Services
Overview
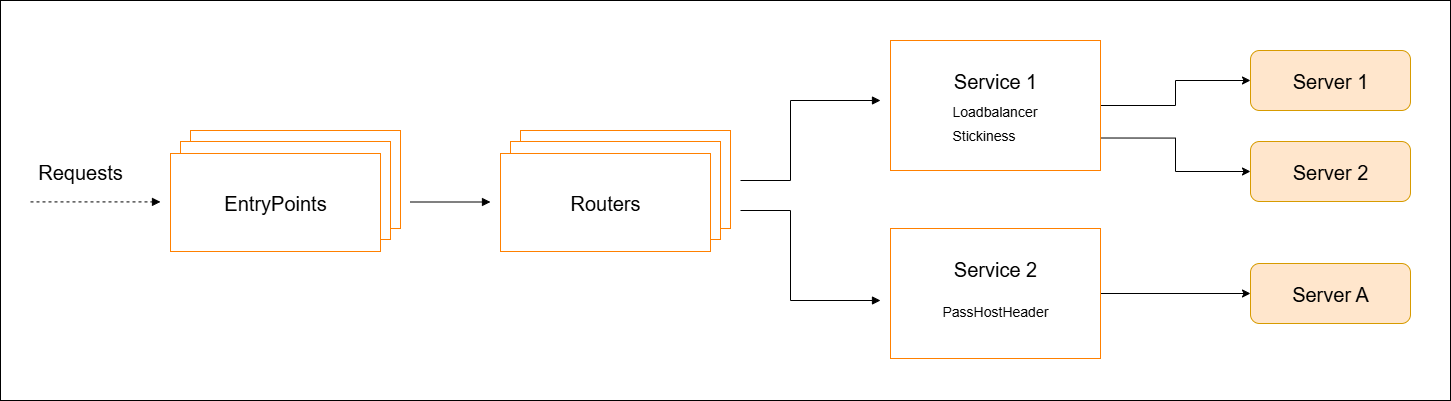
Services in Traefik let you connect your app to the outside world. When you deploy a service, Traefik automatically gives it a way to handle traffic.
- Each service gets a load balancer by default
- If app has more than one instance, traffic is split between them
- Load balancer uses round-robin for multiple app instances
- A service can have health checks to monitor if it's working
- A service can connect to more than one router
This helps spread traffic evenly across your app’s running instances.
Health Checks on Services
Load balancers can check if your service is still healthy.
- You can define custom health check paths like
/healthor/ping - You can also check health by port like
8080
If the service is unhealthy, it’s removed from traffic routing until it's healthy again.
How Requests Travel
Here’s how a request moves through the system.
- Request hits a port like
8443(entry point) - Then it goes to a router that checks the rules
- If it matches, it sends traffic to the right service
- Load balancer in the service splits traffic between app instances
This whole flow lets your service handle many requests at once smoothly.
Common Service Configurations
Here are the most common settings used in real projects.
- `traefik.http.services.myservice.loadbalancer.server.port`
- `traefik.http.services.myservice.loadbalancer.passhostheader=true`
- `traefik.http.services.myservice.loadbalancer.healthcheck.path=/health`
- `traefik.http.services.myservice.loadbalancer.healthcheck.port=42`
These define the app's port, whether to pass headers, and where to run health checks.
These basic settings are enough to start routing traffic properly.
Docker-specific Options
When you use Docker, you need to tell Traefik which containers to watch.
-
Add this to enable service:
traefik.enable=true -
Use this to pick the right network:
traefik.docker.network -
If using Docker Swarm:
traefik.docker.swarmMode=true -
Use Swarm's built-in loadbalancer instead of Traefik:
traefik.docker.lbswarm=true
Here’s a sample Docker Compose:
services:
myapp:
image: myapp:latest
labels:
- "traefik.enable=true"
- "traefik.http.services.myapp.loadbalancer.server.port=8080"
- "traefik.http.services.myapp.loadbalancer.healthcheck.path=/health"
Traefik starts watching this container and can now route traffic to it.
