Securing Azure Solutions
This is not an exhaustive documentation of all the existing Azure Services. These are summarized notes for the Azure Certifications.
To see the complete documentation, please go to: Azure documentation
Azure Active Directory
Main features:
- Single Sign-on (SSO)
- Application Managemenet
- Identity Protection
- Monitoring
- Multi-Factor Authentication
- B2B and B2C
- Hybrid Identities
- Seamless Integration with Azure Services and Third-party Services
To learn more, check out Azure Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Azure AD vs. Azure AD DS vs. ADDS
-
Azure AD (Azure Active Directory)
- Cloud-based identity and access management service.
- Manages user identities and authentication for cloud applications.
- Supports single sign-on (SSO) and multi-factor authentication (MFA).
- Focuses on modern authentication and authorization for cloud resources.
- Enable collaboration with B2B and B2C
- Cloud-based identity and access management service.
-
Azure AD DS (Azure Active Directory Domain Services)
- Fully-managed domain service
- Enables domain-joined resources in Azure
- Supports LDAP, Kerberos, and NTLM authentication
- Useful for lift-and-shift scenarios
- Integrates with existing Azure AD tenant for user sign-in and control
- Scalability and Disaster recovery with multiple replica sets in different Azure regions
-
ADDS (Active Directory Domain Services)
- On-premises Windows Server-based directory service.
- Provides authentication and authorization services
- Requires on-premises domain controllers.
- Integrates with Azure AD for hybrid identity scenarios.
Roles in Azure AD
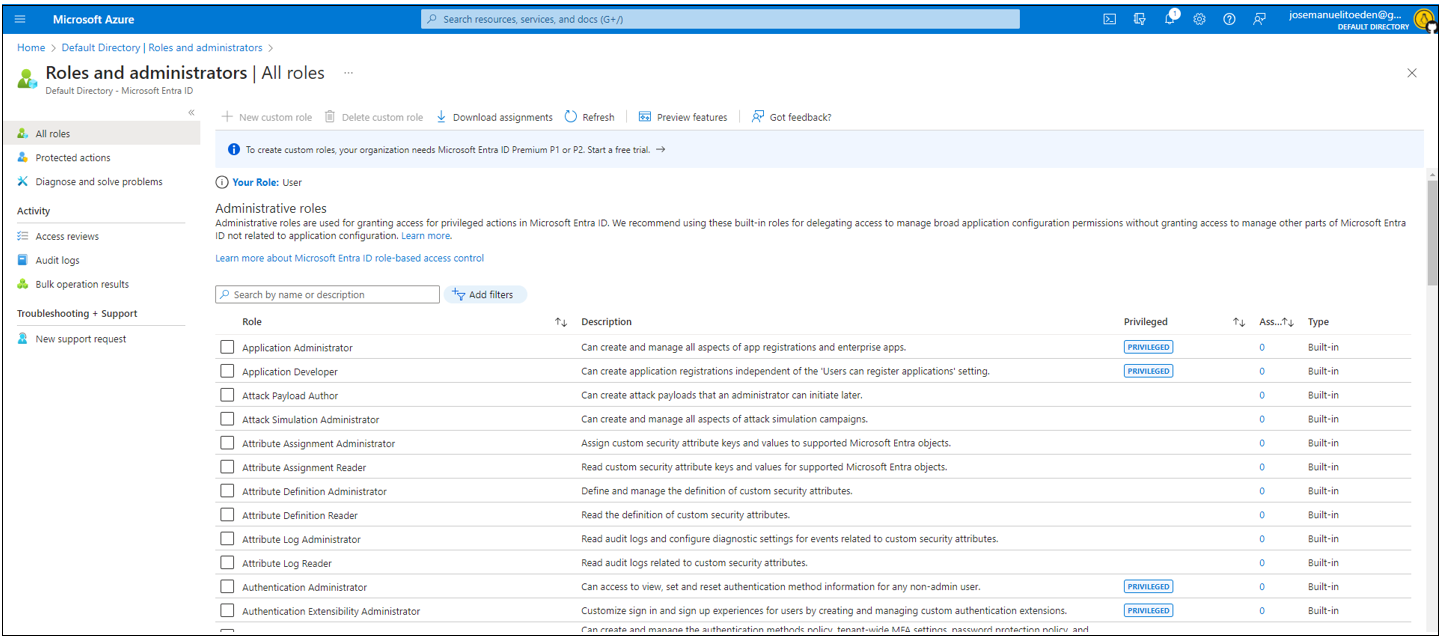
Azure AD Specific Roles
This roles grants specialize permissions exclusively for managing resources within Azure AD.
- Application Administrator
- User Administrator
- Groups Administrator
Service-Specific Roles
Roles specific to major Microsoft 365 services which are non-Azure AD.
- Exchange Administrator
- Intune Administrator
- Sharepoint Administrator
- Teams Administrator
Cross-Service Roles
These are roles that are not confined to a particular service but strethc their influence across multiple solutions.
-
Global Roles
- Grants access across all Microsoft 365 services
- Global Administrator
- Global Reader
-
Security-related Roles
- Grants access across multiple security services
- Security Administrator
- Security Reader
-
Compliance Administrator Role
- For managing compliance-related settings
Built-in Roles
 |
|---|
1. Global Administrator
- Highest level of access.
- Full control over all aspects of Azure AD.
- Can delegate roles to other users.
2. Security Administrator
- Focused on security-related aspects of Azure AD
- Manages security settings, security policies, and security events
- Responsible for ensuring security of Azure AD resources
3. Billing Administrator
- Manages billing and subscription-related tasks in Azure AD
- Handles cost, budgets, and resource optimization
4. Global Reader
- Read-only access to Azure AD resources
- Can view configurations, setting, and reports, but cannot make changes
- Useful for auditors or stakeholders
ADDS - Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Simplified domain service without managing domain controllers
- Supports LDAP, Kerberos, and NTLM authentication
- Integrates with existing Azure AD tenant for user sign-in and control
- Enables domain-joined resources in Azure
- Scalability and Disaster recovery with multiple replica sets in different Azure regions
Cons:
- Limited administrative access
- Restricted customization
- Shipped with pre-defined configurations
- Limited application compatibility
- No domain trust support
- No LDAP write access
- Limited operating system support
- Limited network integration
- Availability may vary based on regions
- Cost considerations