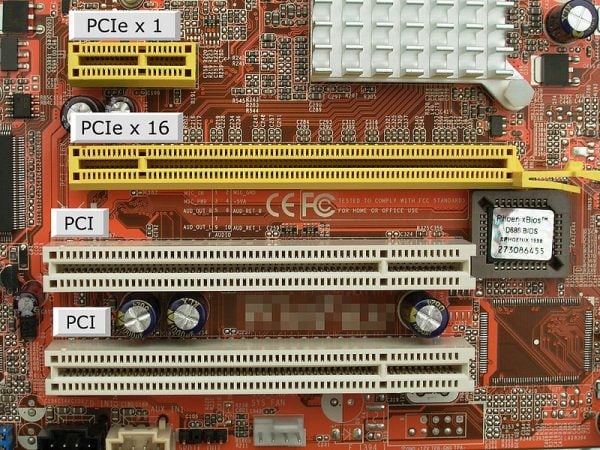
Motherboards also feature expansion slots, which allow us to further enhance the computer's functionality. For instance, if you want to upgrade your graphics card, you can simply install a new one in an available expansion slot. The current standard for expansion slots is PCI Express (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express). A PCIe bus appears as a slot on the motherboard, and a PCIe expansion card resembles a small circuit board.

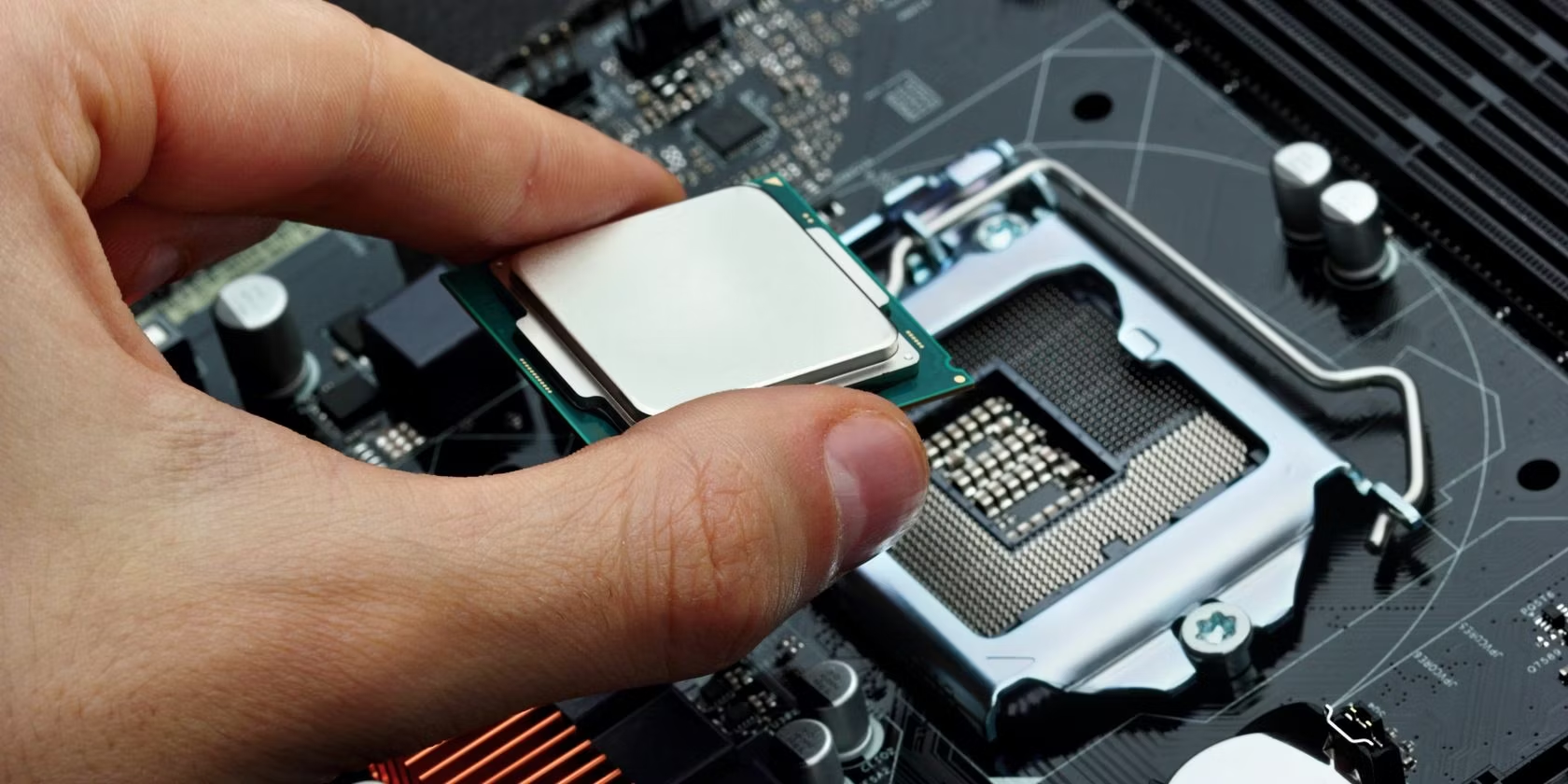
CPU Sockets
The compatibility of your CPU with your motherboard depends on the CPU socket type. There are two major types of CPU sockets:
- Land Grid Array (LGA): Pins are located on the motherboard.