TCP and UDP Services
You can deploy TCP or UDP services just like HTTP.
- Use same settings, just change entry point to TCP or UDP
- Fewer options to configure compared to HTTP
- Services are configured just for the connection between
For example, to create a TCP service:
labels:
- "traefik.tcp.routers.myapp.entrypoints=tcp"
- "traefik.tcp.services.myapp.loadbalancer.server.port=9000"
The setup is the same idea, just simpler.
Clone the Repository
To try out the examples, clone the project repository from GitHub.
- Github repo: joseeden/labs-traefik
Clone and move into the project directory:
git clone https://github.com/joseeden/labs-traefik.git
cd labs-traefik/03-routers-and-services
Project structure:
03-routers-and-services
.
├── docker-compose.yml
└── traefik.yml
Lab: Cat App Router
This lab lets you test how Traefik handles services and routing in a real setup.
- Deploy Traefik
- Add a service
- Add labels step-by-step
- Troubleshoot issues
Inside the lab directory, we have the docker-compose.yml file.
version: "3"
services:
traefik:
image: traefik:v2.3
ports:
- "80:80" # web requests
- "8080:8080" # Traefik dashboard
- "443:443" # HTTPS requests
volumes:
- /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock
- ./traefik.yml:/etc/traefik/traefik.yml
catapp:
