Application Gateway
This is not an exhaustive documentation of all the existing Azure Services. These are summarized notes for the Azure Certifications.
To see the complete documentation, please go to: Azure documentation
Overview
While Azure Load Balancer operates at the transport layer (Layer 4), Azure Application Gateway takes load balancing to the next level by functioning at the application layer (Layer 7) of the OSI model.
Unlike the Load Balancer, Application Gateway makes routing decisions based on additional HTTP attributes.
- Utilizes HTTP attributes such as URI path and host headers for routing decisions. This is called Application Layer Routing.
- Example: Routing requests for /images to servers hosting images and /video to servers hosting videos.
Key Features
Azure Application Gateway offers several powerful features designed to enhance application security and performance:
-
SSL Termination
- Offloads encryption and decryption tasks to the gateway, reducing the load on backend servers.
-
Autoscaling
- Automatically adjusts capacity based on traffic demands.
- Available only with Application Gateway Standard V2.
-
Web Application Firewall (WAF)
- Provides centralized protection against common vulnerabilities and attacks.
- Defends against SQL injection, cross-site scripting, and other exploits.
-
Zone Redundancy
- Standard V2 Application Gateway spans multiple availability zones.
- Removes the need for separate gateways in each zone, enhancing fault tolerance.
Additional Features
Azure Application Gateway includes several additional features that offer flexibility and control:
-
Backend Pool Options
- Supports a variety of backend pool resources, including VMs, VM scale sets, and on-premises servers.
-
Layer 7 Routing
- Facilitates complex routing decisions based on application layer attributes, such as URLs and headers.
-
Centralized Management
- Streamlines management and distribution of traffic to web applications, simplifying operations.
For more details, visit the Azure Application Gateway Features.
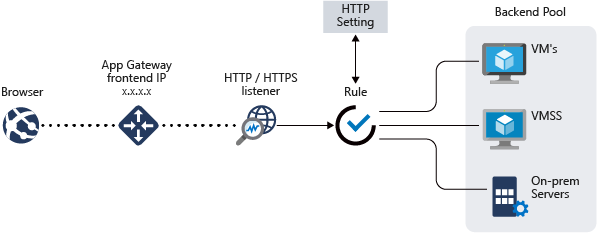
Components of an Application Gateway
Azure Application Gateway is made up of several components that work together to manage web traffic effectively:
 |
|---|
Front-end IP Addresses
This component determines how clients interact with the Application Gateway.
- Can be either public, private, or both.
- Supports one public or one private IP address.
Listeners
Listeners handle incoming connection requests and define how traffic is processed.
- Connection handling
- Monitors incoming requests to the gateway.
- Configurable settings include protocol, port, hostname, and IP address.
Request Routing Rules
These rules control how traffic is directed to backend pools.
- Routing decisions
- Links listeners with backend pools and HTTP settings.
- Defines how traffic should be routed based on listener configurations.
HTTP Settings
HTTP settings determine communication parameters between the gateway and backend servers.
- Port and Protocol Configuration
- Specifies communication ports and protocols.
- Includes settings for encryption and cookie-based session affinity.
Backend Pools
Backend pools manage where traffic is directed within the network.
- Resource Pools
- Routes traffic to various backend resources.
- Can include NICs, VM scale sets, public IP addresses, internal IPs, FQDNs, and multitenant backends.
Health Probes
Health probes monitor the status of resources to ensure they are operational.
- Resource Monitoring
- Checks the health of backend resources.
- Removes unhealthy resources from service and restores them when they recover.
For more details, visit the Azure Application Gateway Components Documentation.
Enabling WAF
To enhance security, you can enable the Web Application Firewall (WAF) on Azure Application Gateway. WAF can log threats and store logs in Azure Diagnostics, which can be directed to a Storage Account or Log Analytics Workspace.
To enable WAF, navigate to the Application Gateways page, select your gateway, and click Web Application Firewall. Toggle the WAF status to activate it.
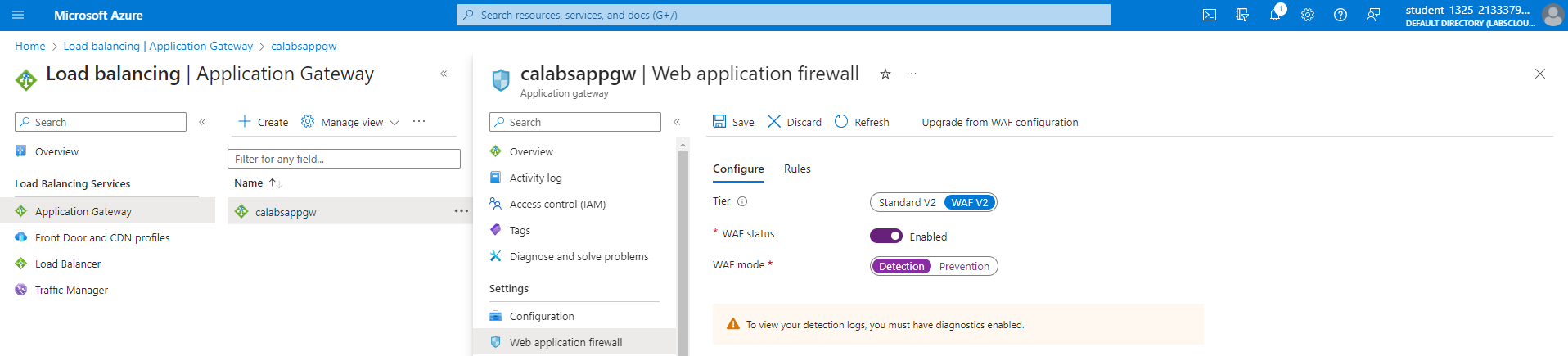
Modes
WAF offers different modes for handling threats:
-
Detection Mode
- Monitors and logs threats without blocking requests.