- Pin Grid Array (PGA): Pins are on the processor itself.
The socket size can vary, so it's essential to ensure compatibility between the CPU and the motherboard. The type of socket will be indicated on the packaging of the CPU and motherboard, and detailed compatibility information can also be found on the manufacturer's website.

Form Factor
Motherboards come in various sizes known as form factors, which determine the number of components that can be installed and the available space. The most common form factor is ATX (Advanced Technology Extended), which itself has several size variations. In desktop systems, the full-sized ATX is prevalent.
Alternatively, you might choose an ITX (Information Technology Extended) form factor, which is much smaller than ATX boards. For example, the Intel NUC uses a variation of the ITX board, available in mini-ITX, nano-ITX, and pico-ITX sizes.
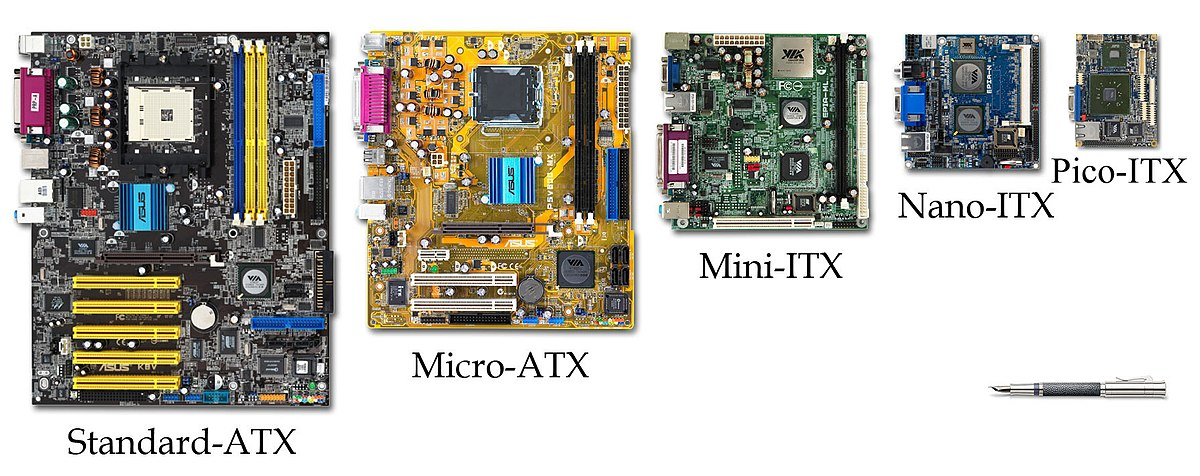
When building a computer, consider the form factor that suits your needs. A smaller form factor may limit the workload capacity, whereas a larger form factor can accommodate more functionality. The form factor also influences the types of expansion slots available.
Understanding motherboards and their features is advantageous when addressing hardware issues, as components like RAM modules and processors must fit the specific motherboard type. For example, if you're responding to a support ticket about video problems, you wouldn't want to arrive at the user's desk only to find that the replacement graphics card is incompatible with their motherboard.