image: mikesir87/cats:1.0
labels:
- "traefik.enable=true"
- "traefik.http.routers.catapp.rule=Host(`catapp.localhost`)"
- "traefik.http.routers.catapp.entrypoints=web"
- "traefik.http.routers.catapp.service=catapp"
- "traefik.http.services.catapp.loadbalancer.server.port=5000"
This configuration tells Traefik:
- Only handle requests for
catapp.localhost - Use the
webentry point (port 80) - Forward traffic to the
appservice - Use port 5000 inside the container
Apply the files:
docker stack deploy -c docker-compose.yml traefik
Output:
Creating network traefik_default
Creating service traefik_traefik
Creating service traefik_catapp
After deploying, you can access the app at:
http://catapp.localhost
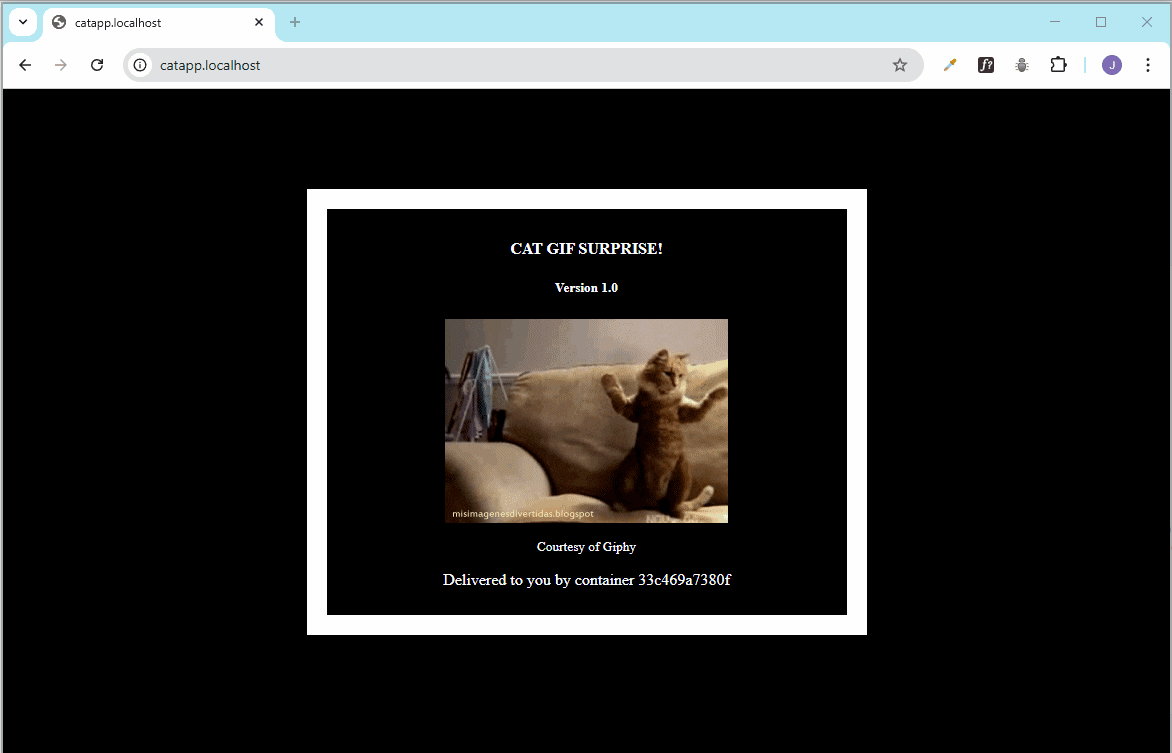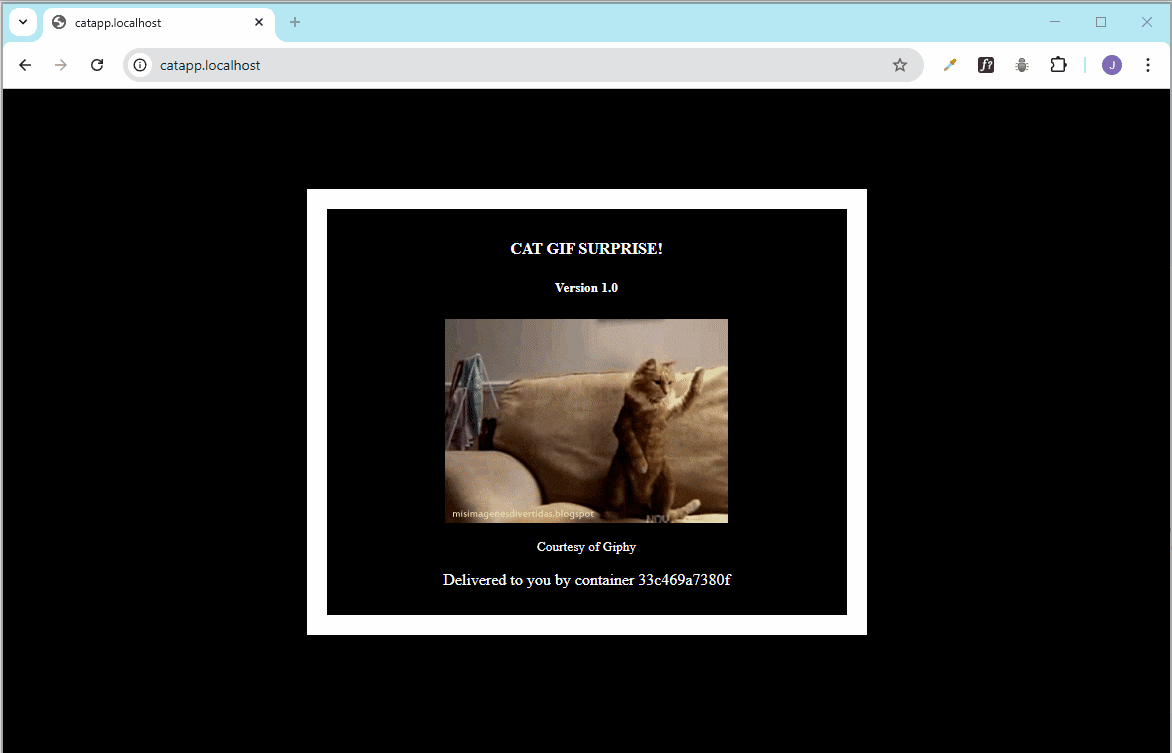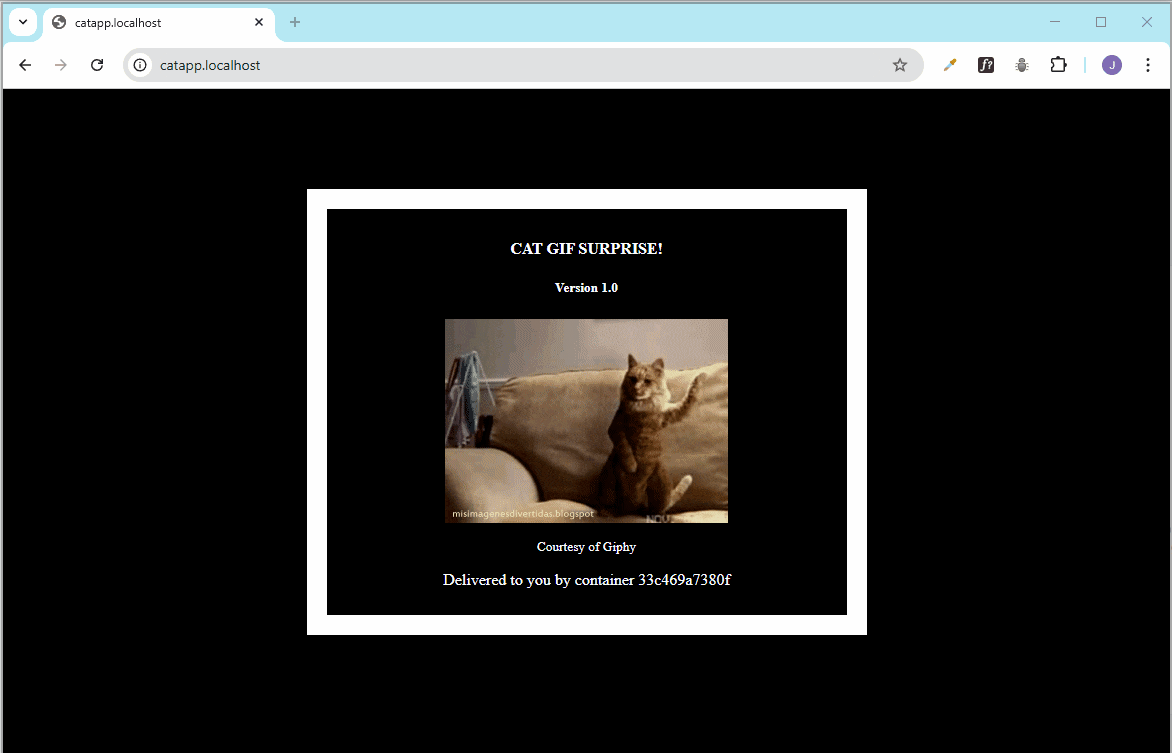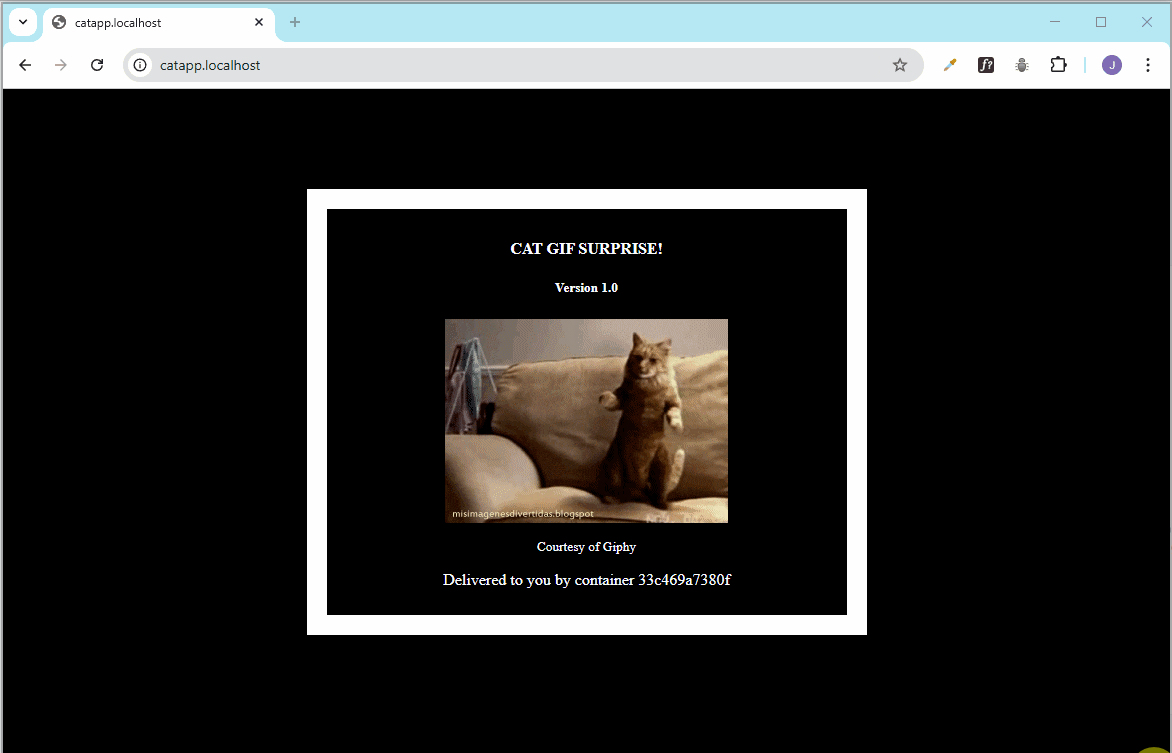
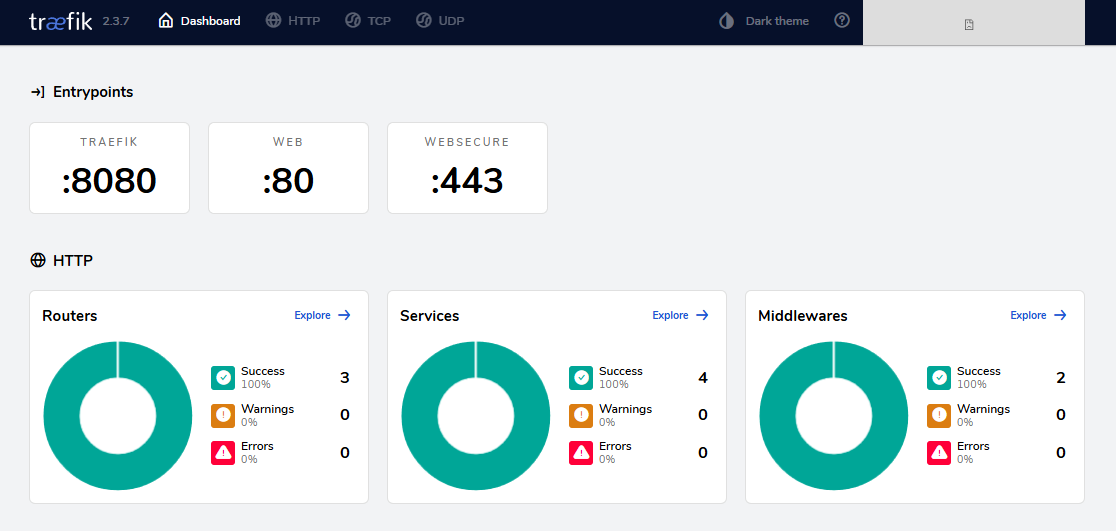
You can also check your setup in the Traefik dashboard.
http://localhost:8080
It will show:
- The router name (
catapp) - The matched host rule
- The assigned service and entry point
This helps confirm everything is working as expected.
Make everything Dynamic
Next, comment out the Service and Load Balancer Labels to see how Traefik will dynamically create the service and Load Balancer.
