Database Security
This is not an exhaustive documentation of all the existing Azure Services. These are summarized notes for the Azure Certifications.
To see the complete documentation, please go to: Azure documentation
Overview
These security options provide a comprehensive approach to securing Azure SQL Databases, offering controls at various levels and addressing different aspects of data protection, access control, and auditing.
Properly configuring and utilizing these features enhances the overall security posture of database environments on Azure.
Azure SQL Firewall Rules
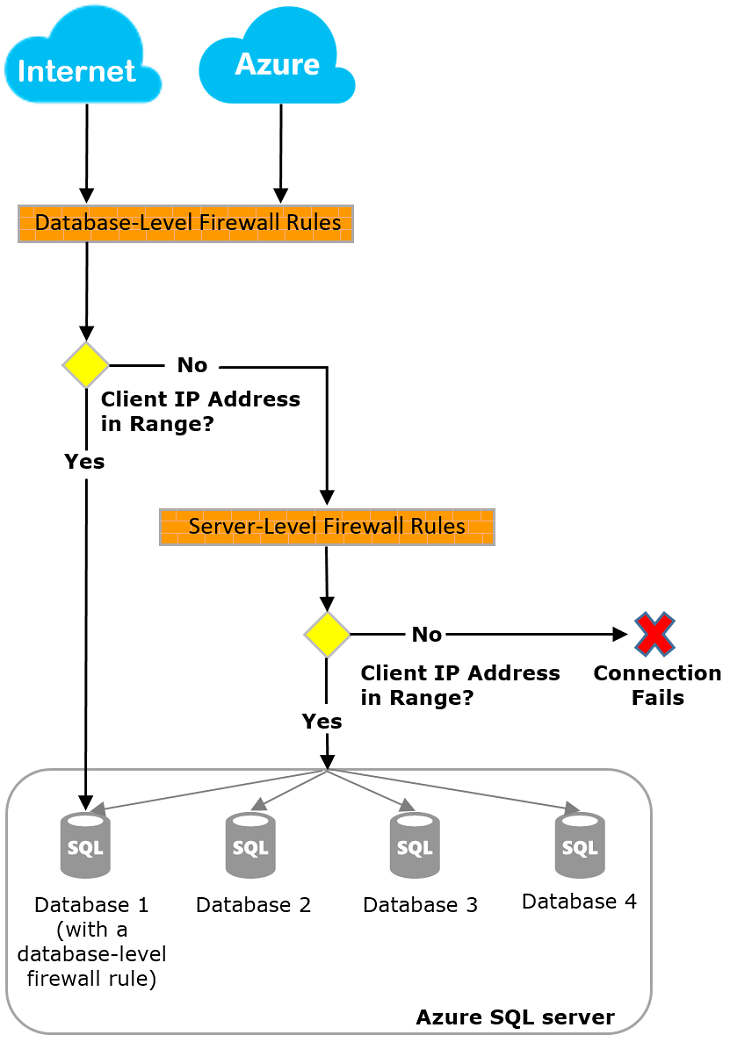
Controls access to the Azure SQL Database server's public endpoint through IP firewall rules.
- Access to the public endpoint for the server are automaticaly blocked when you create a new Azure SQL server
- Has Server-level and Database-level Firewall rules
 |
|---|
Levels
-
Server-level IP Firewall Rules
- Allow access to the entire Azure SQL server, covering all hosted databases.
- Created for the entire server, regardless fo how many databases it holds
- Master database holds these rules.
- Max of 128 rules.
-
Database-level IP Firewall Rules
- Allow access to specific databases on the SQL Database server.
- Created for each database, including the master database
- Max of 128 rules per database.
For more information: SQL Database Firewall Rules Configuration
Azure SQL Always Encrypted
Encrypts sensitive data (e.g., credit card numbers) within client applications, ensuring separation of data owners and managers.
- Clients encrypt sensitive data before sending it to SQL Server, with decryption done transparently on query results.
- Ensures unauthorized users, inclduing database admins, can't access sensitive data.
- Driver needs to be installed on te computer, which then automatically encrypts/decrypts data
- Available in all editions of Azure SQL Database since SQL Server 2016.
For more information: Always Encrypted Documentation
Azure SQL Transparent Data Encryption (TDE)
Encrypts Azure SQL Databases, Azure SQL Managed Instances, and Azure Synapse data at rest to protect against offline attacks.
- Real-time encryption/decryption of database, backups, and transaction log files without application changes
- Enabled by default for newly deployed Azure SQL databases
- However, it cannot be used to encrypt the logical master database because it needs objects that TDE needs to perform the encryption
- Manual enabling required for older databases
For more information: Transparent Data Encryption Documentation
Azure SQL Database Auditing
Azure SQL Database Auditing tracks database events, logging them to an audit log hosted in Azure storage, Log Analytics, or Event Hubs. It facilitates regulatory compliance, monitors database activity, identifies anomalies, and detects security violations.
Configuration
-
Database-Level Auditing
- Specific to a database
- Can be defined in a default server policy for all databases
-
Server-Level Blob Auditing
- Audits all databases on the server
- Auditing always applies regardless of any database-level settings
Considerations
-
When both Database Auditing and Server Blob Auditing is enabled, both audits will exist separately
-
Avoid simultaneous enabling of both server blob auditing and database blob auditing, unless:
- Each used a different storage account
- Each database will have different retention period
-
Recommended to enable server-level blob auditing only, unless there's a specific need for database-level auditing