-
Prevention Mode
- Takes action to block detected threats and alerts.
-
It’s advisable to start with Detection Mode and then switch to Prevention Mode as needed.
Rulesets
Rulesets protect web applications against common vulnerabilities and attacks.
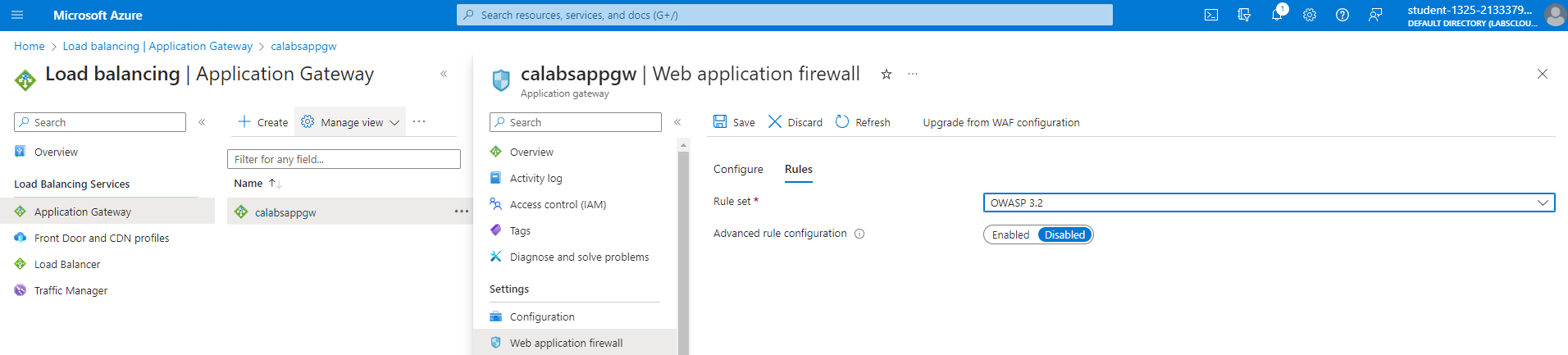
The OWASP core 3.2 ruleset provides updated protection against Java infections and reduces false positives.
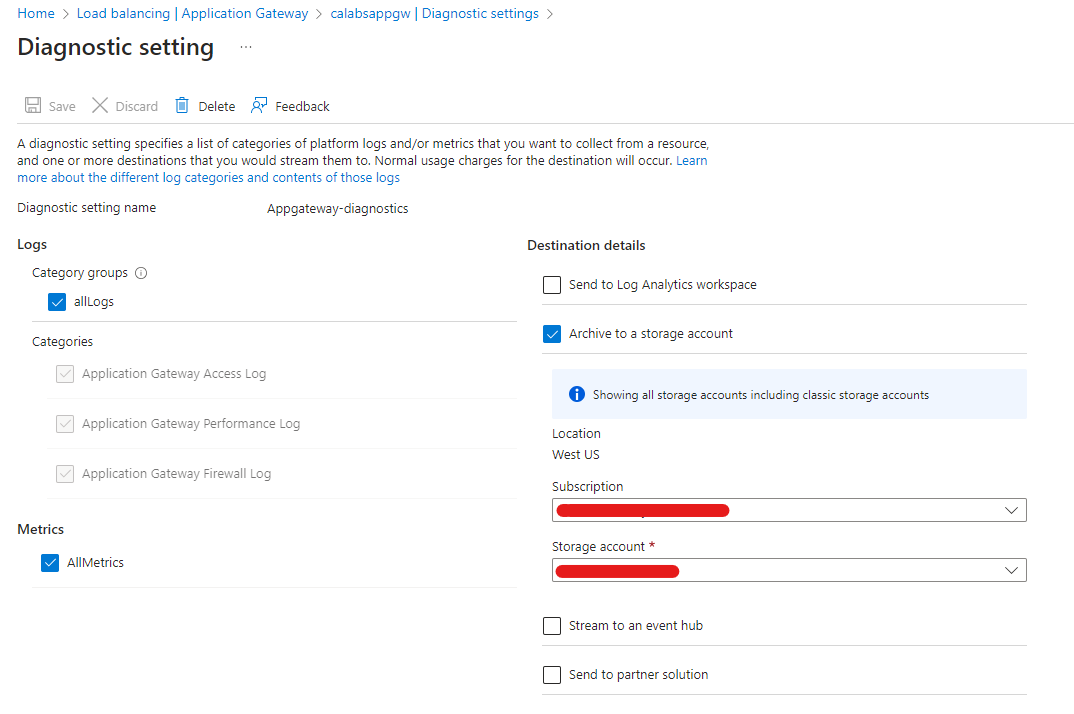
Log Destination
Logs from WAF can be stored in either a Storage Account or Log Analytics Workspace. To set this up, go to Diagnostic settings and add a diagnostic setting to specify:
- Logs
- Metrics
Choose the destination as either Log Analytics Workspace or Storage Account.
WAF Policy
The WAF policy is a standalone resource used to manage security policies across multiple Application Gateways or for specific sites or backend pools within each Application Gateway.