Edit the docker-compose.yml:
version: "3"
services:
traefik:
image: traefik:v2.3
ports:
- "80:80" # web requests
- "8080:8080" # Traefik dashboard
- "443:443" # HTTPS requests
volumes:
- /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock
- ./traefik.yml:/etc/traefik/traefik.yml
catapp:
image: mikesir87/cats:1.0
labels:
- "traefik.enable=true"
- "traefik.http.routers.catapp.rule=Host(`catapp.localhost`)"
- "traefik.http.routers.catapp.entrypoints=web"
# - "traefik.http.routers.catapp.service=catapp"
# - "traefik.http.services.catapp.loadbalancer.server.port=5000"
Re-deploy:
docker stack deploy -c docker-compose.yml traefik
Output:
Updating service traefik_traefik (id: 0q9tjql7txwqnypxsk6k007aw)
Updating service traefik_catapp (id: 7gebiqdo292oowjk31lepkzyh)
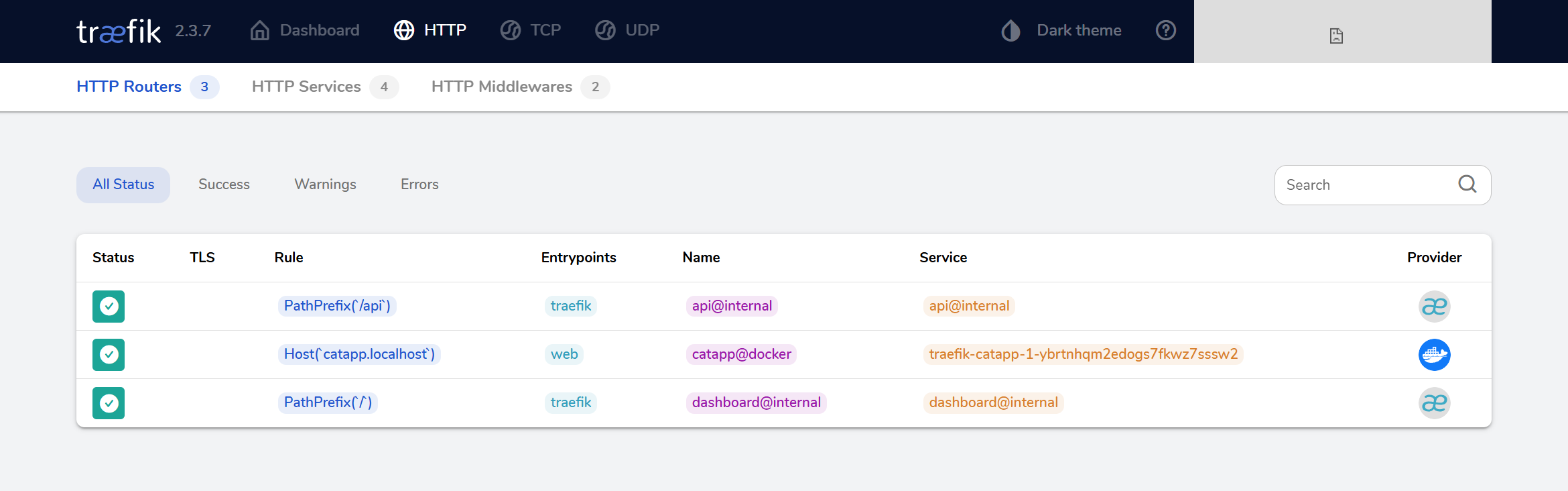
Go back to the Traefik dashboard > Routers > Explore.
As we can see here, Traefik dynamically resolves everything by creating the loadbalancer and assigning random hash to the service.
