Power Supply
Overview
The Power Supply Unit (PSU) converts electrical power from an outlet into a usable form for the computer's components. It provides the necessary voltages and currents to power the CPU, motherboard, storage devices, and peripherals. A reliable PSU is essential for the stable operation of the computer.
There are two types of electricity:
- DC (Direct Current): Flows in one direction.
- AC (Alternating Current): Changes direction constantly.
Our computers use DC voltage, so the PSU converts the AC voltage from our power company into usable DC voltage.
Fans
Most power supplies have a fan to keep them cool. They also provide voltage information, usually listed underneath or on the side, and cables to power the motherboard.
Voltage (220v and 110v)
Understanding electricity can be simplified with a water pipe analogy. Imagine our sinks connected to a pressurized water tank. When we turn on the faucet, water flows out, similar to how electricity works.
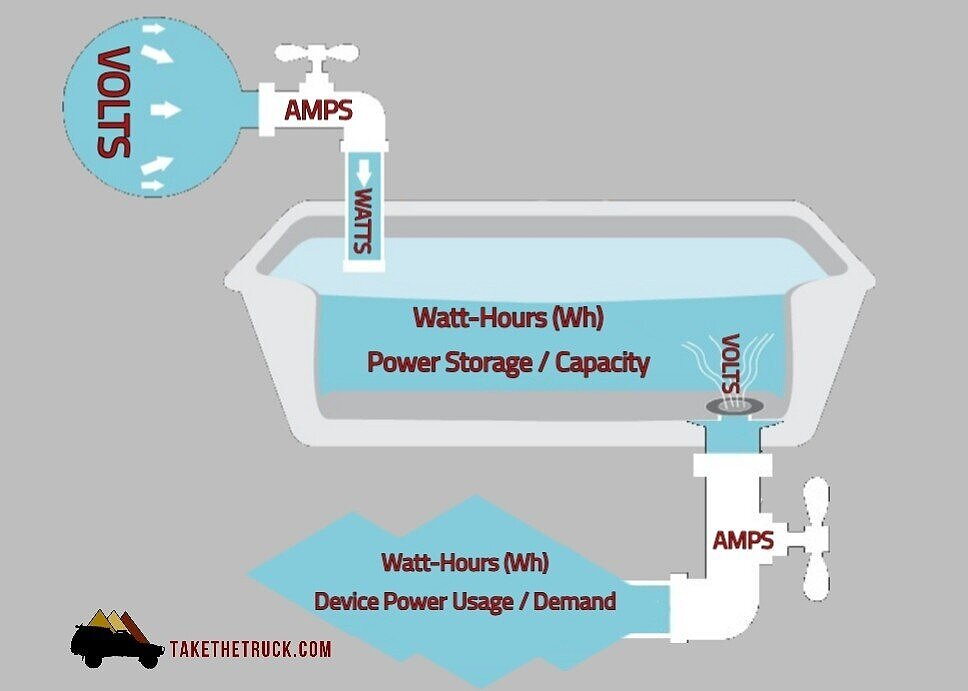
If we increase the pressure in the water tank, more water flows out. In electricity terms, this pressure is referred to as voltage.
Example: If you plug a 120-volt appliance into a 220-volt outlet, it will overload and fry the appliance. Conversely, a 220-volt appliance in a 120-volt outlet will work, but inefficiently, similar to a half-pressurized water tank. Using the proper voltage for your electronics is crucial to avoid damage.
Amps
The amount of electricity flowing is called current or amperage, measured in amps. Amps are like pulling electricity, whereas voltage pushes it. Amps pull as much electricity as needed, while voltage provides everything available.
Example: Look at your device chargers; they may show something like 1 or 2.1 amps. Charging with 2.1 amps will charge a device faster than using a 1 amp charger.
Watts
Wattage is the product of volts and amps, indicating the total power a device needs. A PSU with too low wattage won't power your computer effectively, so it's important to have enough wattage.
Insight: Having a larger PSU doesn't mean you'll overpower your computer. PSUs only supply the amount of power your system needs. It's better to have a larger PSU than a smaller one. A basic desktop can usually run on a 500-watt PSU, but more demanding tasks like high-resolution gaming or video production may require a higher wattage.