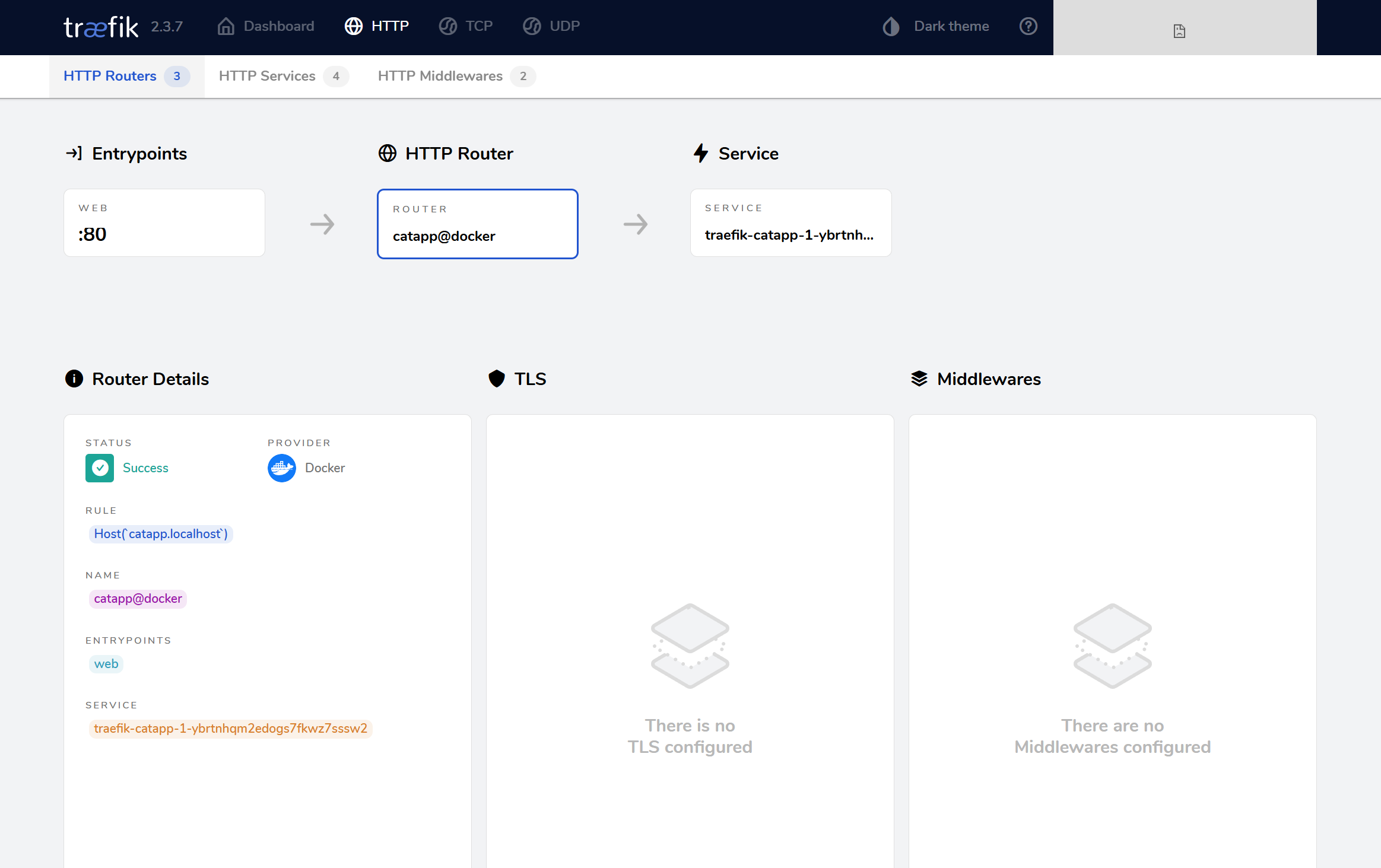
Click the Host(catapp.localhost) to see more details:
Checking the app again, we see that it still works:
http://catapp.localhost

Cleanup
To remove the resources:
docker compose -f <CONFIG_FILE_PATH> down
To check all stacks in your Swarm:
docker stack ls
To remove the specific stack:
docker stack rm <STACK_NAME>
To remove all stacks currently deployed in your Swarm:
docker stack ls --format '{{.Name}}' | xargs -r docker stack rm